Aspen Malnutrition Criteria Chart
Aspen Malnutrition Criteria Chart - Web the top five ranked criteria included three phenotypic criteria (weight loss, low body mass index, and reduced muscle mass) and two etiologic criteria (reduced food intake or assimilation, and inflammation or disease burden). Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition and the severity of malnutrition. Contents lists available at sciencedirect. To diagnose malnutrition at least one phenotypic criterion and one etiologic criterion should be present. Malnutrition is the result of inadequate food and nutrient intake or assimilation, thus recent intake compared to estimated requirements is a primary criterion defining malnutrition. Criteria (1 of 8 required) weight for height z score. Nutrition support in head and neck cancer. Web the comprehensive nutritional assessment consisted of: Web it scores body mass index (bmi), unintentional weight loss, and acute disease effect (which bapen defines as no or unlikely dietary intake for >5 days because of activity of disease) and separates patients into three risk groups: Web aspen | malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. Malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community 2019 glim provides a framework for diagnosing adult malnutrition. Web global leadership initiative on malnutrition (glim): Web glim criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition: Web the comprehensive nutritional assessment consisted of: Here are some resources and tools to help advocate for yourself or your loved ones. Congenital heart disease and liver disease (part 1) 2019; Web 6 characteristics of aspen malnutrition criteria (1): Jpen j parenter enteral nutr. Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition and the severity of malnutrition. Criteria (at least 2 must be present) Length/height z score (severe) muac. A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Web global leadership initiative on malnutrition (glim): You might be at risk for malnutrition due to your disease or condition and this may impact your clinical outcome. A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition and the severity of malnutrition. Low risk, medium risk, and high risk (table 1 ). Adult guidelines for nutrition support in enhanced recovery after surgery Web it scores body mass index (bmi), unintentional weight loss, and acute disease effect. Low risk, medium risk, and high risk (table 1 ). Clinical characteristics that the rd can obtain and document to support a diagnosis of malnutrition. Web aspen uses the grade system of guideline development and clearly delineates this methodology in each guideline. Malnutrition is the result of inadequate food and nutrient intake or assimilation, thus recent intake compared to estimated. Web we recommend characteristics for the identification of adult malnutrition (and/aspen tool).1 suspect malnutrition if two or more characteristics are present: Adult guidelines for nutrition support in enhanced recovery after surgery Length/height z score (severe) muac. A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Web glim criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition: Congenital heart disease and liver disease (part 1) 2019; Nutrition support in head and neck cancer; Web the top five ranked criteria included three phenotypic criteria (weight loss, low body mass index, and reduced muscle mass) and two etiologic criteria (reduced food intake or assimilation, and inflammation or disease burden). Malnutrition in children with chronic disease: Web it scores body. Length/height z score (severe) muac. Malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. To diagnose malnutrition at least one phenotypic criterion and one etiologic criterion should be present. Web the comprehensive nutritional assessment consisted of: Bmi for age z score. Web aspen uses the grade system of guideline development and clearly delineates this methodology in each guideline. Malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. Criteria (at least 2 must be present) Web 6 characteristics of aspen malnutrition criteria (1): Guidance on validation of the operational criteria for the diagnosis of protein‐energy malnutrition in adults. Malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. Adult guidelines for nutrition support in enhanced recovery after surgery Guidance on validation of the operational criteria for the diagnosis of protein‐energy malnutrition in adults. Cystic fibrosis and renal disease (part 2) 2019 Nutrition support in head and neck cancer. Cystic fibrosis and renal disease (part 2) 2019 Web the academy of nutrition and dietetics (academy) and the american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (a.s.p.e.n.) recommend that a standardized set of diagnostic characteristics be used to identify and document adult malnutrition in routine clinical practice. Characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation. Web malnutrition matters for pediatric patients 2018; Web an international consensus guideline committee has proposed an approach to diagnosing malnutrition in adults based on etiology, thus integrating the present understanding of inflammatory responses to disease and trauma. A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Each of these criteria have guidelines to determine the type of malnutrition and the severity of malnutrition. 8, 9 the committee proposed the following nutrition diagnoses: Length/height z score (severe) muac. Web we recommend characteristics for the identification of adult malnutrition (and/aspen tool).1 suspect malnutrition if two or more characteristics are present: Weight gain velocity (malnutrition</strong> (adult) severe malnutrition (adult) Clinical characteristics that the rd can obtain and document to support a diagnosis of malnutrition. Web aspen | malnutrition tools and resources for patients and caregivers. Guidelines under development or update: Jpen j parenter enteral nutr. Malnutrition in children with chronic disease:
Understanding ASPEN Malnutrition Criteria The Geriatric Dietitian

ASPEN Malnutrition Solution Center

Studies Comparing the Standard Reference Charts for Malnutrition

Aspen Academy Malnutrition Criteria Chart

ASPEN Malnutrition Solution Center
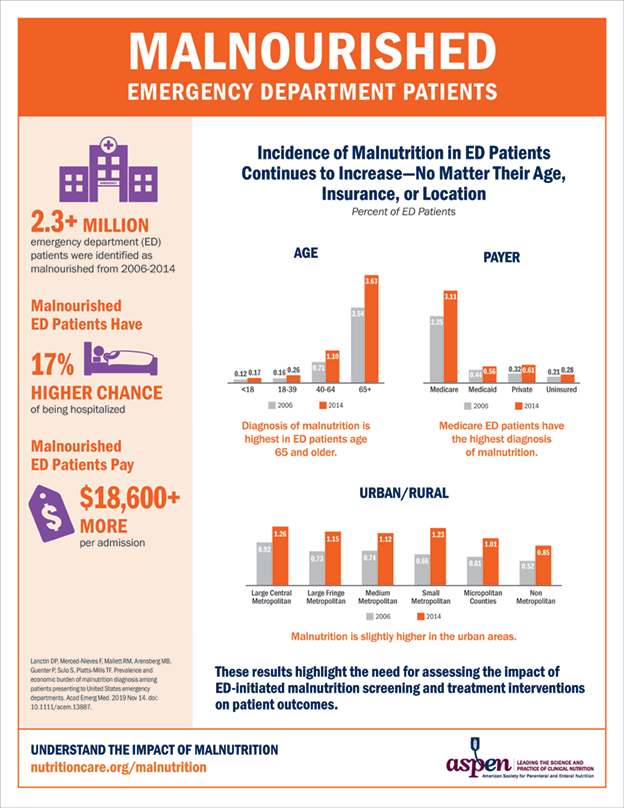
ASPEN Malnutrition Solution Center

Evaluation of muscle and fat loss as diagnostic criteria for

Table 4 from GLIM Criteria for the Diagnosis of Malnutrition A

ASPEN Malnutrition

Aspen Malnutrition Diagnosis Chart
Contents Lists Available At Sciencedirect.
Inflammation Is Chronic And Of Mild To Moderate Degree (E.g., Organ Failure, Pancreatic Cancer, Rheumatoid Arthritis Or.
You Might Be At Risk For Malnutrition Due To Your Disease Or Condition And This May Impact Your Clinical Outcome.
Nutrition Support In Head And Neck Cancer.
Related Post: