Binomial Probability Chart
Binomial Probability Chart - It can calculate the probability of success if the outcome is a binomial random variable, for example if flipping a coin. Let’s work through an example calculation to bring the formula to life! Web this binomial distribution table has the most common cumulative probabilities listed for n. Web this applet computes probabilities for the binomial distribution: Web this document is designed to allow you to determine probabilities related to binomial distribution Hitting tab or enter on your keyboard will. P (2) p ( 2) probability of exactly 2 successes: Click the link below that corresponds to the n from your problem to take you to the correct table, or scroll down to find the n you need. * type of probability:* answer: Web click the calculate button to compute binomial and cumulative probabilities. To understand the effect on the parameters \ (n\) and \ (p\) on the shape of a binomial distribution. Web statistical tables for students binomial table 1 binomial distribution — probability function p x 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.300.35 0.400.45 0.50 n=1 0.9900.9500.9000.8500.8000.7500.7000.6500.6000.5500.5000 1 1.0100.0500.1000.1500.2000.2500.3000.3500.4000.4500.5000 0 The number of “successes” during n trials. P ( x = 3). Web the binomial distribution formula takes the number of combinations, multiplies that by the probability of success raised by the number of successes, and multiplies that by the probability of failures raised by the number of failures. P (2) p ( 2) probability of exactly 2 successes. The mean, μ, and variance, σ2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ. That is, there is a 25% chance, in sampling 15 random americans, that we would find exactly 3 that had no health insurance. It can calculate the probability of success if the outcome is a binomial random variable, for example if flipping a coin. The random variable x = the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. $$x. P (2) p ( 2) probability of exactly 2 successes: Web using the probability mass function for a binomial random variable, the calculation is then relatively straightforward: It can calculate the probability of success if the outcome is a binomial random variable, for example if flipping a coin. A binomial distribution shows either (s)uccess or (f)ailure. Let’s work through an. Web the binomial distribution formula takes the number of combinations, multiplies that by the probability of success raised by the number of successes, and multiplies that by the probability of failures raised by the number of failures. Enter the number of trials in the $n$ box. Number of successes (x) binomial probability: Web the binomial is a type of distribution. P ( # of successes getting exactly some) = ( arrangements # of) ⋅ ( of success probability) ( successes # of) ⋅ ( of failure probability) ( failures # of) using the example from problem 1: N x 0.01 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95 P. Web here's a summary of our general strategy for binomial probability: Web this applet computes probabilities for the binomial distribution: Web this binomial distribution table has the most common cumulative probabilities listed for n. Web click the calculate button to compute binomial and cumulative probabilities. Web use this binomial probability calculator to easily calculate binomial cumulative distribution function and probability. Web the binomial is a type of distribution that has two possible outcomes (the prefix “ bi ” means two, or twice). * type of probability:* answer: Web this binomial distribution table has the most common cumulative probabilities listed for n. Web this applet computes probabilities for the binomial distribution: Web the outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial. Probability of success on a trial. For example, a coin toss has only two possible outcomes: The mean, μ, and variance, σ2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ2 = npq. To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random variable. Web use this binomial probability calculator to easily calculate binomial cumulative distribution. Web the outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. Web this document is designed to allow you to determine probabilities related to binomial distribution A binomial distribution shows either (s)uccess or (f)ailure. Web table 4 binomial probability distribution c p r qn − r n, r this table shows the probability of r successes in n independent. Heads or tails and taking a test could have two possible outcomes: The mean, μ, and variance, σ2, for the binomial probability distribution are μ = np and σ2 = npq. * type of probability:* answer: Web use this binomial probability calculator to easily calculate binomial cumulative distribution function and probability mass given the probability on a single trial, the number of trials and events. It can calculate the probability of success if the outcome is a binomial random variable, for example if flipping a coin. Enter the number of trials in the $n$ box. Web binomial formula and binomial probability. To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random variable. Web in the chart, each bar represents the probability of rolling a specific number of sixes out of ten die rolls. Number of successes (x) binomial probability: Web this applet computes probabilities for the binomial distribution: Web table 4 binomial probability distribution c p r qn − r n, r this table shows the probability of r successes in n independent trials, each with probability of success p. Web statistical tables for students binomial table 1 binomial distribution — probability function p x 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.300.35 0.400.45 0.50 n=1 0.9900.9500.9000.8500.8000.7500.7000.6500.6000.5500.5000 1 1.0100.0500.1000.1500.2000.2500.3000.3500.4000.4500.5000 0 P ( # of successes getting exactly some) = ( arrangements # of) ⋅ ( of success probability) ( successes # of) ⋅ ( of failure probability) ( failures # of) using the example from problem 1: The standard deviation, σ, is then σ = npq−−−√ n p q. That is, there is a 25% chance, in sampling 15 random americans, that we would find exactly 3 that had no health insurance.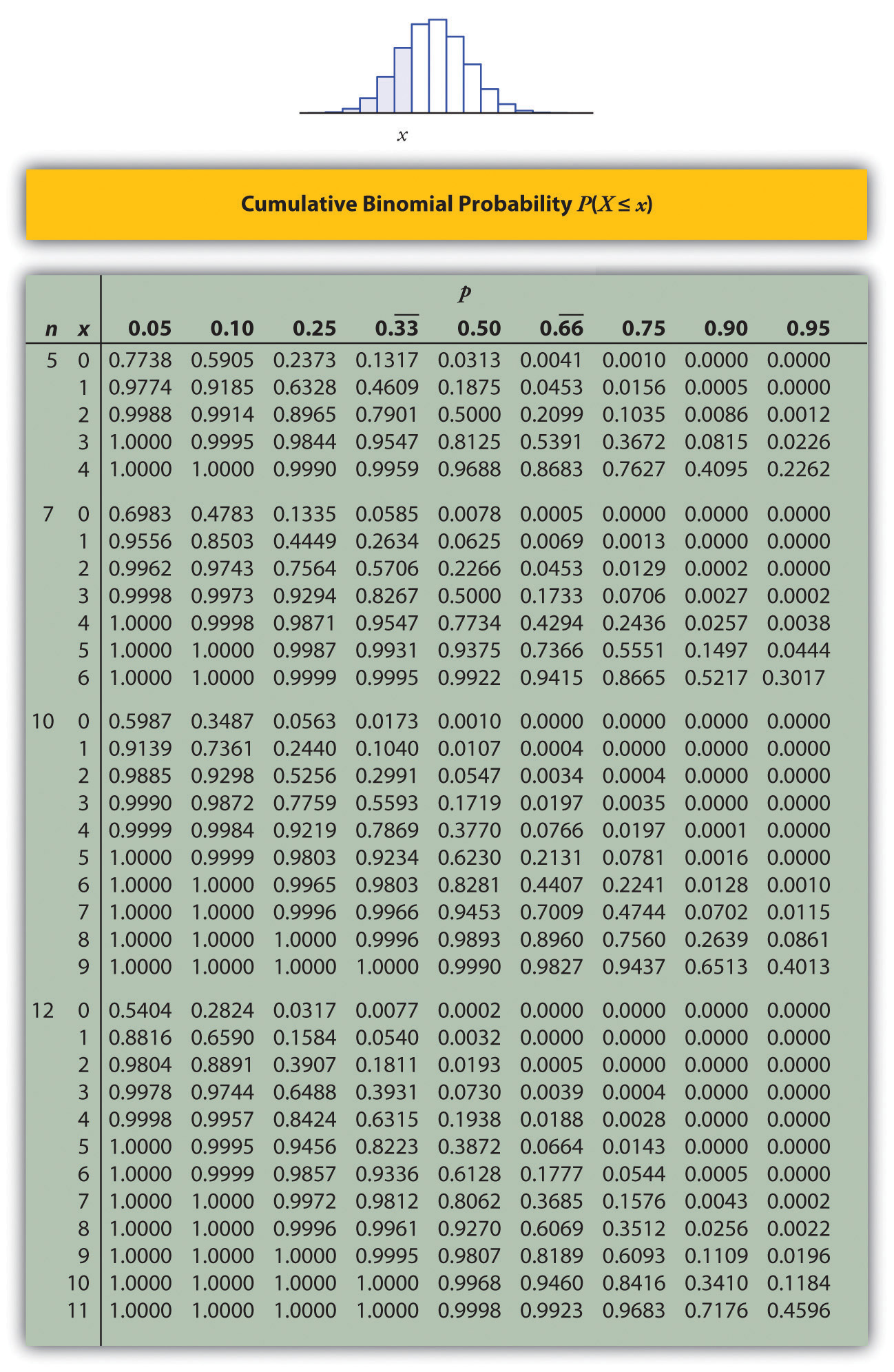
Solved X Is A Binomial Random Variable With Parameters N

Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
Probability Archives Statistics Tutorials

Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
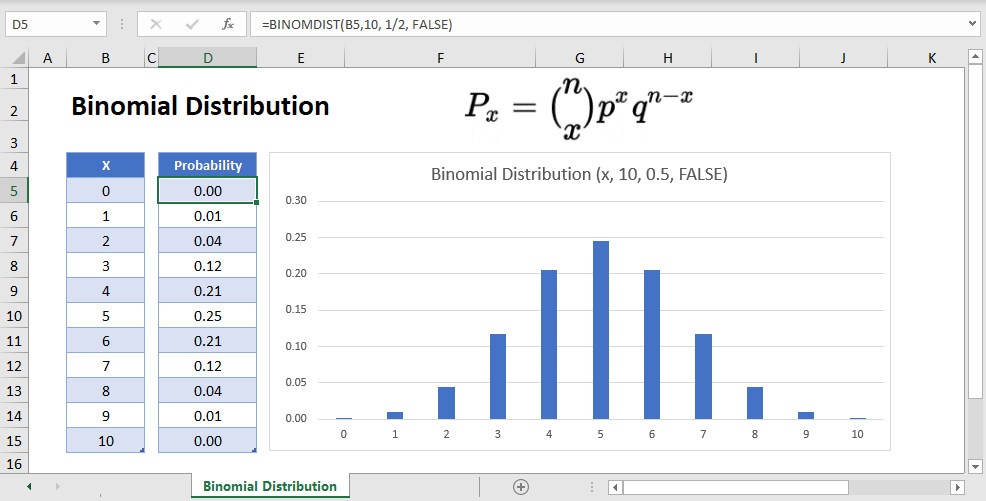
Binomial Distribution in Excel & Google Sheets Automate Excel

pgfmath Binomial distribution in table TeX LaTeX Stack Exchange

Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using the Binomial Table dummies

How to Read the Binomial Distribution Table Statology
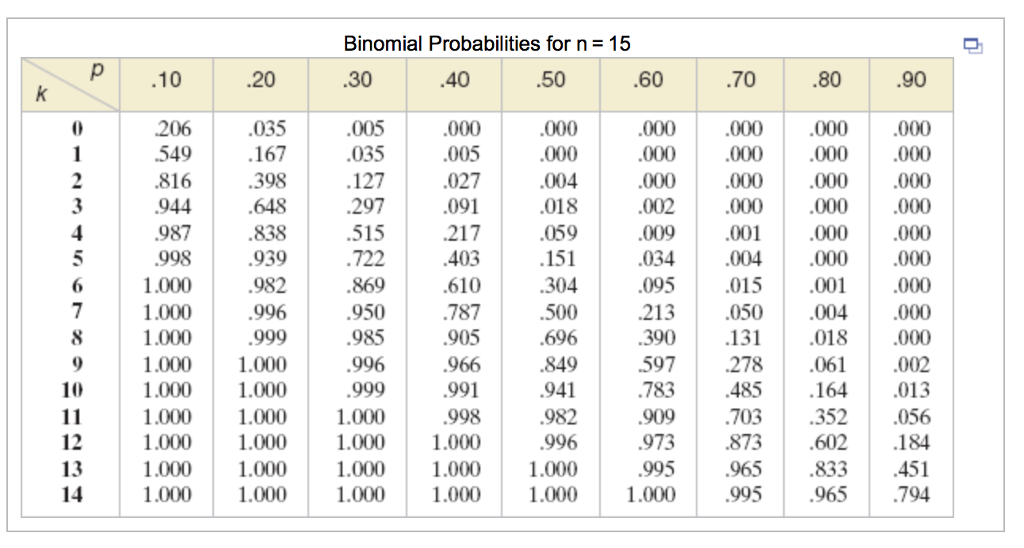
Solved If x is a binomial random variable, use the binomial
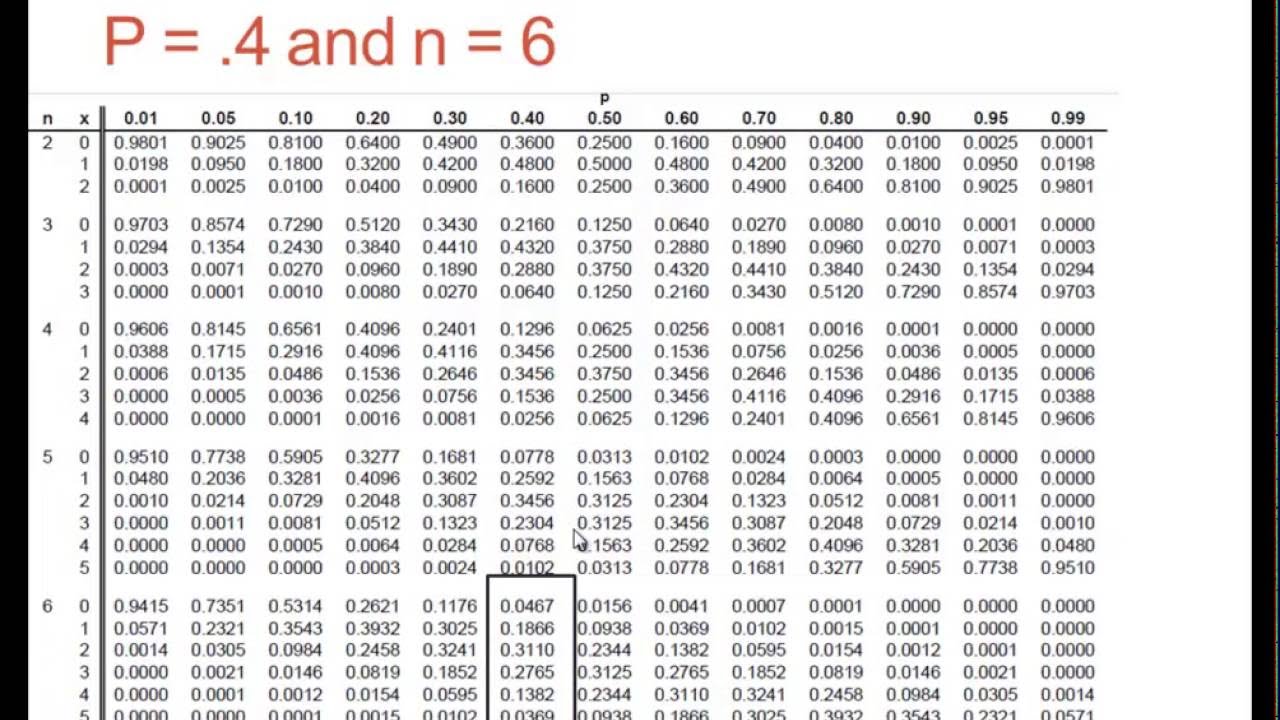
Download Binomial Probability Distribution Table N 20 Gantt Chart
N X 0.01 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.55 0.6 0.65 0.7 0.75 0.8 0.85 0.9 0.95
P (2) P ( 2) Probability Of Exactly 2 Successes:
A Binomial Distribution Shows Either (S)Uccess Or (F)Ailure.
A Pdf May Also Be A Formula That You Can Use To Find The Probability Of Any Outcome Of An Experiment.
Related Post: