Cell Cycle Pie Chart
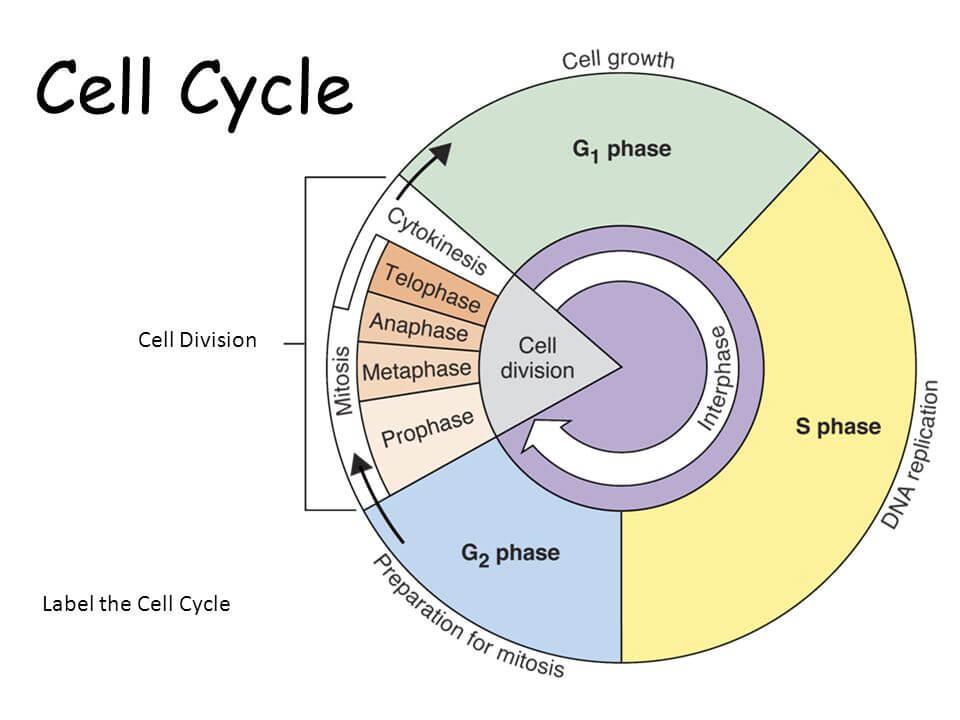
Cell Cycle Pie Chart - Most of the cell cycle is the period during which the cell is not dividing, which is called interphase. A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. Web result cell cycle pie chart diagram | quizlet. The bigger part of this pie chart, labeled c, divides into three sectors. The second sector is labeled d. Which of these phases encompasses all of the stages of mitosis but no other events? It is the first part of interphase. The cell cycle in prokaryotes is quite simple: Web result the cell cycle put the steps of the cell cycle in the correct area on the pie chart using the hints provided interphase mitosis anaphase prophase s phase cytokinesis s phase metaphase telophase ga phase proceed to division guphase remain specialized restriction checkpoint reset apoptosis. Web result each pie chart shows the fraction of the cell cycle devoted to each of the primary stages of the cell cycle. These initially remain attached to each other with each strand called a chromatid. Web result in mitosis, two cells called. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. The. Web result the cycle is divided into four (4) main stages or phases: In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Web result cell cycle pie chart diagram | quizlet. The bigger part of this pie chart, labeled c, divides into three. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Yeast for example, can progress through the cell. Web result 10.1.1 phases of cell cycle a typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture. Typical timing of somatic cell division. The second sector is labeled d. Interphase and the mitotic (m) phase. A d c e b Web result we show how cell proportions (pie charts) change across time, with apical progenitors (relatively fast cycling cells) decreasing in frequency as the average cell cycle duration increases. It is the first part of interphase. Download and install a custom pie chart font. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. G 1, s and g 2 are collectively called interphase ( figure 3.2.1 ). Focus your studying with a path. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. During the growth phase of the cell cycle, the genetic material of the cell. These initially remain attached to each other with each strand called a chromatid. Web result cell cycle pie chart diagram | quizlet. Once you have it correct draw and label the pie chart in the circle below. How do you want to study today? The second sector is labeled d. Web result the cycle is divided into four (4) main stages or phases: The smaller part of the pie chart divides into two sectors. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. Are produced, each identical to the parent cell. Download and install a custom pie chart font. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. Cell cycle durations reflect minimal doubling times under ideal conditions. Web result the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Web result the cell cycle is a series of stages in the life cycle of a cell. These initially remain attached to each other with each strand called a chromatid. Most of the cell cycle is the period during which the cell is not dividing, which is called interphase. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Web result we show how cell proportions (pie charts) change across time, with apical progenitors (relatively fast cycling cells) decreasing in frequency as the average cell cycle duration increases. Web result each. The second sector is labeled d. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. Web result the cell cycle put the steps of the cell cycle in the correct area on the pie chart using the hints provided interphase mitosis anaphase prophase s phase cytokinesis s phase metaphase telophase ga phase proceed to division. Web result the figure shows the pie chart of the cell cycle, which consists of two parts. How do you want to study today? In eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. Web result the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. G 1, s and g 2 are collectively called interphase ( figure 3.2.1 ). Web result the cytokinesis phase takes about half of that time. These cells divide once in approximately every 24 hours (figure 10.1). Web result the following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. The cell continues to grow and synthesize proteins and organelles necessary for the last phase. Web result cell cycle pie chart. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. It is the first part of interphase. Two copies of each chromosome are produced; However, this duration of cell cycle can vary from organism to organism and also from cell type to cell type.
Cell cycle phases Biology Lessons, Science Biology, Science Education

explain cell cycle with the help of a neat diagram Biology Cell

Nicholas Baker's Creative Studio For CGAA The Cell Cycle Research

Confusion about the duration of different phases of the cell cycle such
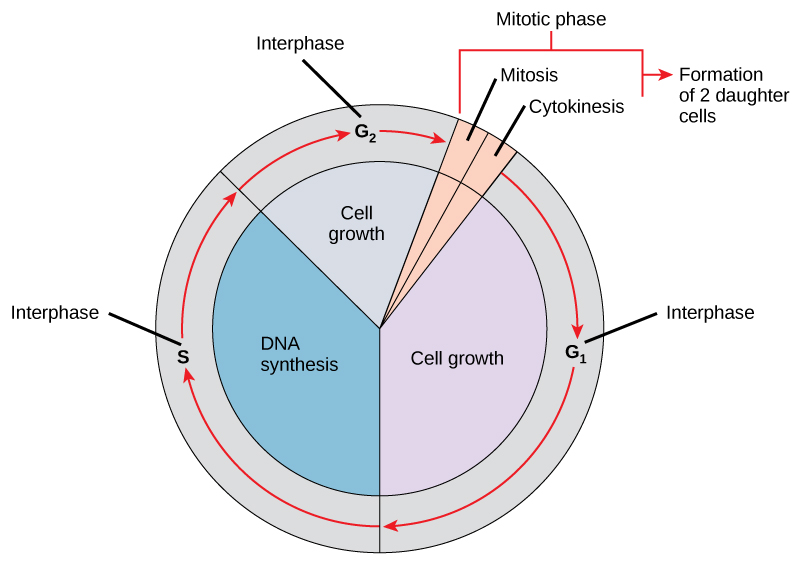
The Cell Cycle OpenStax Biology 2e
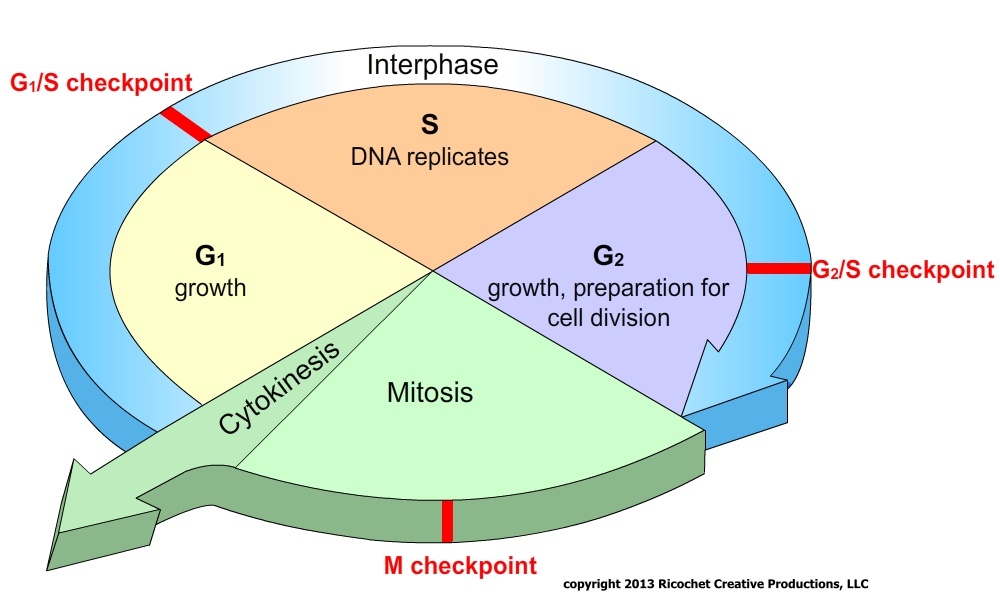
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division

Quia Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
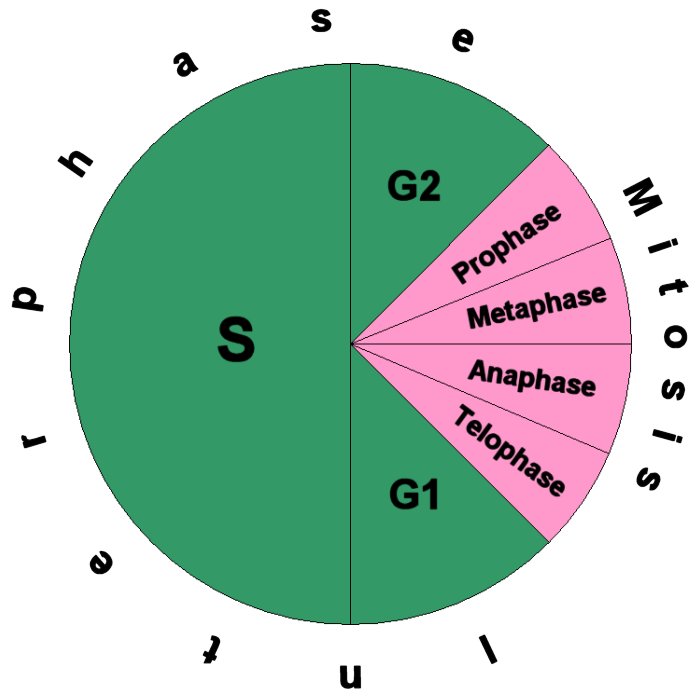
Cell Cycle Diagram ClipArt Best
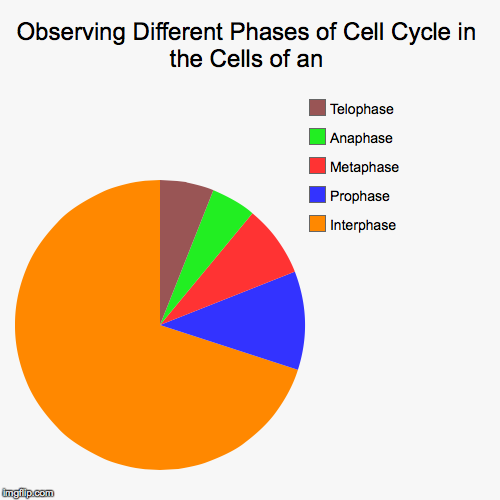
Observing Different Phases of Cell Cycle in the Cells of an Imgflip
NCERT Solutions Cell Cycle and Cell Division NEET Notes EduRev
Web Result Each Pie Chart Shows The Fraction Of The Cell Cycle Devoted To Each Of The Primary Stages Of The Cell Cycle.
The Cell Cycle In Prokaryotes Is Quite Simple:
In Eukaryotic Cells, Or Cells With A Nucleus, The Stages Of The Cell Cycle Are Divided Into Two Major Phases:
The Cell Grows, Its Dna Replicates, And The Cell Divides.
Related Post: