Chart Of Macromolecules
Chart Of Macromolecules - In this reaction, the monomers which. Web macromolecules are very large molecules consisting of thousands of atoms. They are usually the product of smaller molecules, like proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. And nucleic acids, including dna and rna. Different types of biological macromolecules. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Alanine is an example of standard amino acid containing methyl side chain. Target population high school biology students. Web four classes of biological macromolecules. They can have very different shapes, although the most common structure involves a long chain. The four biomolecules specific to life on earth are carbohydrates, such as sugars and starch; Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Each molecule can contain a side chain or r group, e.g. Web macromolecules are very large molecules consisting of thousands of atoms. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. In this reaction, the monomers which. Web four classes of biological macromolecules. Each of these types of macromolecules performs a wide array of important functions within the cell; Web carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and. With a huge variety of different functions from chemical catalysts to structural building blocks. Condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) polymers are made through a chemical reaction called condensation. An example of this is seen when amino acids are bonded together to form a polypeptide chain. Web macromolecules are called polymers are defined as a long chain of repeating subunits (monomers). A. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Alanine is an example of standard amino acid containing methyl side chain. And nucleic acids, including dna and rna. A molecule that is a building block for. Their monomers are called amino acids and there are 20 different amino acids. And nucleic acids, including dna and rna. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Web learn about monomers, polymers, dehydration synthesis, and hydrolysis reactions! Web macromolecules are large, complex molecules. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Brief description of the lessons. Web carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell and provide structural support to plant cells, fungi, and all of the. Web learn about monomers, polymers, dehydration synthesis, and hydrolysis reactions! The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Web macromolecules are very large molecules consisting of thousands of atoms. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. With a huge variety of different functions from chemical catalysts to structural building blocks. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. “macromolecules are very large molecules that are formed by the polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers.” table of contents. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. Macromolecules are made up of single units known. Web all four are macromolecules (big molecules) macro/mega=big. Web macromolecules are very large molecules consisting of thousands of atoms. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Different types of biological macromolecules. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler, smaller subunits. Different types of biological macromolecules. Proteins are involved in nearly all cellular functions and are a major part of all living organisms. Each of these types of macromolecules performs a wide array of important functions within the cell; A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Now that we’ve discussed the four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), let’s talk about macromolecules as a whole. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler, smaller subunits (monomers). The four biomolecules specific to life on earth are carbohydrates, such as sugars and starch; [how is that formula different from carbohydrates in general?] Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. A large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. And nucleic acids, including dna and rna. Each molecule can contain a side chain or r group, e.g. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: An example of this is seen when amino acids are bonded together to form a polypeptide chain.
24 best images about Macromolecules (B.9A) on Pinterest
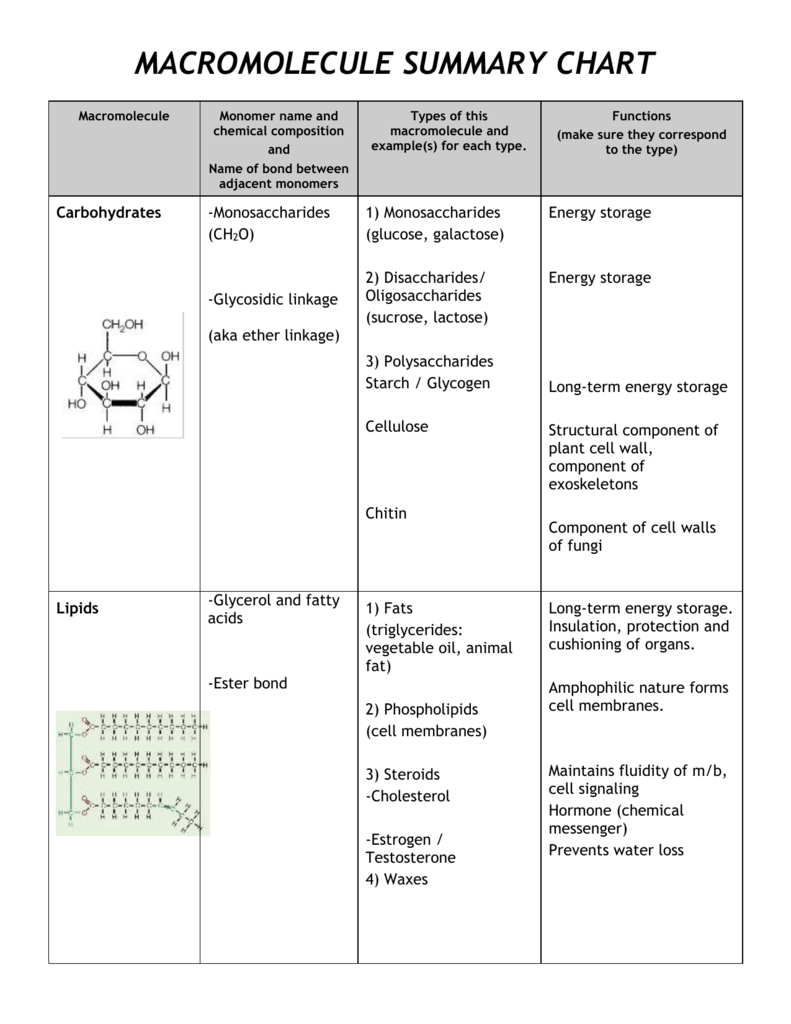
macromolecule summary chart
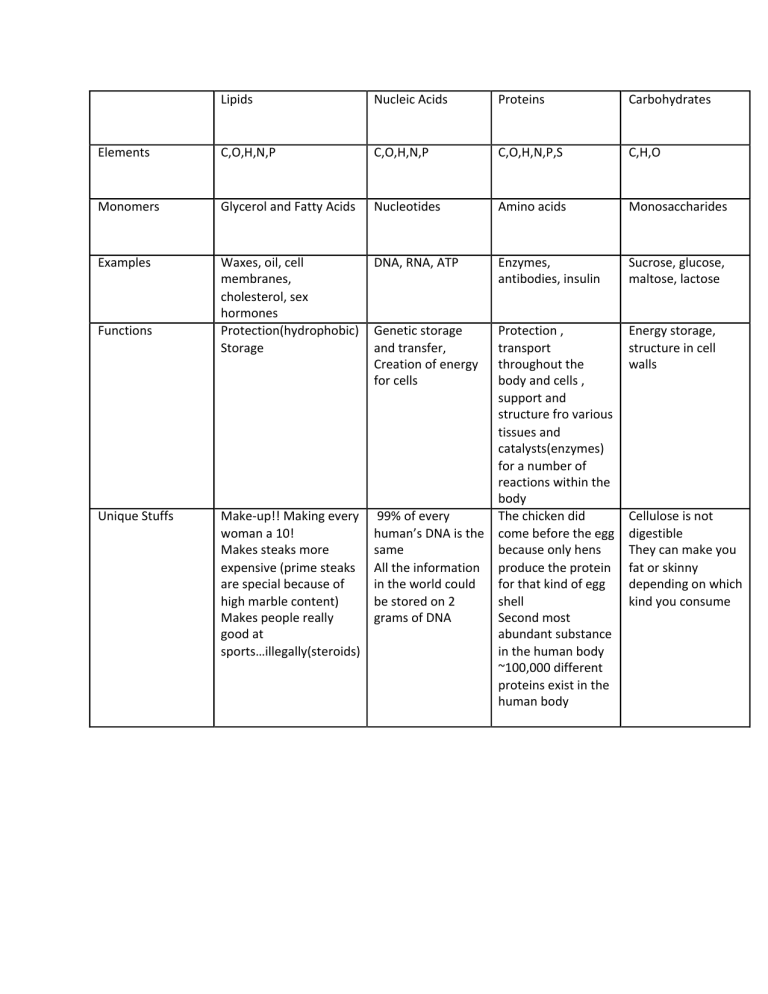
Macromolecule chart
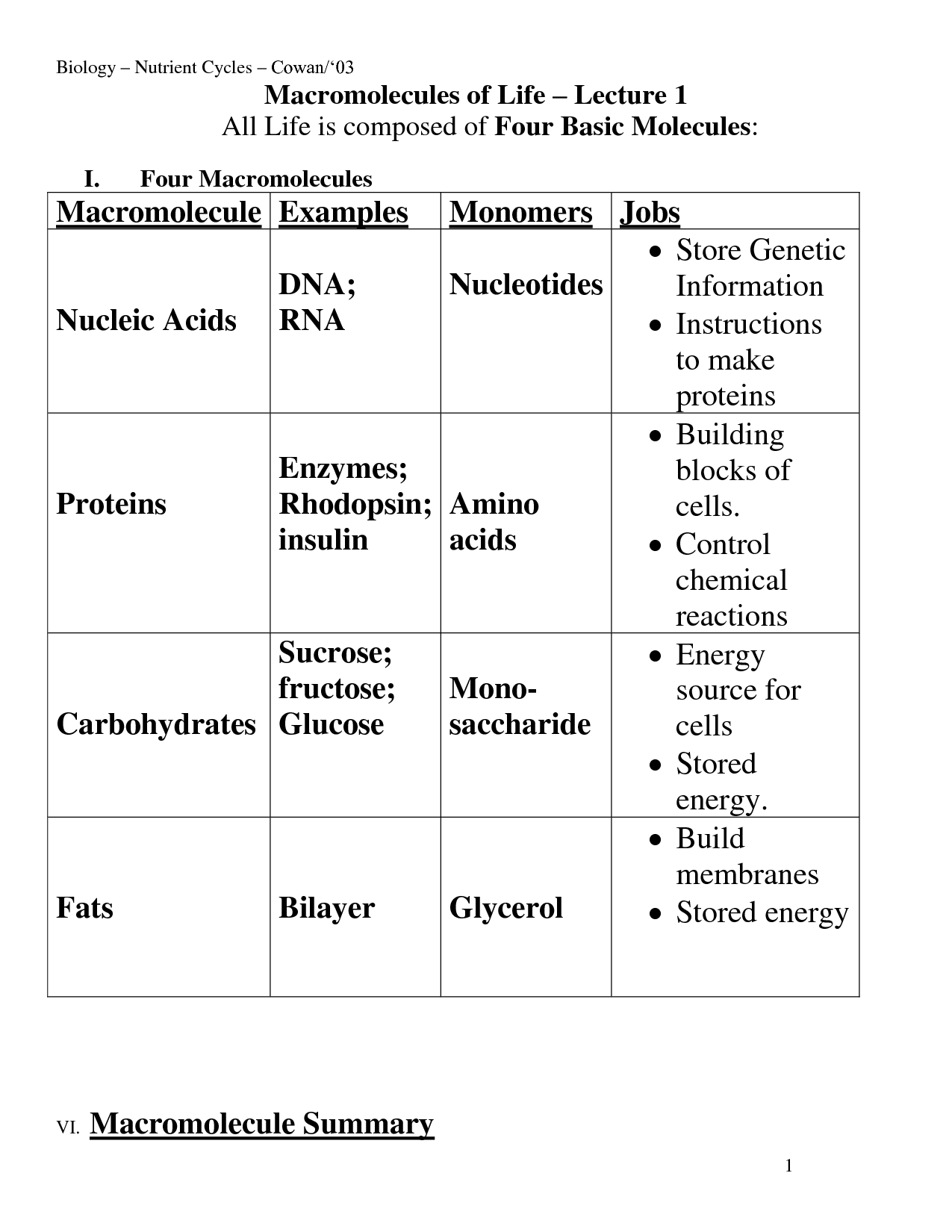
15 Biological Molecules Worksheet /
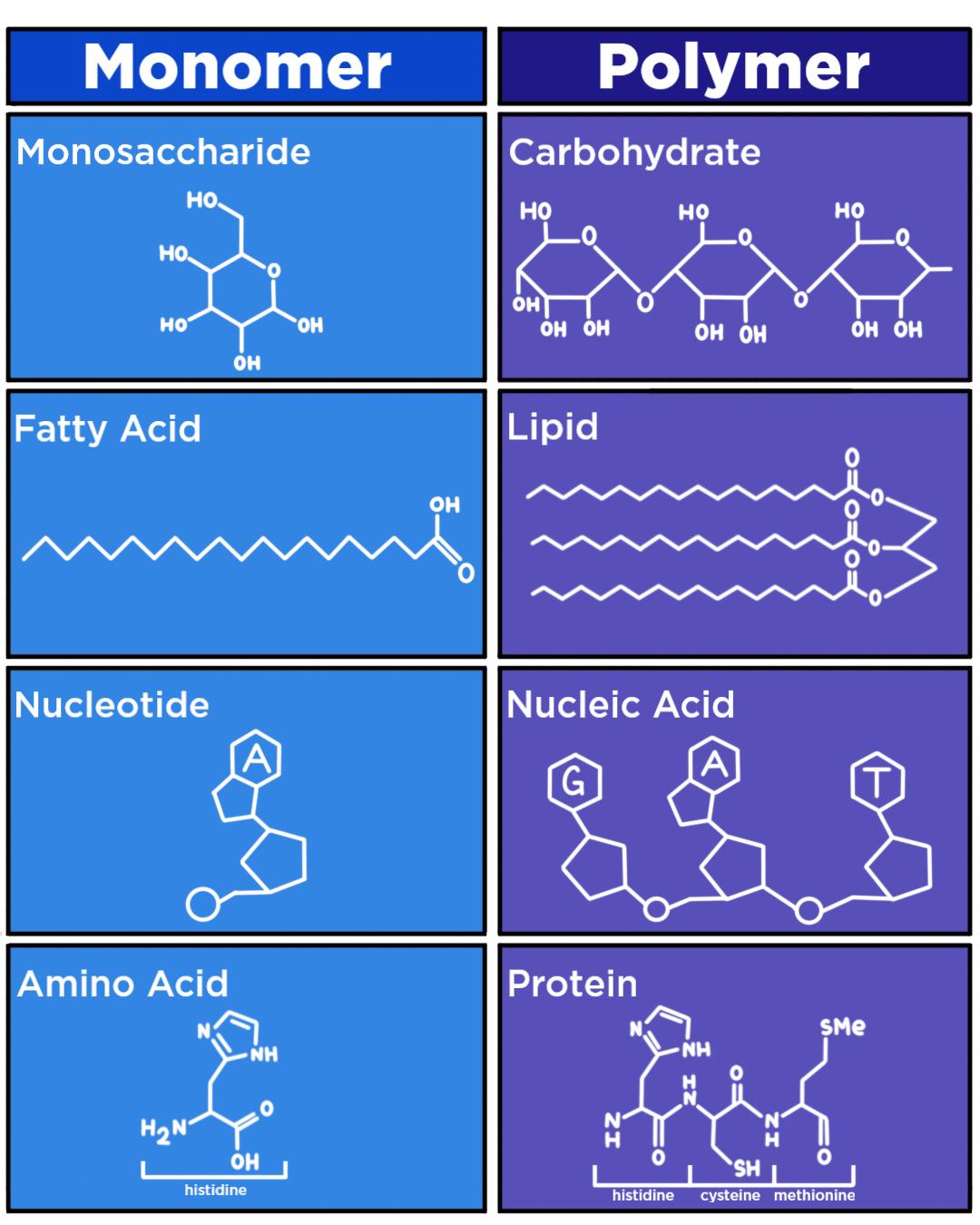
How Do Macromolecules Form? — Overview & Process Expii
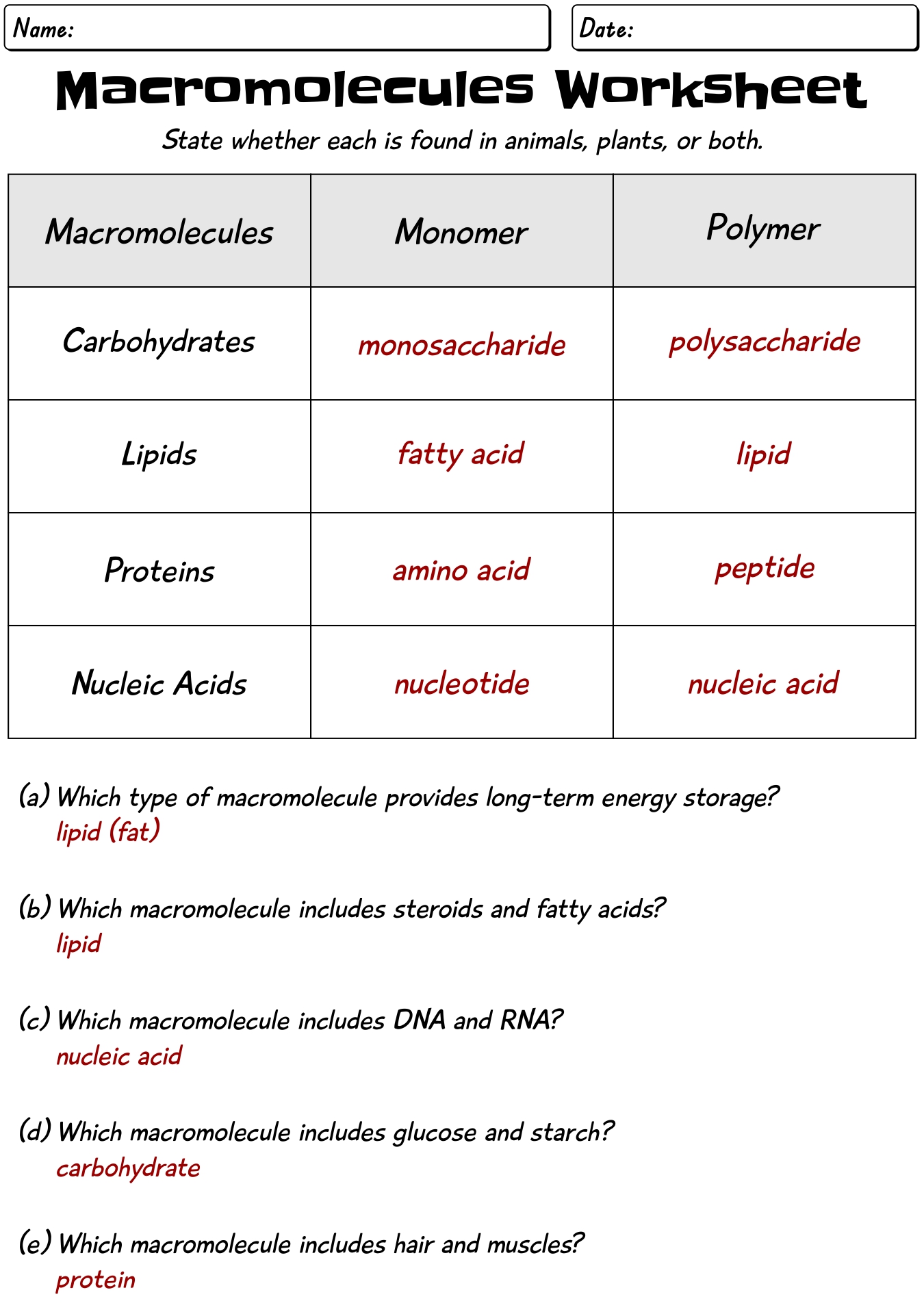
14 Biology Macromolecules Worksheets And Answers /
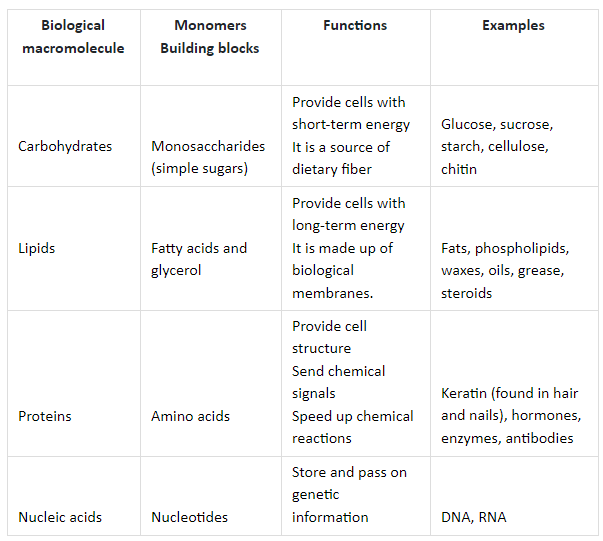
Macromolecules Chart Structures
15 Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet /
Macromolecules Chart Rae Rocks Teaching

PDF Macromolecules Chart PDF document
In This Reaction, The Monomers Which.
Target Population High School Biology Students.
Monosaccharides Have A Formula Of ( Ch 2 O) N , And They Typically Contain Three To Seven Carbon Atoms.
In Biology, Macromolecules Refer To Large Organic Molecules That Form By Polymerization, A Process That Joins Smaller Units Called Monomers Via Covalent Bonds.
Related Post: