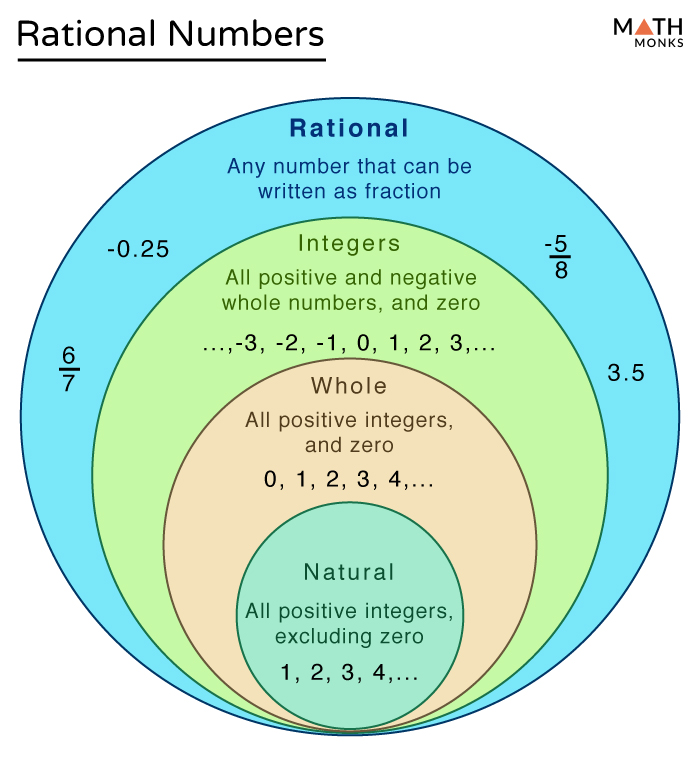
Chart Of Rational And Irrational Numbers
Chart Of Rational And Irrational Numbers - All fractions, both positive and negative, are rational numbers. Some of the examples of rational numbers are 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so on. It is a contradiction of rational numbers. Rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots. We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. Does not stop and does not repeat, the number is irrational. ∗ − as terminating or repeating decimals. Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal, they continue indefinitely without. In this article, we are going to discuss the differences between rational and irrational numbers. Web result their answer in short: In rational numbers (p/q form), q ≠ 0. The exuberance is rational says chief global market strategist kristina hooper. Web result determine if the number is rational (r) or irrational (i). An irrational number cannot be expressed as a ratio, such as p/q, where p and q are integers, q≠0. They have decimal representations that either terminate or do not. Web result the nroc project. Some of the examples of rational numbers are 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so on. Unit 9 data & probability. Rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots. All fractions, both positive and negative, are rational numbers. Rational numbers are sometimes called fractions. In maths, a rational number is a type of real number, which is in the form of p/q where q is not equal to zero. Review related articles/videos or use a hint. In this article, we are going to discuss the differences between rational and irrational numbers. All fractions, both positive and negative, are. Does not stop and does not repeat, the number is irrational. But √25 (= 5), √0.04 (=0.2 = 2/10), etc are rational numbers. An irrational number cannot be expressed as a ratio, such as p/q, where p and q are integers, q≠0. Unit 9 data & probability. It is a contradiction of rational numbers. It is a contradiction of rational numbers. Web result learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are actually irrational. Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be represented as simple fractions. Web result let's summarize a method we can. Web result q irrational numbers rational numbers all real numbers that are not rational numbers; But √25 (= 5), √0.04 (=0.2 = 2/10), etc are rational numbers. Unit 9 data & probability. An irrational number is a real number that cannot be written as a simple fraction: For every rational number, we can write them in the form of p/q,. It is a contradiction of rational numbers. For example √2, √3, √26, etc are irrational. Web result amber watkins. Learn other forms, such as decimals, in which these types of numbers can appear. The venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. Some of the examples of rational numbers are 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so on. Web result learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are actually irrational. Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal, they continue indefinitely without. We can. Web result their answer in short: 1.3 is a rational number because it is equivalent to. Web result unit 8 transformations & similarity. As per the definition, rational numbers include all integers, fractions and repeating decimals. We can write any rational number as the ratio of two integers. So, a rational number can be: For every rational number, we can write them in the form of p/q, where p and q are integer values. Web result differences between rational and irrational numbers. They have decimal representations that either terminate or do not terminate but contain a repeating. Each numerator and each denominator is an integer. Web result rational numbers. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course. We cannot write irrational numbers, such as the square root of 8 and pi, in this way. Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be represented as simple fractions. Some of the examples of rational numbers are 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so on. An irrational number is a real number that cannot be written as a simple fraction: Web result amber watkins. But √25 (= 5), √0.04 (=0.2 = 2/10), etc are rational numbers. Web result differences between rational and irrational numbers. All fractions, both positive and negative, are rational numbers. Web result let us see how to identify rational and irrational numbers based on the given set of examples. Did you know that there's always an irrational number between any two rational numbers? (7.1.1) 4 5, − 7 8, 13 4, a n d − 20 3. Fraction) , where a and b are integers (and b ≠ 0 ). Identifying rational and irrational numbers math www.commoncoresheets.com name: 6 is a rational number because it is equivalent to 6 1.Rational Numbers Other,Mathematics Quizizz

In math, the real numbers contains both rational numbers and irrational
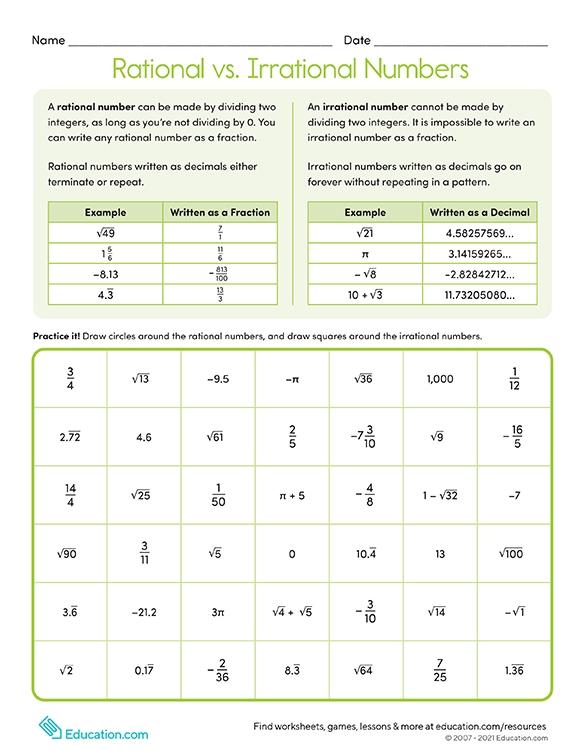
Printables Rational vs. Irrational Numbers HP® Official Site
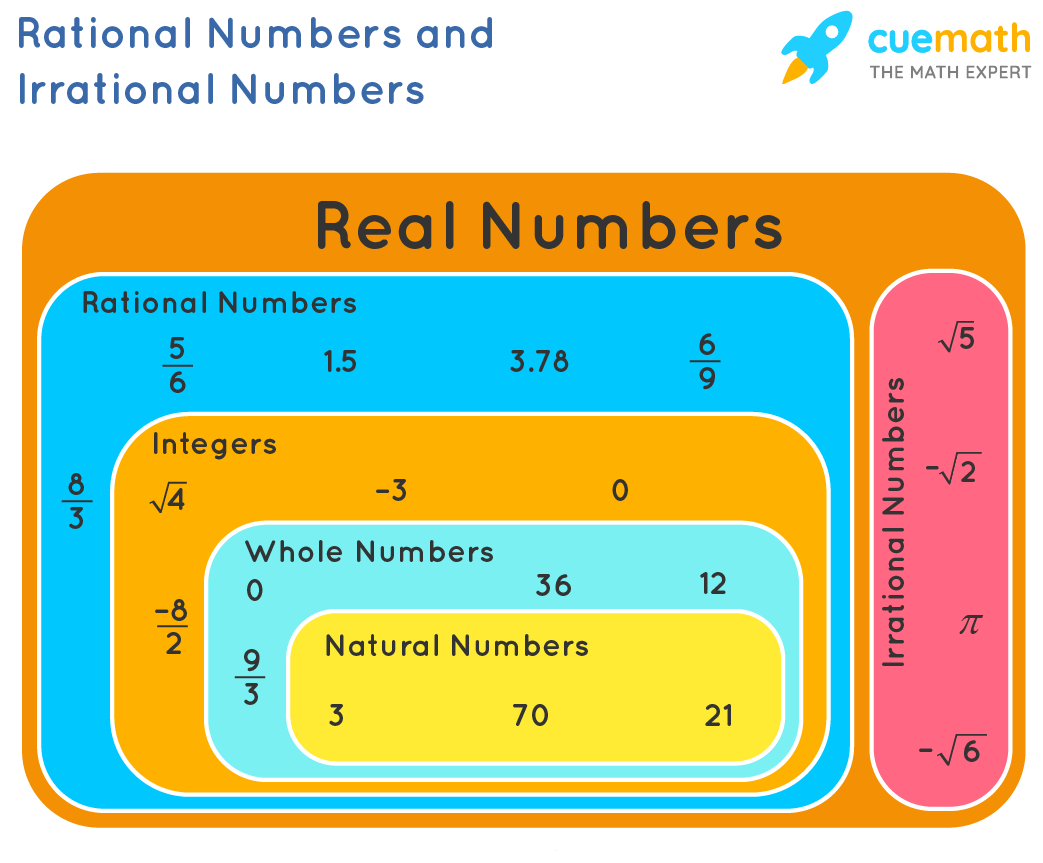
Describe the Relationship Between Rational Numbers and Ratios
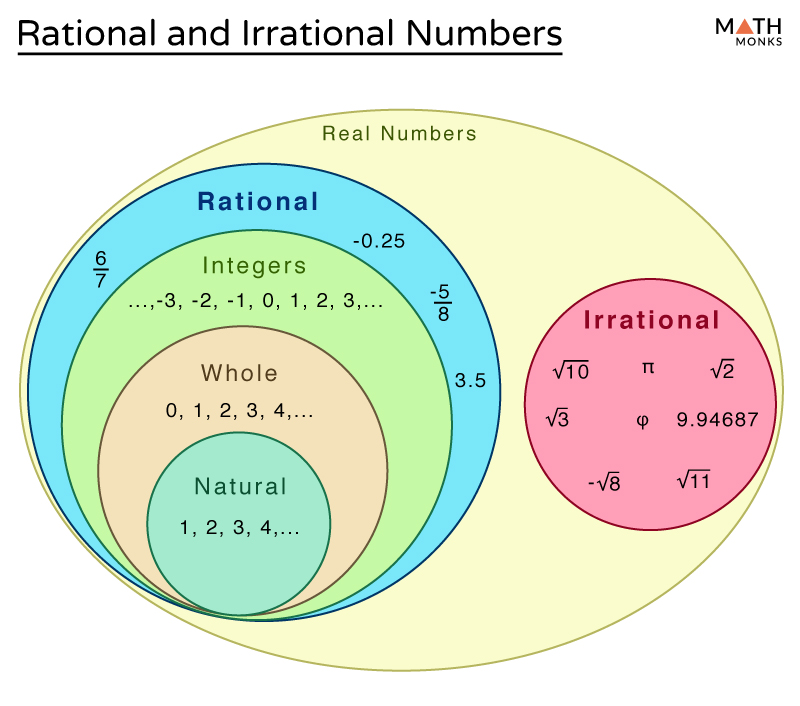
Rational and Irrational Numbers Differences & Examples
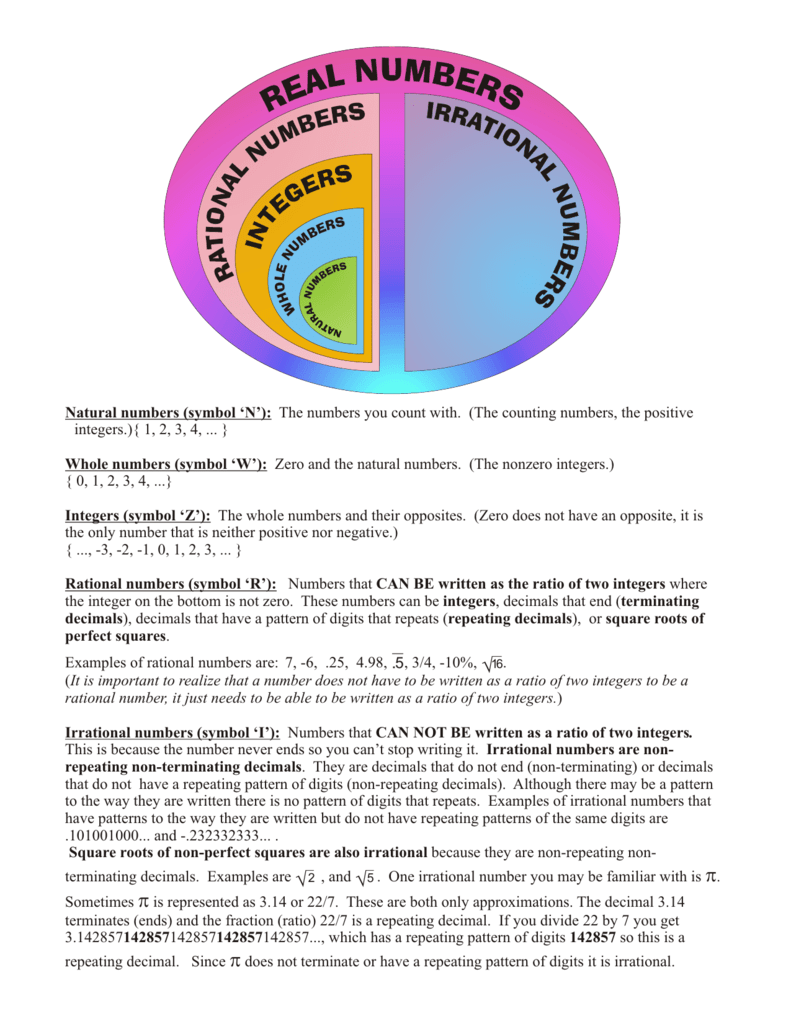
Real numbers chart includes definitions for rational and irrational

Real Numbers Chart With Examples Maxwell Carver

What's the Difference Between Rational and Irrational Numbers? in 2021

What are Irrational Numbers? List, Properties, Arithmetic Operations

Irrational Numbers
Stops Or Repeats, The Number Is Rational.
Web Result A Rational Number Is A Number That Can Be In The Form P/Q Where P And Q Are Integers And Q Is Not Equal To Zero.
∗ − As Terminating Or Repeating Decimals.
They Have Decimal Representations That Either Terminate Or Do Not Terminate But Contain A Repeating.
Related Post: