Chart Of Rocks
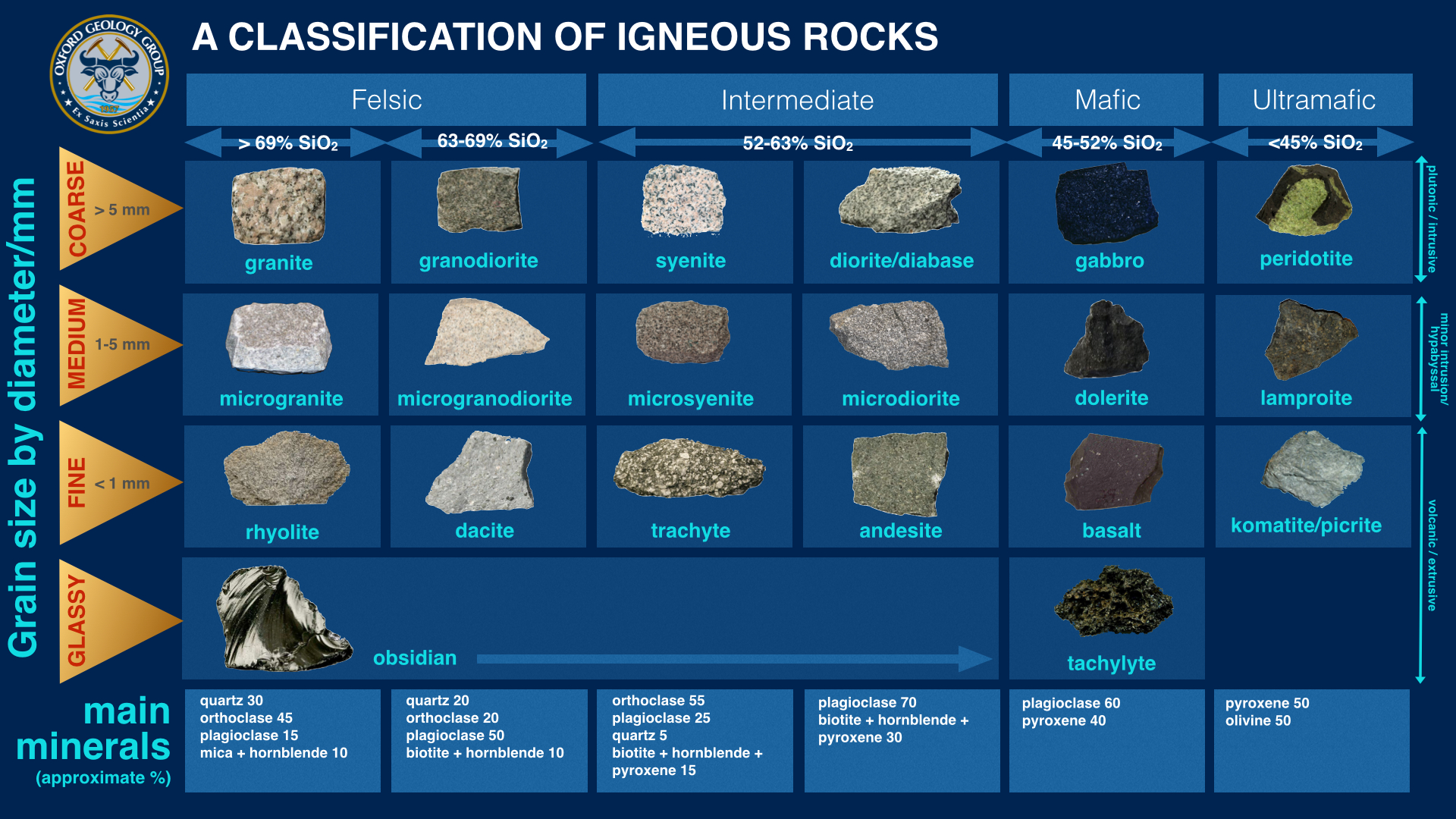
Chart Of Rocks - Igneous , sedimentary , and metamorphic. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Physical geology (lumen) chapter 5: Photos, descriptions and facts about intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. This classification is essential to geologists as it provides critical information about the history of specific regions on earth. Web the following is a list of rock types recognized by geologists. Extremely common in the earth's crust, igneous rocks are volcanic and form from molten material. Web rocks fall into these three groups: Queen’s winning streak begins just below the top 10. Any unique combination of chemical composition, mineralogy, grain size, texture, or other distinguishing characteristics can describe a rock type. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice and obsidian are not included on this diagram. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. The three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are formed from particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments of material. Metamorphic rocks formed from other rocks that are changed. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Rocks on earth are classified according to the way they were formed. Note that glassy igneous rocks pumice. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Web the following is a list of rock types recognized by geologists. Physical geology (lumen) chapter 5: Main types of igneous rocks. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming —that are part of the rock cycle. This classification is essential to geologists as it provides critical information about the history of specific regions on earth. The rock cycle is a natural process that describes how rocks are formed, broken down, and transformed into. Metamorphic rocks formed from other rocks that are changed by heat and pressure underground. Together, all these particles are called sediment. 1 on billboard ’s rock & alternative airplay chart for. Rocks hold the history of the earth and the materials that will be used to build its future. Web the three types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed from melted rock deep inside the earth. Once you've determined what type of rock you've got, look closely at its color and composition. There is no agreed number of specific types of rock. Rocks hold the history of the earth and the materials that will be used to build its future. Their color ranges from light. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Follow the links to pictures and more information. These rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath earth’s crust, allowing for larger crystals to. Igneous rocks come from magma or lava. Web the three types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. These rocks form when magma cools slowly beneath earth’s crust, allowing for larger crystals to. Web the three main types, or classes, of rock are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous and the differences among them have to do with how they are formed. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. There is no agreed number of specific types. (2 min) the region surrounding california’s toxic salton sea has enough lithium to make the u.s. Sedimentary rocks are formed from particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments of material. Web rock, in geology, naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of one or more minerals. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster,. A simplified classification diagram for igneous rocks based on their mineral compositions. Sedimentary rocks are formed from particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments of material. Lower income areas are where the median household income is. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. This classification is essential to geologists as it provides critical information about the history of. Their color ranges from light (in rocks with high silica content) to dark (in rocks with low silica content). Once you've determined what type of rock you've got, look closely at its color and composition. Sedimentary rocks are formed from layers of sand, silt, dead plants, and animal skeletons. How to identify your rock: There are three main types of rocks: Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming —that are part of the rock cycle. Web there are three basic types of rock: They contain a variety of minerals, including quartz, feldspar, mica, and olivine. The three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rocks are the result of great heat and pressure that have changed existing rocks into new rocks. Sedimentary rocks are made from sediments. Igneous rocks are formed from melted rock deep inside the earth. This will help you identify it. Igneous rocks come from magma or lava. Photos, descriptions and facts about intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks. Such aggregates constitute the basic unit of which the solid earth is composed and typically form recognizable and mappable volumes.
Metamorphic Rock Chart Flinn Scientific

Rocks And Minerals Chart Identification
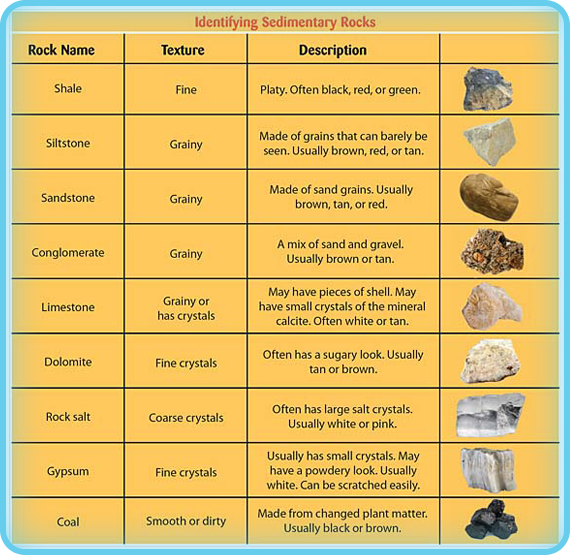
Studying Rocks PowerKnowledge Earth & Space Science

Vintage Geology Wall Chart Rocks & Minerals Etsy

Rock Classification Tables A Practical Guide to Introductory Geology
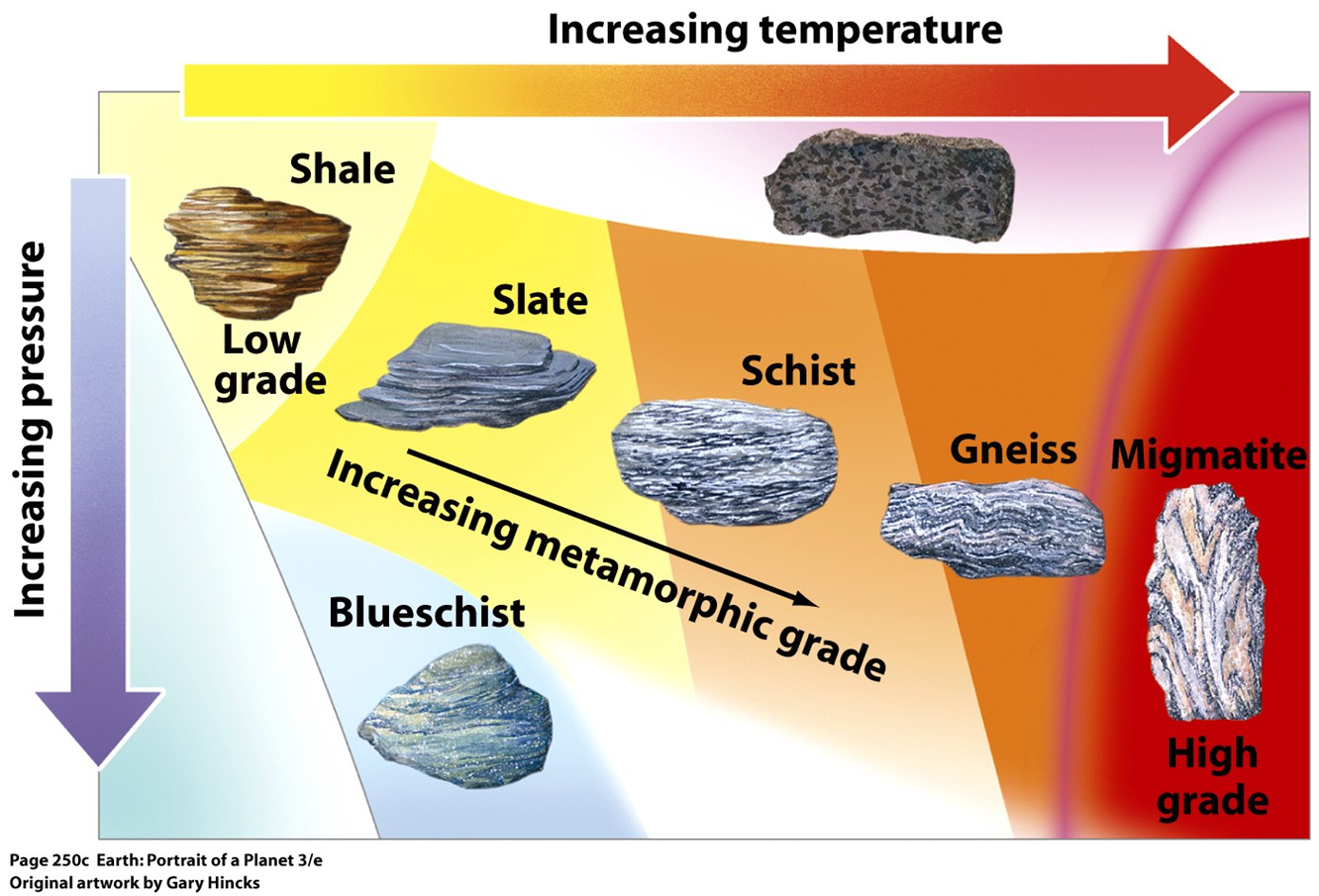
Classifications of Rocks Sedimentary, Igneous and Metamorphic
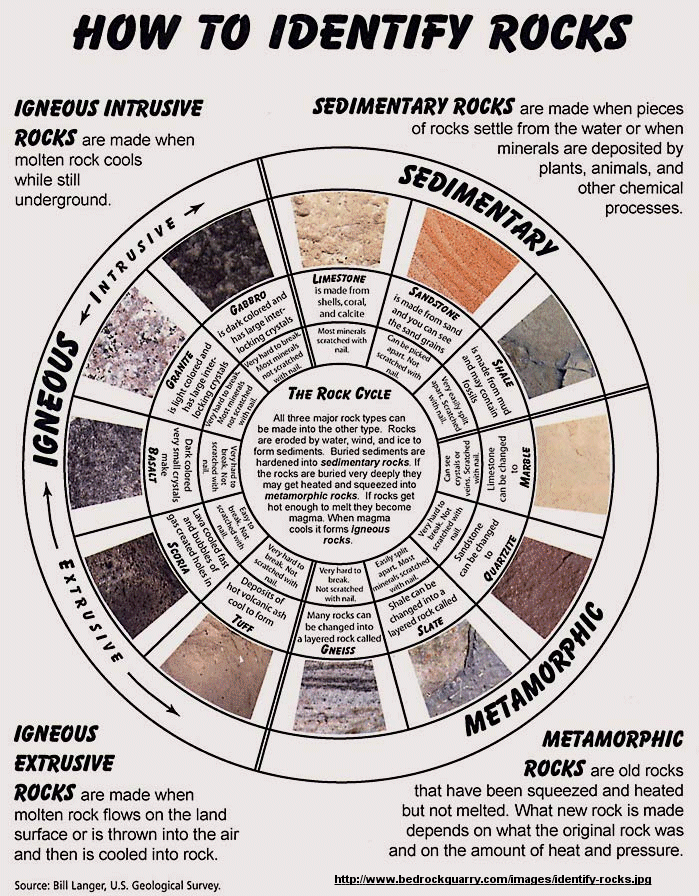
Identifying Rocks Science 6 at FMS
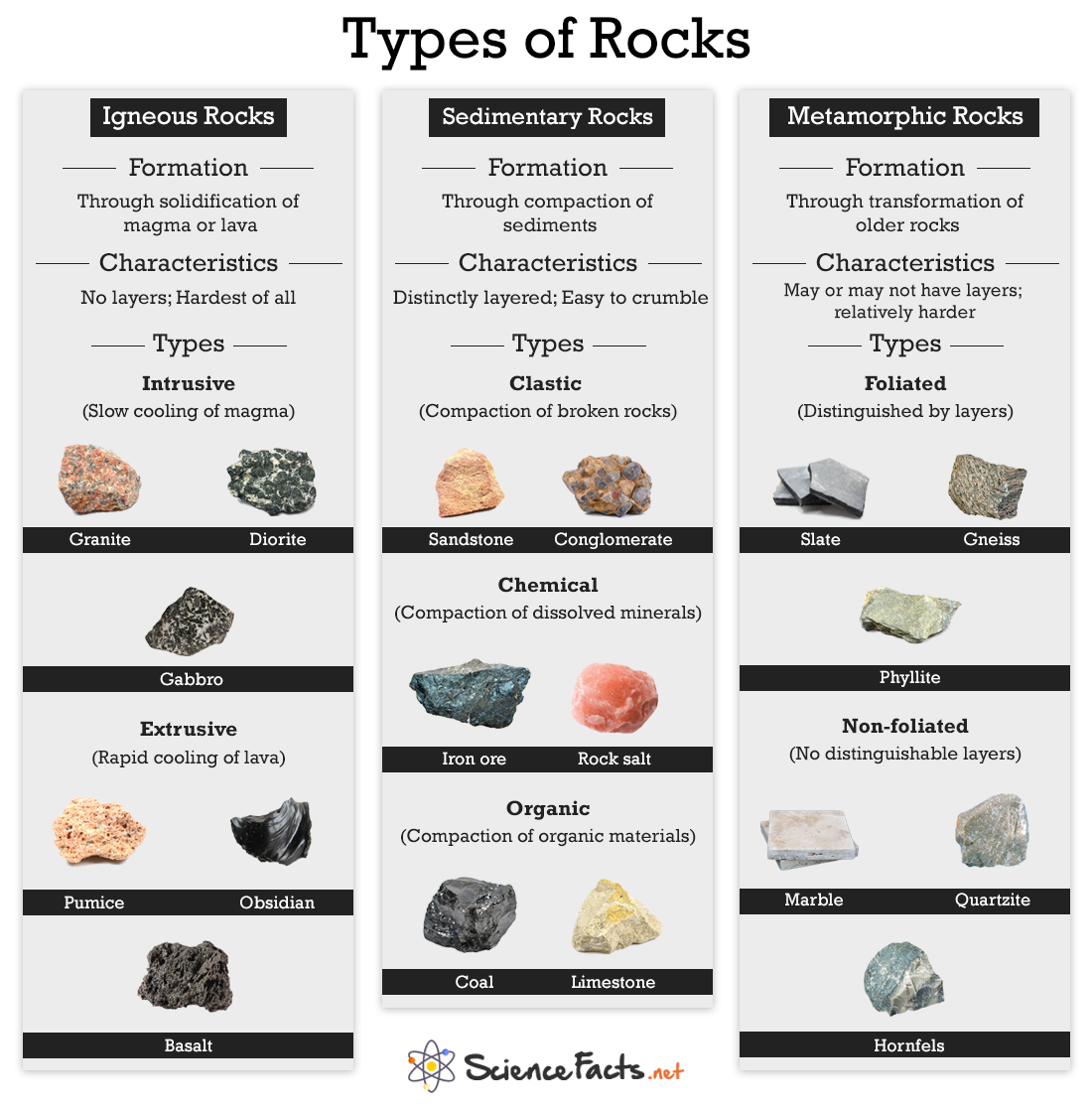
Types of Rocks Science Facts
Rocks Earth Science Review

Overview of Sedimentary Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science
Web Rock Identification Chart.
These Rocks Form When Magma Cools Slowly Beneath Earth’s Crust, Allowing For Larger Crystals To.
Web Rock, In Geology, Naturally Occurring And Coherent Aggregate Of One Or More Minerals.
Igneous Rocks Form From The Cooling And Solidification Of Molten Magma Or Lava.
Related Post: