Crosswind Component Chart
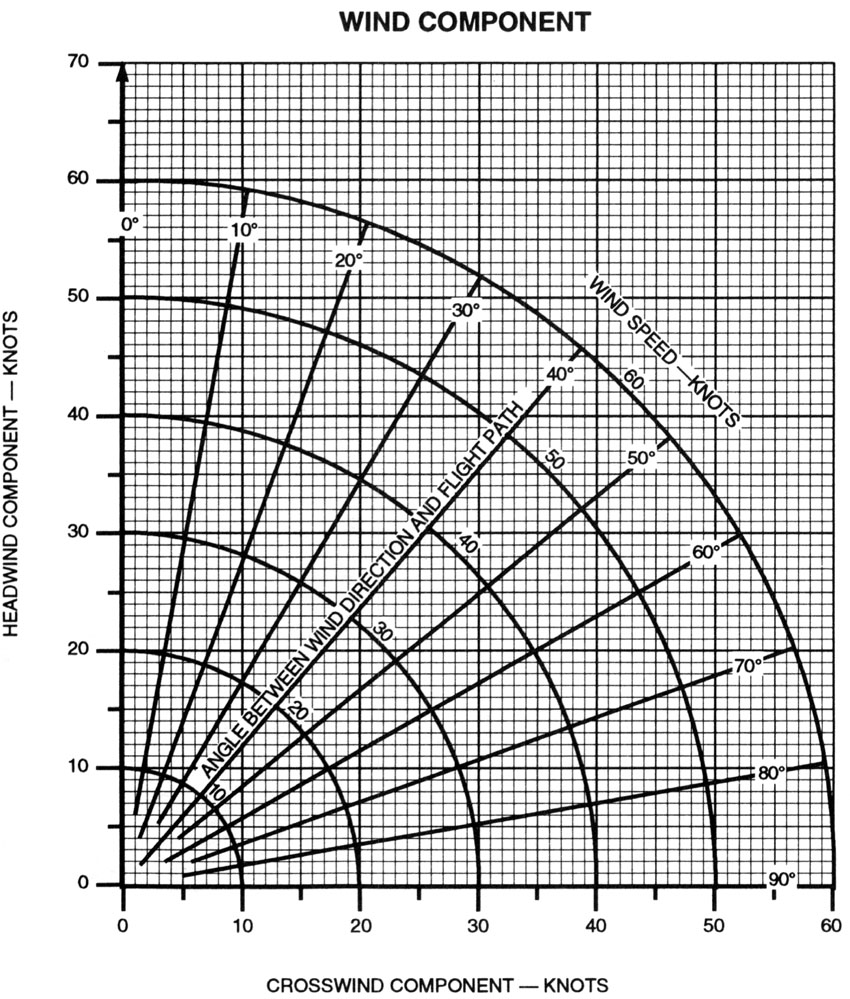
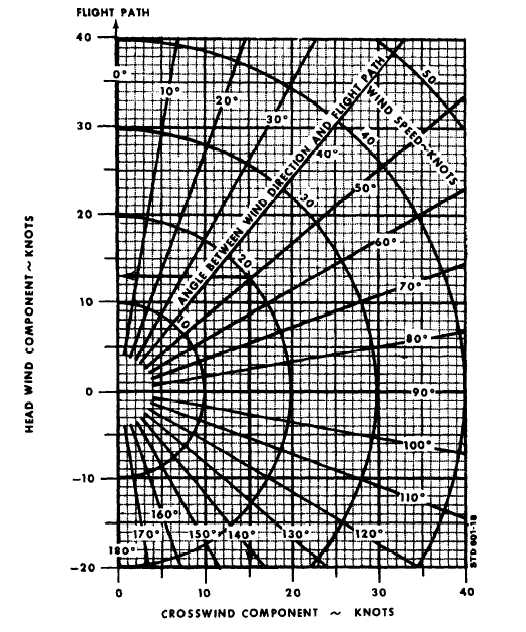
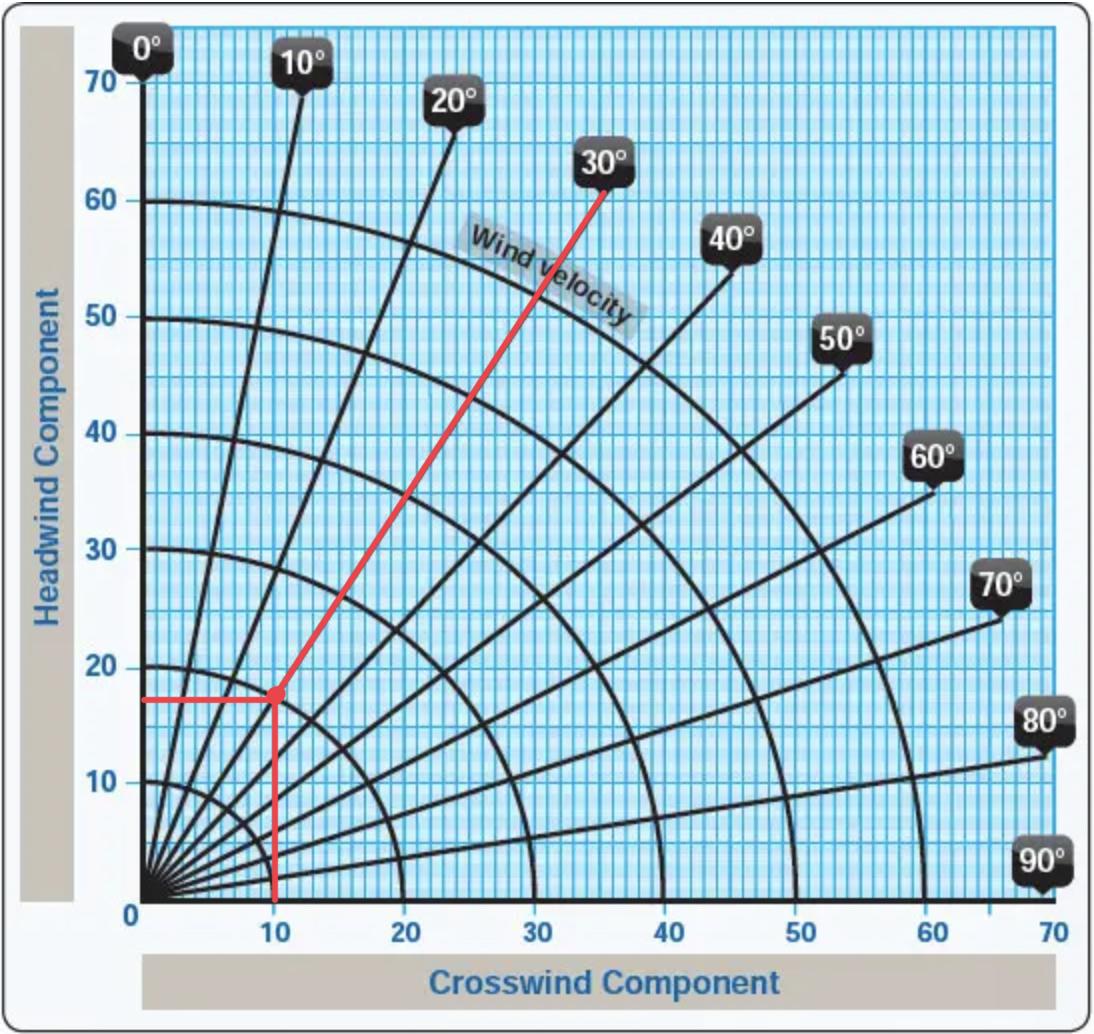
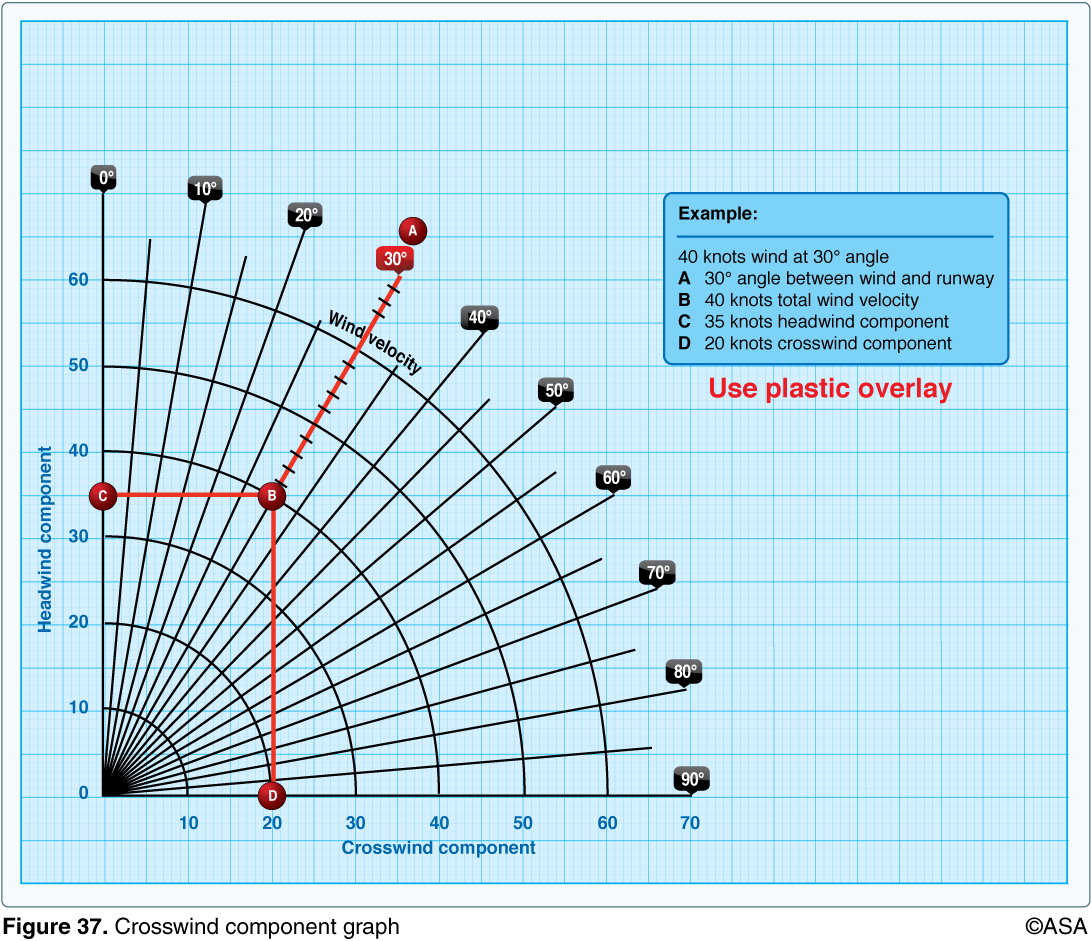
Crosswind Component Chart - 270 is the wind direction, 230 is the runway alignment, the angle is 40). Follow that line until you reach the correct wind speed (the arches describe the wind speed). If you like charts, you can lay out common numbers and interpolate between them: Web this blog explains how to determine the headwind and crosswind component for a given set of conditions by using the wind component chart. Web use the ratio of 1/2 or 0.5 and multiply the ratio by the wind speed. Web to use a crosswind component chart follow these few steps: The crosswind component is the result of the wind blowing at an angle across the runway or the aircraft's heading. Winds are 270 at 10 kt., follow the 30̊ line down to 10 knots on the arc). 10 minutes, which is 1/6 around clockface. 1) determine the angle between the wind and the runway (ex. Winds are 270 at 10 kt., follow the 30̊ line down to 10 knots on the arc). Web quickly and and easily determine and visualize the parallel and crosswind components of the wind relative to the runway heading. 14 x 0.5 = 7. The crosswind component is the result of the wind blowing at an angle across the runway or. To calculate the crosswind, divide the number of minutes (or degrees) by 60 and then multiply this value by the wind speed. If you like charts, you can lay out common numbers and interpolate between them: Web use the ratio of 1/2 or 0.5 and multiply the ratio by the wind speed. If the difference is 60 or more, you. Winds are 270 at 10 kt., follow the 30̊ line down to 10 knots on the arc). 2) follow that line down to the correct wind speed using the arc (ex. If you like charts, you can lay out common numbers and interpolate between them: A detailed description of the methodology used to perform the calculation is given below the. Crosswind = 1/6 * total wind. It is nearly always a factor to consider; To calculate the crosswind, divide the number of minutes (or degrees) by 60 and then multiply this value by the wind speed. In this example, 10 knots * 1/3 = 3.3 knots of crosswind. 14 x 0.5 = 7. Follow that line until you reach the correct wind speed (the arches describe the wind speed). 14 x 0.5 = 7. Web quickly and and easily determine and visualize the parallel and crosswind components of the wind relative to the runway heading. In this example, 10 knots * 1/3 = 3.3 knots of crosswind. Winds are 270 at 10 kt.,. 270 is the wind direction, 230 is the runway alignment, the angle is 40). 1) determine the angle between the wind and the runway (ex. Web this blog explains how to determine the headwind and crosswind component for a given set of conditions by using the wind component chart. Web to calculate a crosswind component, you must know the wind. Web use the ratio of 1/2 or 0.5 and multiply the ratio by the wind speed. Web to calculate a crosswind component, you must know the wind direction, speed, and runway heading. 1) determine the angle between the wind and the runway (ex. From this point go straight. If you like charts, you can lay out common numbers and interpolate. The only time there is no crosswind is if you fly directly into the wind (relative bearing of 0 degrees) or have a tailwind (relative bearing of 180 degrees). From this point go straight. Find the line with the value of an angle between the wind direction and the direction you're facing (it should be. In this example, 10 knots. 14 x 0.5 = 7. Winds are 270 at 10 kt., follow the 30̊ line down to 10 knots on the arc). The crosswind component is the result of the wind blowing at an angle across the runway or the aircraft's heading. It is nearly always a factor to consider; Web what is the crosswind component? A detailed description of the methodology used to perform the calculation is given below the calculator. 14 x 0.5 = 7. The crosswind component is the result of the wind blowing at an angle across the runway or the aircraft's heading. It is nearly always a factor to consider; 270 is the wind direction, 230 is the runway alignment, the. 14 x 0.5 = 7. If you like charts, you can lay out common numbers and interpolate between them: In this example, 10 knots * 1/3 = 3.3 knots of crosswind. Find the line with the value of an angle between the wind direction and the direction you're facing (it should be. The only time there is no crosswind is if you fly directly into the wind (relative bearing of 0 degrees) or have a tailwind (relative bearing of 180 degrees). 2) follow that line down to the correct wind speed using the arc (ex. Web to calculate a crosswind component, you must know the wind direction, speed, and runway heading. The crosswind component is the result of the wind blowing at an angle across the runway or the aircraft's heading. 10 minutes, which is 1/6 around clockface. Follow that line until you reach the correct wind speed (the arches describe the wind speed). Using a crosswind component chart (above), follow the radial line that represents the angle between the wind direction and runway heading. Crosswind = 1/6 * total wind. A detailed description of the methodology used to perform the calculation is given below the calculator. Web what is the crosswind component? Web this blog explains how to determine the headwind and crosswind component for a given set of conditions by using the wind component chart. If the difference is 60 or more, you can assume that the crosswind is equivalent to 100% of the wind speed.
Crosswind takeoff Studyflight
XWind Calculator Jetcareers
Crosswind Component Chart

How to Find a Crosswind Component 6 Steps Instructables
Printable Crosswind Component Chart
CFI Brief Crosswinds Learn To Fly
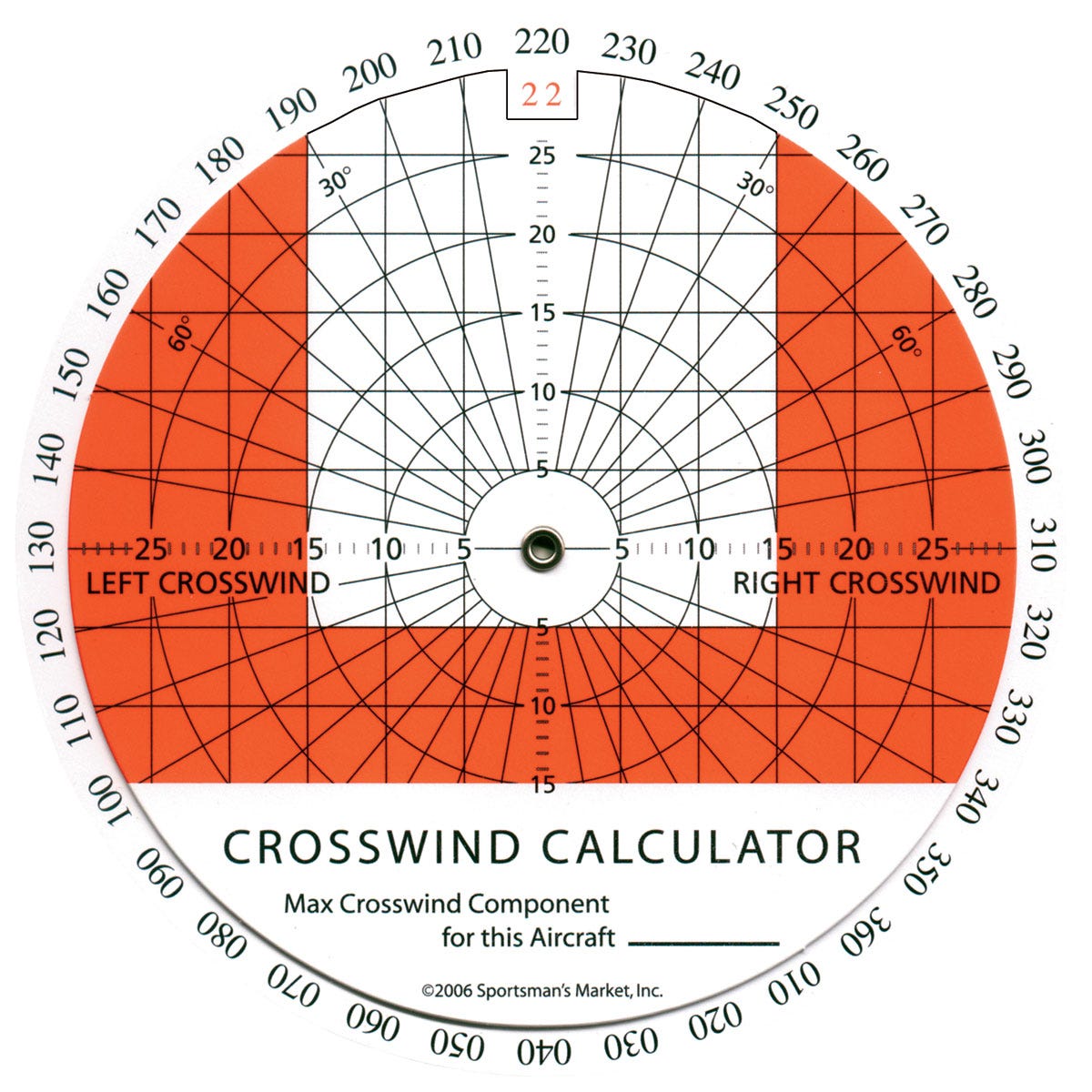
Crosswind Calculator from Sporty's Pilot Shop
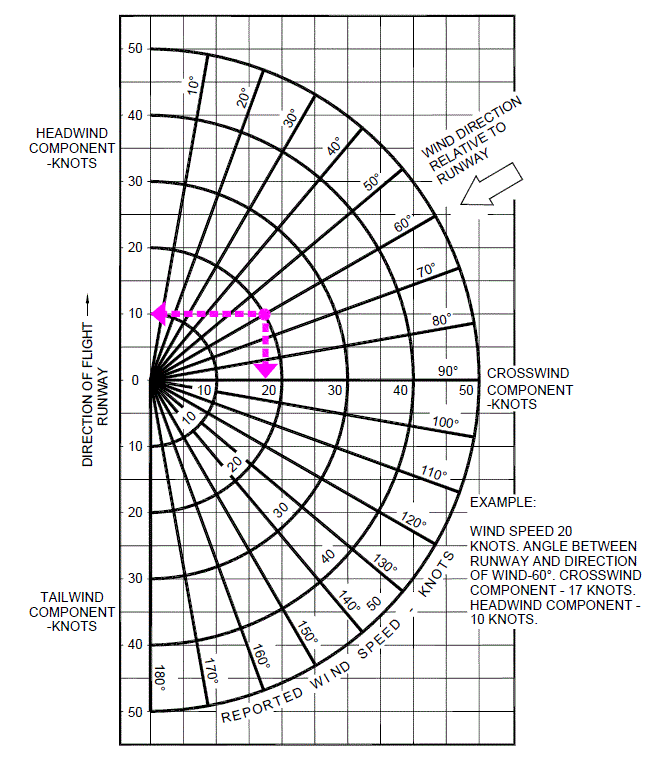
Touring Machine Company » Blog Archive » Crosswind Component
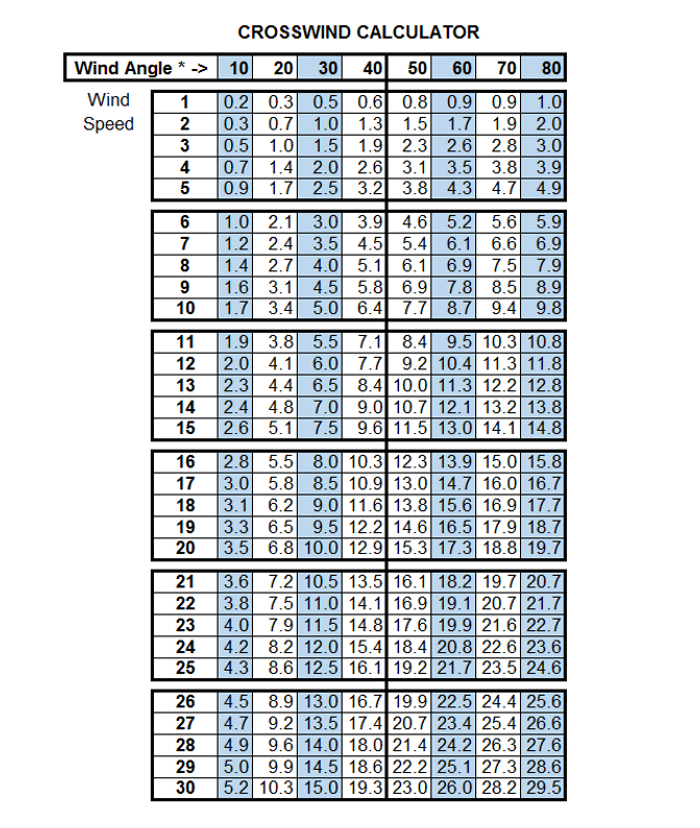
Bobbie Lind Page 3 of 3 Living Life to the Fullest And Loving
Performance and Limitations
Web To Use A Crosswind Component Chart Follow These Few Steps:
270 Is The Wind Direction, 230 Is The Runway Alignment, The Angle Is 40).
Web Quickly And And Easily Determine And Visualize The Parallel And Crosswind Components Of The Wind Relative To The Runway Heading.
To Calculate The Crosswind, Divide The Number Of Minutes (Or Degrees) By 60 And Then Multiply This Value By The Wind Speed.
Related Post:
