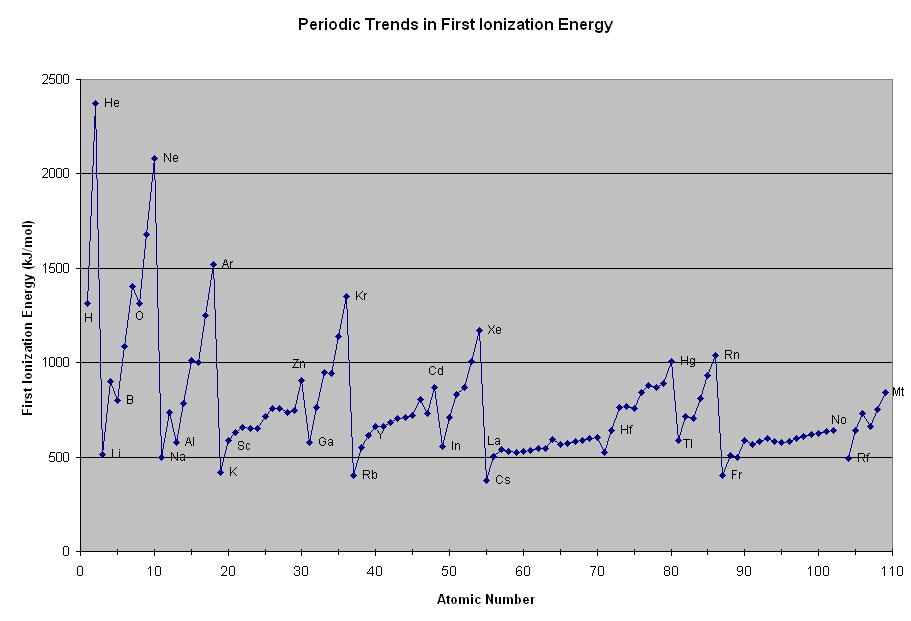
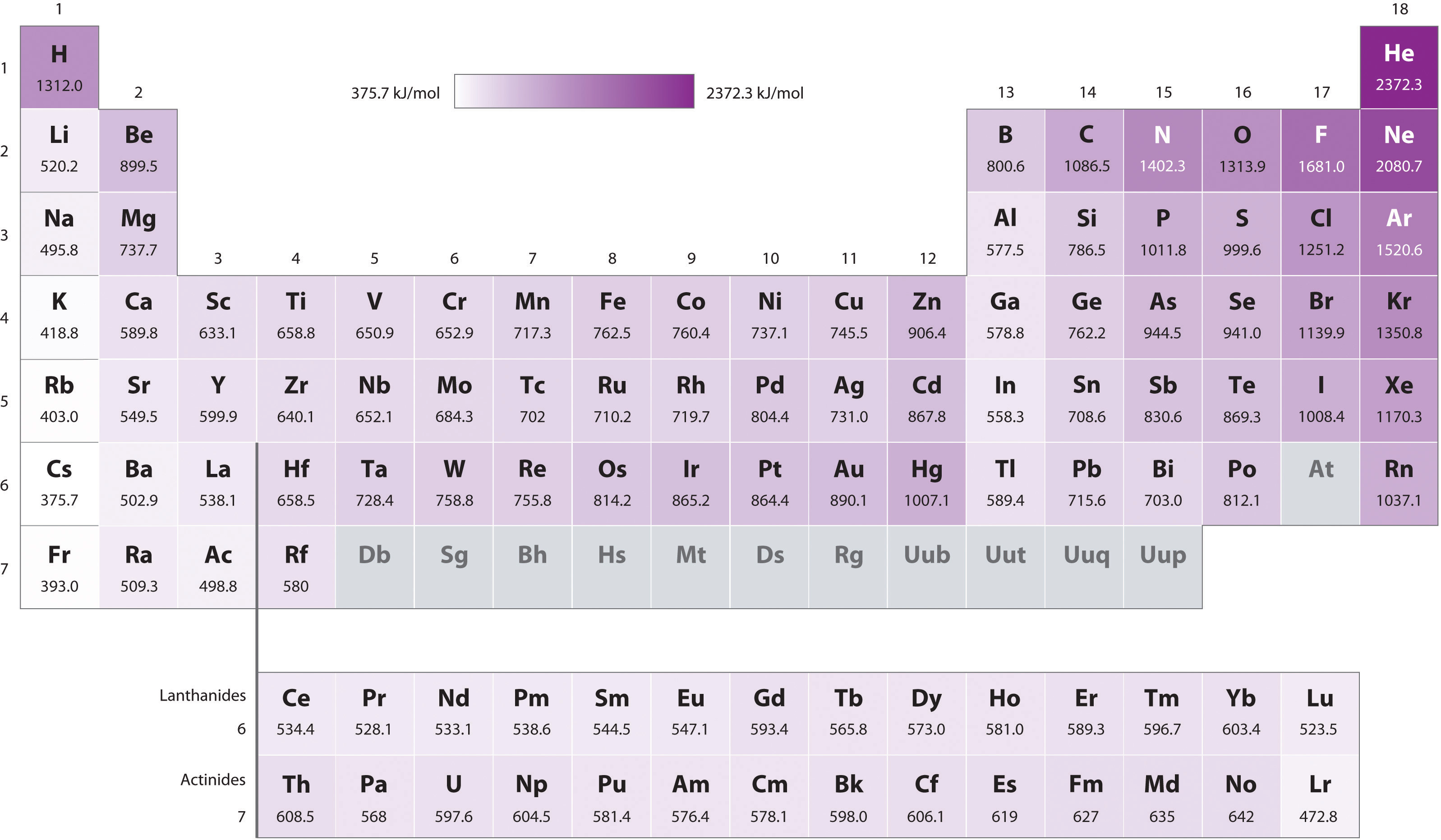
First Ionization Energy Chart
First Ionization Energy Chart - Web result the first ionization energy is the energy required to remove 1 electron from the valence shell. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. The process by which the first ionization energy of hydrogen is measured would be represented by the following equation. That means that it varies in a repetitive way as you move through the periodic table. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. First ionisation energy shows periodicity. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. 2nd ionization energy is the energy that enables the reaction x + x 2+ + e −. These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Second, third, and higher ionization energies. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. For example, look at the pattern from li to ne, and then compare it with the identical pattern from na to ar. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. The s blocks are purple, the p blocks are green, the. First ionization energy increase from left to right and from bottom to top. Web result the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. First. For chemistry students and teachers: That means that it varies in a repetitive way as you move through the periodic table. Web result march 23, 2023. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Or especially the first electron, and then here you have a high ionization energy. Web result the values mentioned in the above periodic table is the first ionization energy and are given in electron volts (ev). Web result patterns of first ionisation energies in the periodic table. First ionization energy trend in the periodic table. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. Second, third, and. For example, look at the pattern from li to ne, and then compare it with the identical pattern from na to ar. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the amount of energy required to remove. Web result an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. The most notable influences that determine ionization energy include: The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. First ionization energy trend in the periodic table. Low energy, easy to remove electrons. The most notable influences that determine ionization energy include: Web result we can define a first ionization energy ( i1 ), a second ionization energy ( i2 ), and in general an n th ionization energy ( in) according to the following reactions: Web result helium has two which is full for the first shell, and so it's very hard. Low energy, easy to remove electrons. The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. Web result an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web result for each atom, the column marked 1. Web result the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. The first ionization energy of hydrogen is about half in a chemical reaction. Low energy, easy to remove electrons. The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization. The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. The process by which the first ionization energy of hydrogen is measured would be represented by the following equation. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom. Each succeeding ionization energy is larger than the. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. First ionization energy shows periodicity. Low energy, easy to remove electrons. Ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization energy. These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. Web result 1st ionization energy is the energy that enables the reaction x x + + e −. Web result ionization energy (ie): Web result the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. E(g) → e+(g) +e− i1 = 1st ionization energy (8.4.3) (8.4.3) e ( g) → e ( g) + + e − i 1 = 1st ionization energy. Web result the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. Web result trends of first ionization energies. Web result an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web result by definition, the first ionization energy of an element is the energy needed to remove the outermost, or highest energy, electron from a neutral atom in the gas phase.
Periodic Trends Definition and Properties
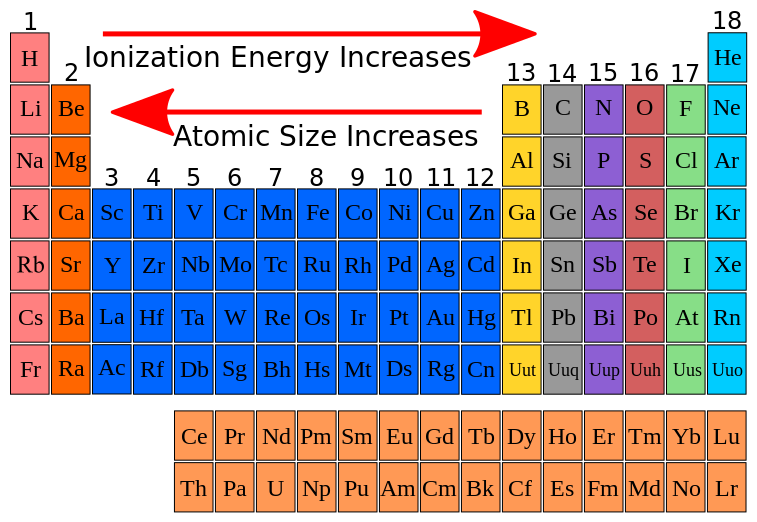
FileIonization energy atomic size.svg Wikimedia Commons

Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
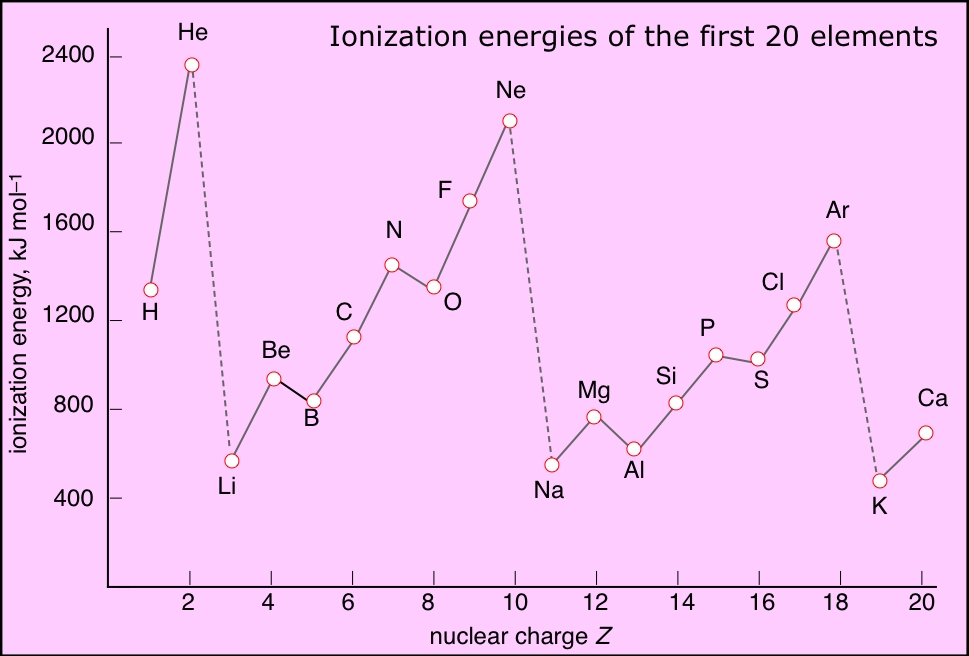
kem korner Periodic Trends
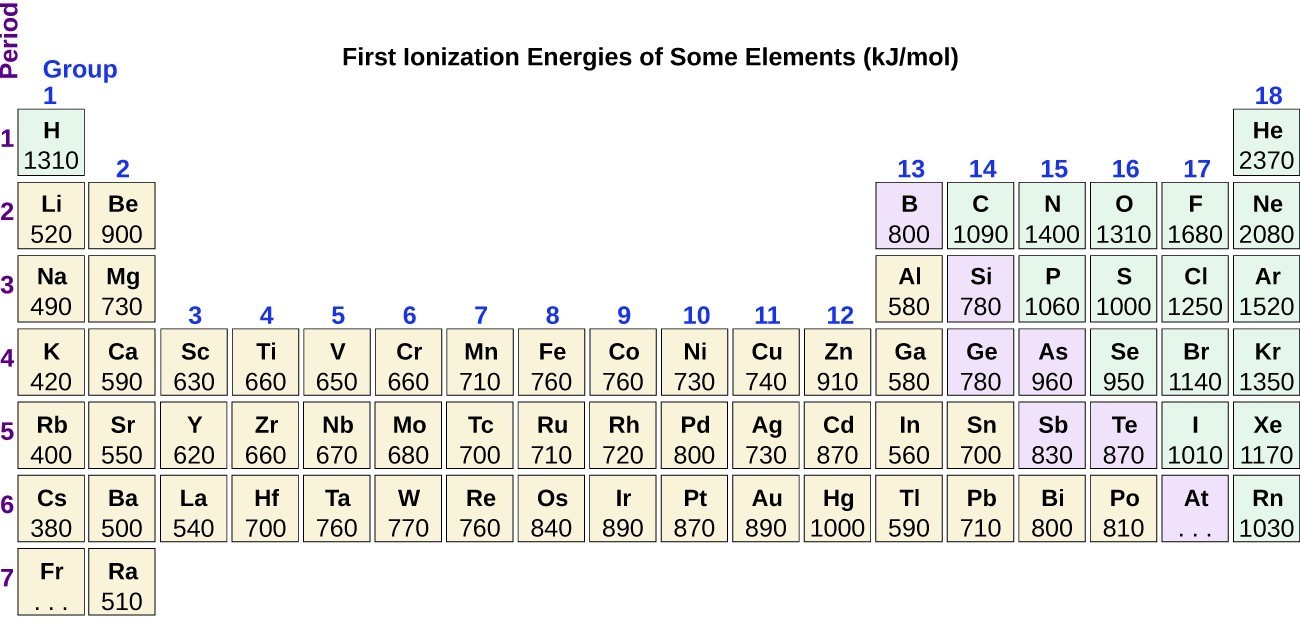
Periodic Variations in Element Properties CHEM 1305 General

Ionization Energy the amount of energy required to remove an electron
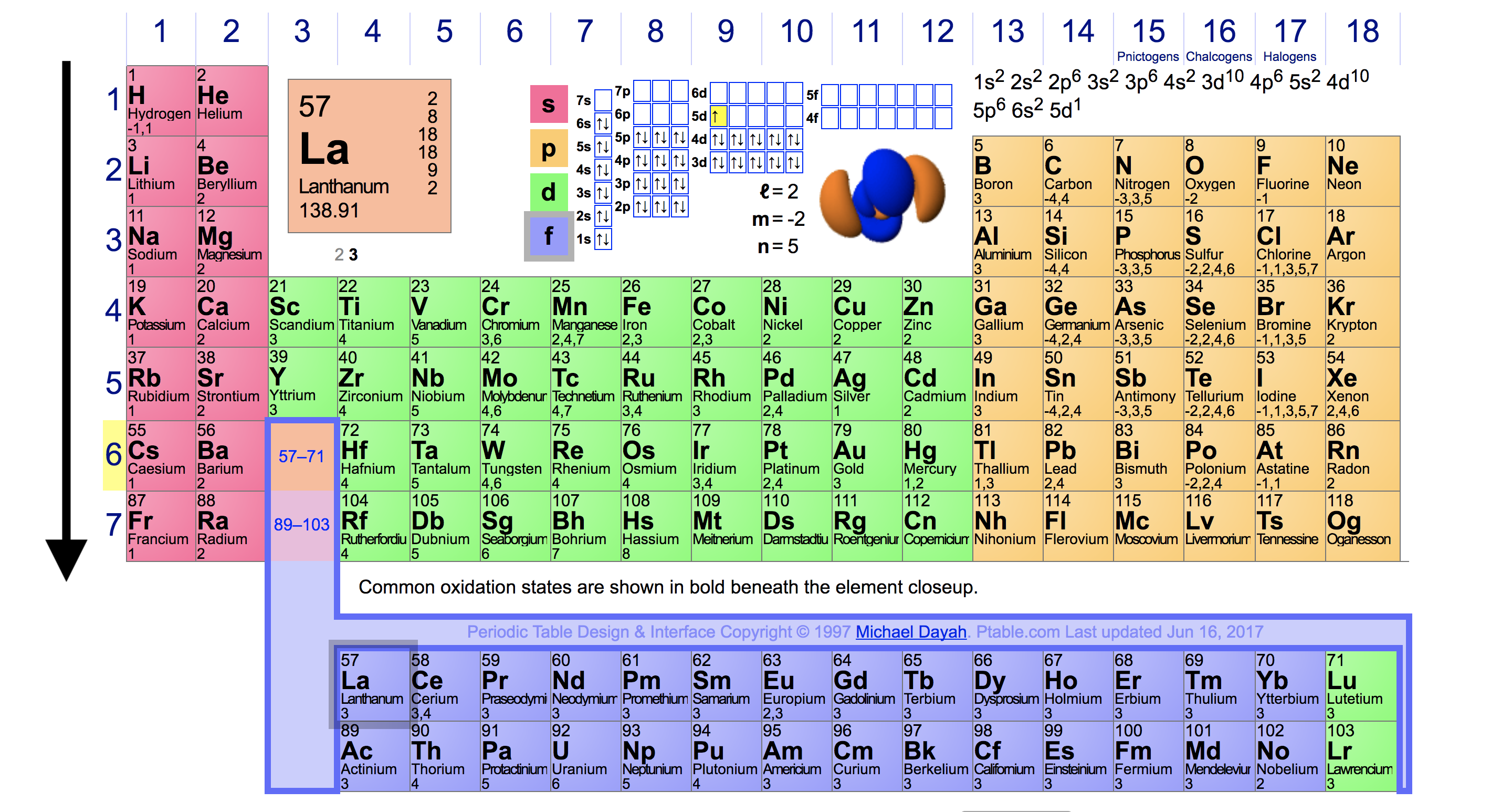
Energy Level In Periodic Table
Why is there an exception in the ionization energy trend in the second

The Parts of the Periodic Table
Chapter 3.3 Energetics of Ion Formation Chemistry LibreTexts
The S Blocks Are Purple, The P Blocks Are Green, The D Blocks Are Red, And The F Blocks Are Blue.
Web Result First And Second Ionization Energy.
Web Result Table Of Contents.
Web Result Patterns Of First Ionisation Energies In The Periodic Table.
Related Post: