Generalized Compressibility Chart
Generalized Compressibility Chart - It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. The calculator falls under the category of thermodynamics calculators, primarily used in the field of chemistry and engineering. As seen in the figure, at all temperatures z tends to 1 as p r tends to 0. This means that the behavior of the actual gas closely approaches ideal gas behavior, as the pressure approaches zero. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. Web alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts [1] that plot as a function of pressure at constant temperature. The example of a reciprocating compressor serves to introduce operating principles of engineering devices that have closed system compression and expansion of a trapped gas as well as open system processes that involve gas exchange (intake and. It would be nice if someone could explain that a little more. The main goal of this chapter is to develop working relationships for ideal gases. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in fig. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed. As seen in the figure, at all temperatures z tends to 1 as p r tends to 0. V 1 • t 2 = v 2 • t 1. P 1 • v 1 = p 2 • v 2. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range. Compressibility factor definition and equation. This means that the behavior of the actual gas closely approaches ideal gas behavior, as the pressure approaches zero. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. If you rather get 1:1 study help, try 30 minutes of free online tutoring with chegg tutors. For example, see the following figures: As seen in the figure, at all temperatures z tends to 1 as p r tends to 0. Figure 2.21 shows the chart for sweet natural gases as prepared by standing and katz [ 62 ]. Compressibility factor definition and equation. Web the compressibility chart calculator is a specialized calculator that calculates the compressibility factor (z) of a gas using. This means that the behavior of the actual gas closely approaches ideal gas behavior, as the pressure approaches zero. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. Web organized. If you rather get 1:1 study help, try 30 minutes of free online tutoring with chegg tutors. V 1 • t 2 = v 2 • t 1. 8.3144626181532 j/ (k⋅mol) boyle's law calculator: It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a. If you rather get 1:1 study help, try 30 minutes of free online tutoring with chegg tutors. Web organized by textbook: For example, see the following figures: Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in fig. It is valid for many substances, especially those that have simple molecular structures. 8.3144626181532 j/ (k⋅mol) boyle's law calculator: It would be nice if someone could explain that a little more. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. The calculator falls under the category of thermodynamics calculators, primarily used in the field of chemistry and engineering. Compressibility factor definition. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Web alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts that plot as a function of pressure at constant temperature.” the compressibility factor z, as cited above, may also be defined as actual volume. Web a generalized compressibility chart z=f(p r, t r) is presented in fig. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. The calculator falls under the category of thermodynamics. Web to be used only for generalized compressibility charts and gas mixtures. Web with the reduced temperature and specific volume, we can refer to a generalized compressibility chart (or function), which specifies the compressiblity factor as a function of reduced temperature, reduced pressure, and/or reduced specific volume for general gas mixtures. How to read a compressibility. P 1 • v 1 = p 2 • v 2. The reduced pressure and temperature are defined by and , respectively, where is the critical pressure and is the critical temperature. Compressibility factor definition and equation. Web alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts that plot as a function of pressure at constant temperature.” the compressibility factor z, as cited above, may also be defined as actual volume divided by the ideal volume: Web alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts [1] that plot as a function of pressure at constant temperature. The main goal of this chapter is to develop working relationships for ideal gases. This means that the behavior of the actual gas closely approaches ideal gas behavior, as the pressure approaches zero. Web the key parameter is the compressibility factor, z, which can be estimated using a generalised chart. As seen in the figure, at all temperatures z tends to 1 as p r tends to 0. 218 views 10 months ago 101 solved engineering thermodynamics. Web the generalized compressibility chart can be viewed as a graphical representation of the gas behaviour over a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Web on a generalized compressibility chart, the compressibility z z is plotted as a function f = f(pr,tr) f = f ( p r, t r) of the reduced pressure and temperature. I don't understand why exactly;
Mixture properties — Computational Thermodynamics
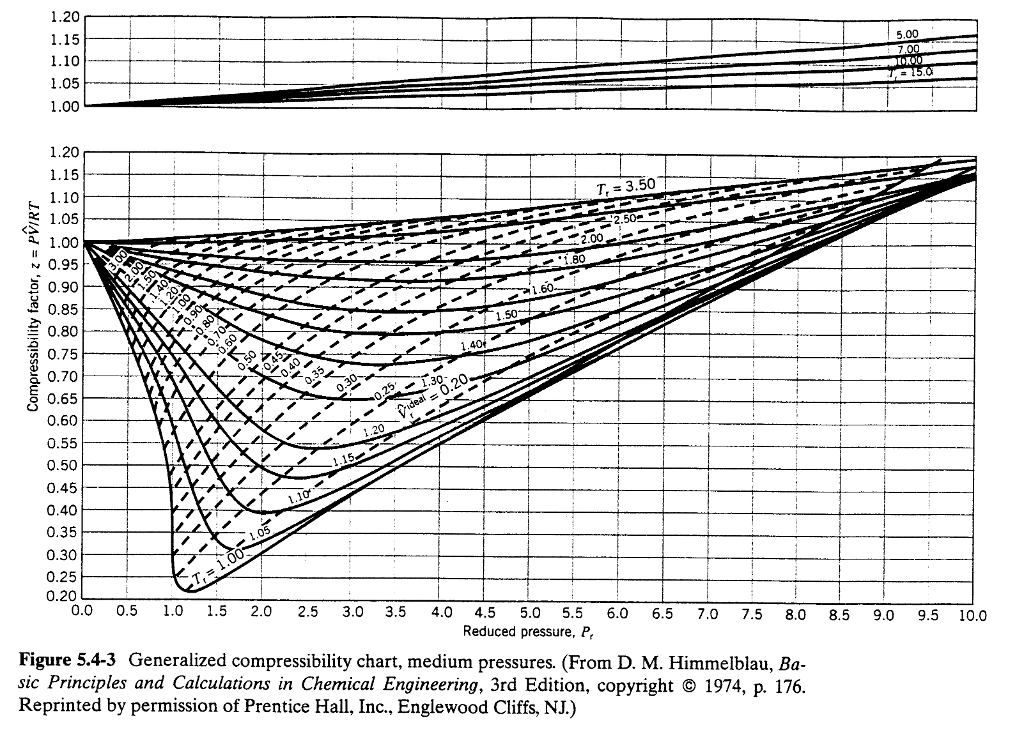
Solved Use the generalised compressibility chart to estimate

Figure 2 from Compressibility Chart for Hydrogen and Inert Gases
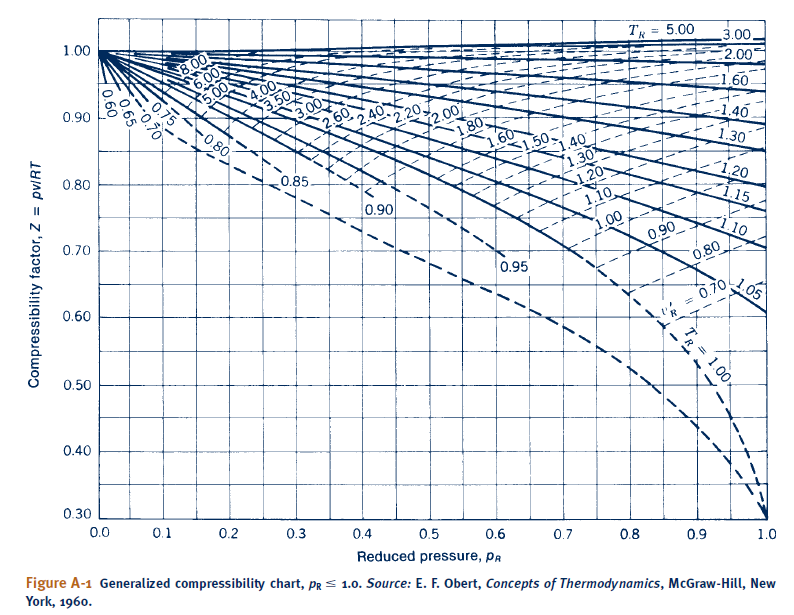
Solved Since critical Pressure of CO2 is 73.9 bar (7.39

Mixture properties — Computational Thermodynamics

Reading Compressibility Factor Charts YouTube
Generalized Compressibility Chart PDF Thermodynamics

physical chemistry How to understand NelsonObert charts? Chemistry
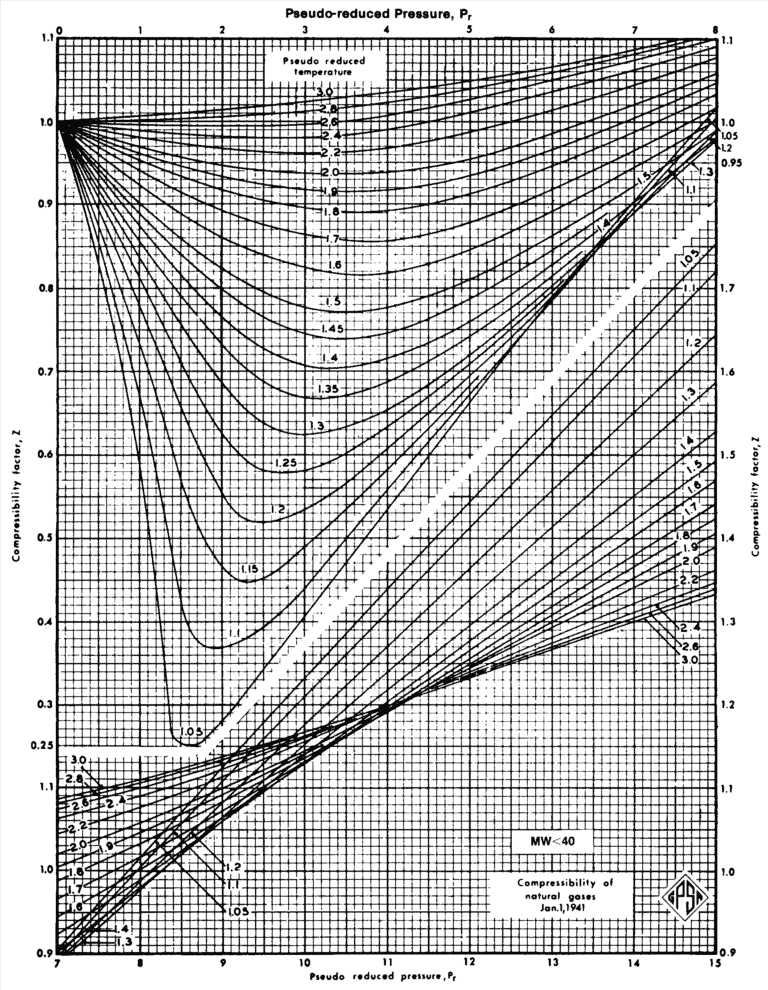
Determine Compressibility Factor, Z Factor Engineering Units
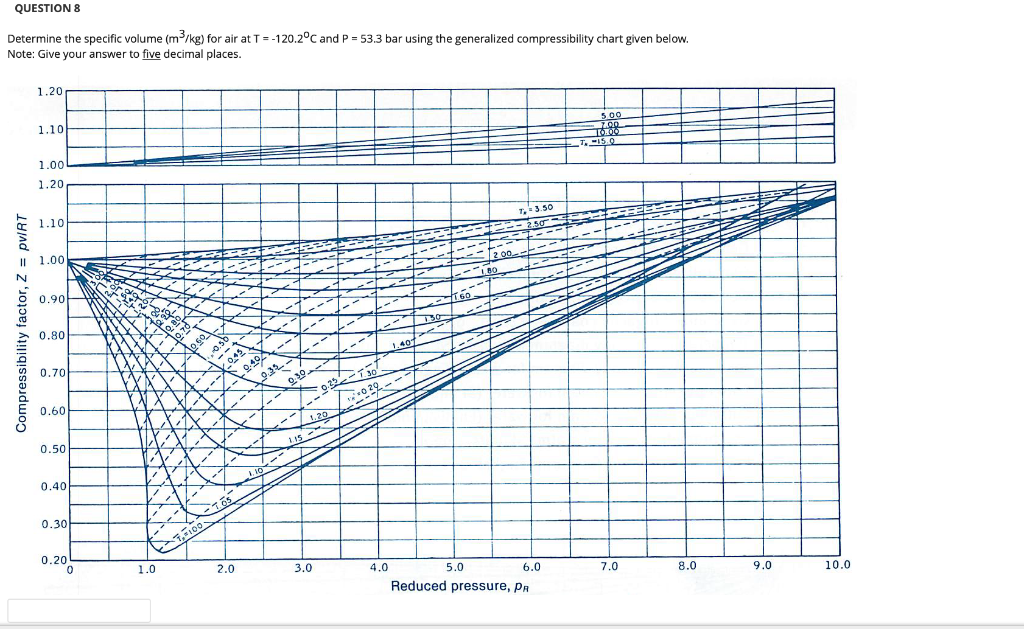
Solved QUESTION 3 Determine the compressibility
For Example, See The Following Figures:
V 1 • T 2 = V 2 • T 1.
Web A Generalized Compressibility Chart Z=F(P R, T R) Is Presented In Fig.
Web Organized By Textbook:
Related Post:
