German Cases Chart
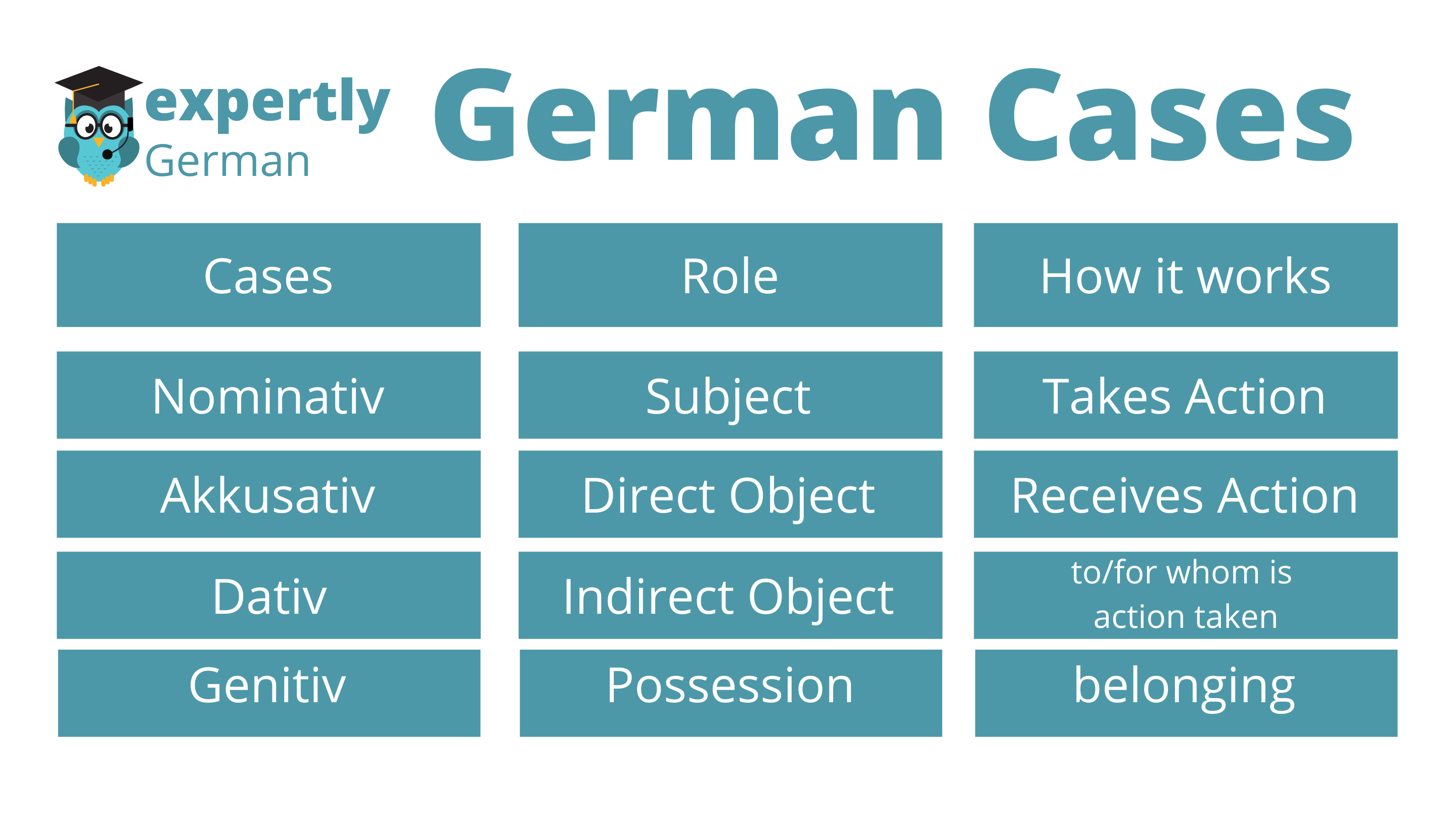
German Cases Chart - An indirect object is a noun that’s on the receiving end of something; If you are learning german, one of the important early lessons is. How do german cases work? To show the case, we change the endings of the article, pronoun and adjective that accompany the noun. Which is the person or thing performing the action. The german four really aren’t the end of the world. Why adjective endings are important. You could fill a library with books written about what cases are exactly, but in short it’s when a noun or pronoun changes form depending how it’s. Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in german. But at their core, all the german case charts out there are the same thing: The nominative case in german is used to identify the subject of a sentence, which is the person or thing performing the action. At the beginning of this article, you can read in short about the cases. Web in this guide, i explain the german cases in a simple and easy to understand way. For english speakers, this can be. Why do german adjectives need endings? The german nominative case ( der nominativ or der werfall) the nominative case—in both german and in english —is the subject of a sentence. Web overview of the german cases. The german four really aren’t the end of the world. As the most basic case, it’s a good starting point for learning the german. Me, you, him, her, it, us, them. An indirect object is a noun that’s on the receiving end of something; Are you looking for a chart like this? And the case you choose depends on the word’s role within the sentence: At the beginning of this article, you can read in short about the cases. Nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. I, you, he, she, it, we, they. Web here you can see a chart of the four cases in german. Web the four cases are nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. Continuous practice will help you get good at using and identifying the cases. Learn the two charts on this page well, and everything else you. At the beginning of this article, you can read in short about the cases. Web german has four cases: The nominative case denotes the subject of the sentence: It answers the question to who or what something is going — or with in some cases. Web the four german cases are the nominative, genitive, dative, and accusative. Learn german cases with conversation based chunking. What are the german cases? In english, this is mostly done with word order, so it can take some getting used to! Which ‘slot’ the noun goes into depends on what role that noun is performing in the sentence. There are some differences in the details, like the order of articles being switched or some clever use of colors to highlight the similarities. Cases in german influence not only the form of the nouns but also the articles and adjectives associated with them. Web ‘cases’ is a grammar term for ‘slots’ in a sentence that get filled up with. How german prepositions affect pronouns. Web german has four cases: And the case you choose depends on the word’s role within the sentence: In german, we have 4 different roles a noun might play. Web so in this guide, i’ll cover the four german cases so you can get a better understanding of how they work, when to use them,. Web hungarian has 18. I've created these charts to remind you of the different changes you've seen so far. It answers the question to who or what something is going — or with in some cases. Prepositions and the german cases. Web ‘cases’ is a grammar term for ‘slots’ in a sentence that get filled up with nouns. Why do german adjectives need endings? Learn german cases with conversation based chunking. As the most basic case, it’s a good starting point for learning the german case system. Web most of you are familiar with charts for german case endings, and pretty much all of them look something like this: You could fill a library with books written about. I've created these charts to remind you of the different changes you've seen so far. Web here you can see a chart of the four cases in german. You can think of these as the equivalent of the subject, possessive, indirect object, and direct object in english. Master the nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive cases in german. Web so in this guide, i’ll cover the four german cases so you can get a better understanding of how they work, when to use them, and what to do when you’re not sure. Cases in german influence not only the form of the nouns but also the articles and adjectives associated with them. Although it's a foreign concept in english, german cases play an important role in identifying which noun is the subject and how the supporting verbs or prepositions relate to that subject. What are the german cases? In english, we have the personal pronouns we use when someone is the subject of the sentence: At the beginning of this article, you can read in short about the cases. Prepositions and the german cases. The case of a noun is determined by certain verbs and prepositions. As the most basic case, it’s a good starting point for learning the german case system. For each german case (kasus) you can find a detailed explanation, including declension, usage, verbs and prepositions forcing you to use a certain case. Web by emma november 24, 2021. How german prepositions affect pronouns.
The four cases are in order from how often they occur in a sentence

German grammar tables jordculture
![German Cases Simply Explained A Guide to German Cases [Grammar Guide]](https://lingopie.com/blog/content/images/2022/08/German-cases-2-copia.jpg)
German Cases Simply Explained A Guide to German Cases [Grammar Guide]

German Grammar Dative Case and the DER CHART YouTube

German Cases Learn German Cases easily with

A new kind of case chart

Pin on German lessons
German Cases Easy Guide The four German cases

German cases and adjective endings chart The German Professor

history Origins of the unified German declensions chart? German
Are You Looking For A Chart Like This?
Web German Preposition Charts:
If So, You’re Learning It Wrong.
Me, You, Him, Her, It, Us, Them.
Related Post: