Ionization Energies Chart
Ionization Energies Chart - The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is helium. (here you will get the first, second and third ionization energy of all the elements in a single chart). Second, third, and higher ionization energies. The 3rd ie corresponds to the energy required to remove an electron from the gaseous m2+ species of any element, i.e. Science > chemistry library > periodic table > periodic table trends. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. An electron volt is the appropriate unit to describe the energy needed to remove an electron from one atom. In general, what happens to the 1st ionization energy as you go down a group / family? Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Why can't the identity of the element be p? The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization energy. Web looking at the graph of ionization energies, it is clear that indium(atomic number 49) does have a lower ionization energy than cadmium (atomic number 48), and the same is true of mercury, the element preceding thallium (atomic number 81).. The unity for ionization energy is ev. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): How to write a chemical equation for first ionization energy. Why can't the identity of the element be p? [4] ionization energy generally increases from left to right within a given period (that is, row). In general, what happens to the 1st ionization energy as you go across a period? Ionization energy chart of all the elements. Why can't the identity of the element be p? 1 ev/atom = 96.49 kj/mol. As described above, ionization energies are dependent upon the atomic radius. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Web [3] comparison of ionization energies of atoms in the periodic table reveals two periodic trends which follow the rules of coulombic attraction: We have shown the list of elements ionization energies of the elements for which reliable data is available. Since. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. The unity for ionization energy is ev. How to write a chemical equation for first ionization energy. [4] ionization energy generally increases from left to. Refer to table and property element trend below for ionization energies of all the elements in the periodic table. Web for instance, the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous ion m while the 2nd ionization energy of the element m is a. [4] ionization energy generally increases from left to right within a given period (that is, row). Web the first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. Web looking at the graph of ionization energies, it is clear that indium(atomic number 49) does have a lower ionization energy. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. Web looking at the graph of ionization energies, it is clear that indium(atomic number 49) does have a lower ionization energy than cadmium. Ionization energies of all the elements in the periodic table. Web [3] comparison of ionization energies of atoms in the periodic table reveals two periodic trends which follow the rules of coulombic attraction: 1 ev/atom = 96.49 kj/mol (8.4.2) (8.4.2) 1 e v / a t o m = 96.49 k j / m o l. The units are kj. Why can't the identity of the element be p? Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): Science > chemistry library > periodic table > periodic table trends. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus. List the elements for which. Since going from right to left on the periodic table, the atomic radius increases, and the ionization energy increases from left to right in the periods and up the groups. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): Why can't the identity of the element be p? Ionization energy chart of all the elements. The 3rd ie corresponds to the energy required to remove an electron from the gaseous m2+ species of any element, i.e. First ionization energy trend in the periodic table. Ionization energies of all the elements in the periodic table. We have shown the list of elements ionization energies of the elements for which reliable data is available. [4] ionization energy generally increases from left to right within a given period (that is, row). Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom or molecule. Periodic trends and coulomb's law. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. There is most certainly a third ionization energy, and fourth, and fifth.! Web molar ionization energies of the elements. Web ionization energy is a measure of the energy needed to pull a particular electron away from the attraction of the nucleus.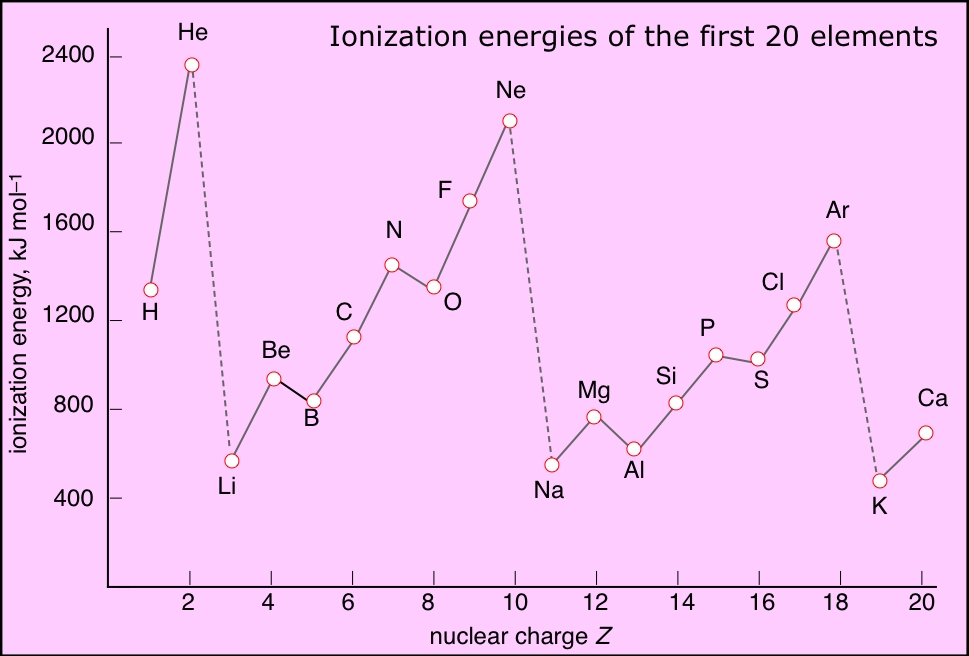
kem korner Periodic Trends

chemical compound Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
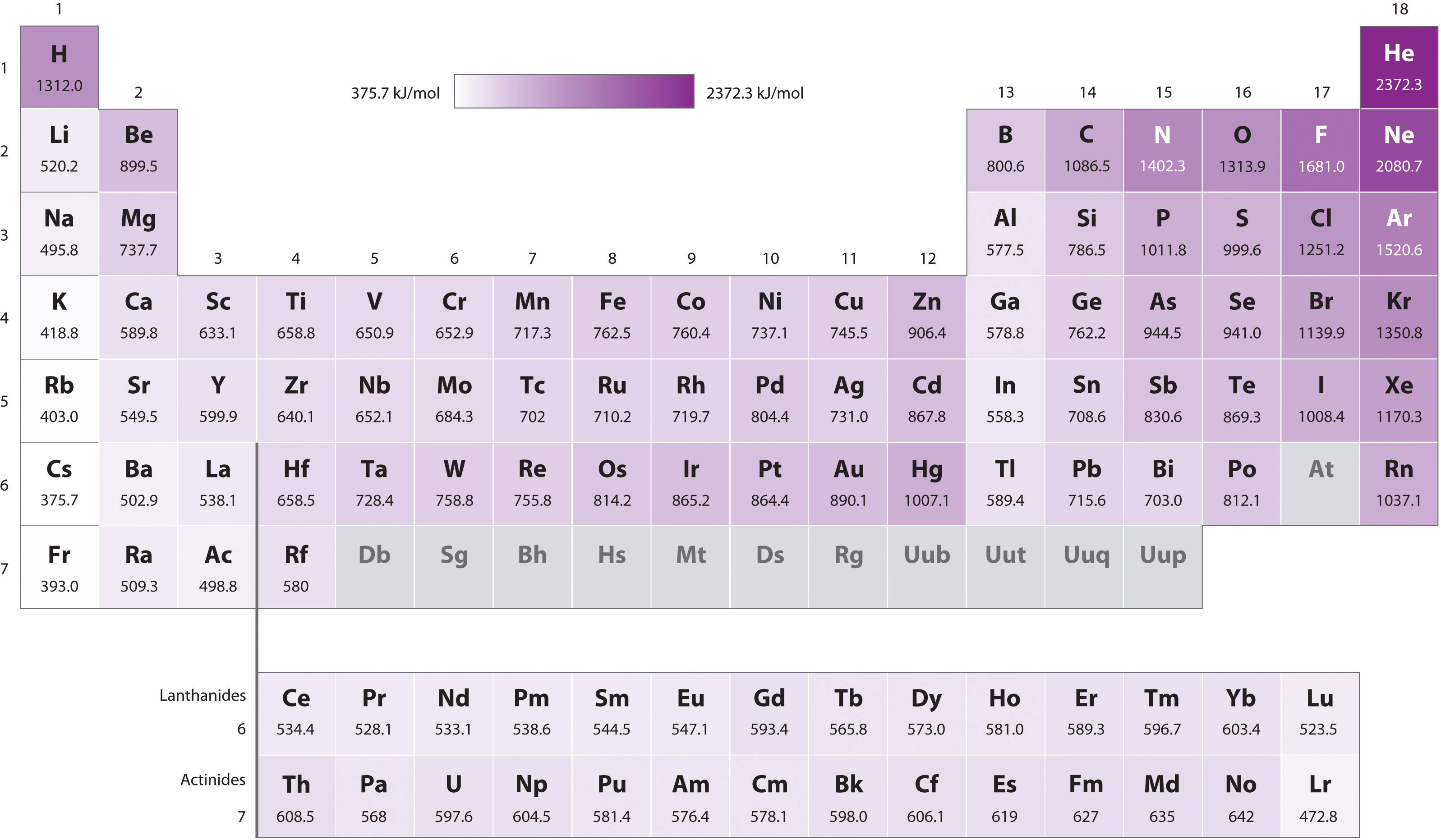
6.6 Ionization Energies Chemistry LibreTexts
Which of the following has highest first ionization energy? 1)Sc 2)K
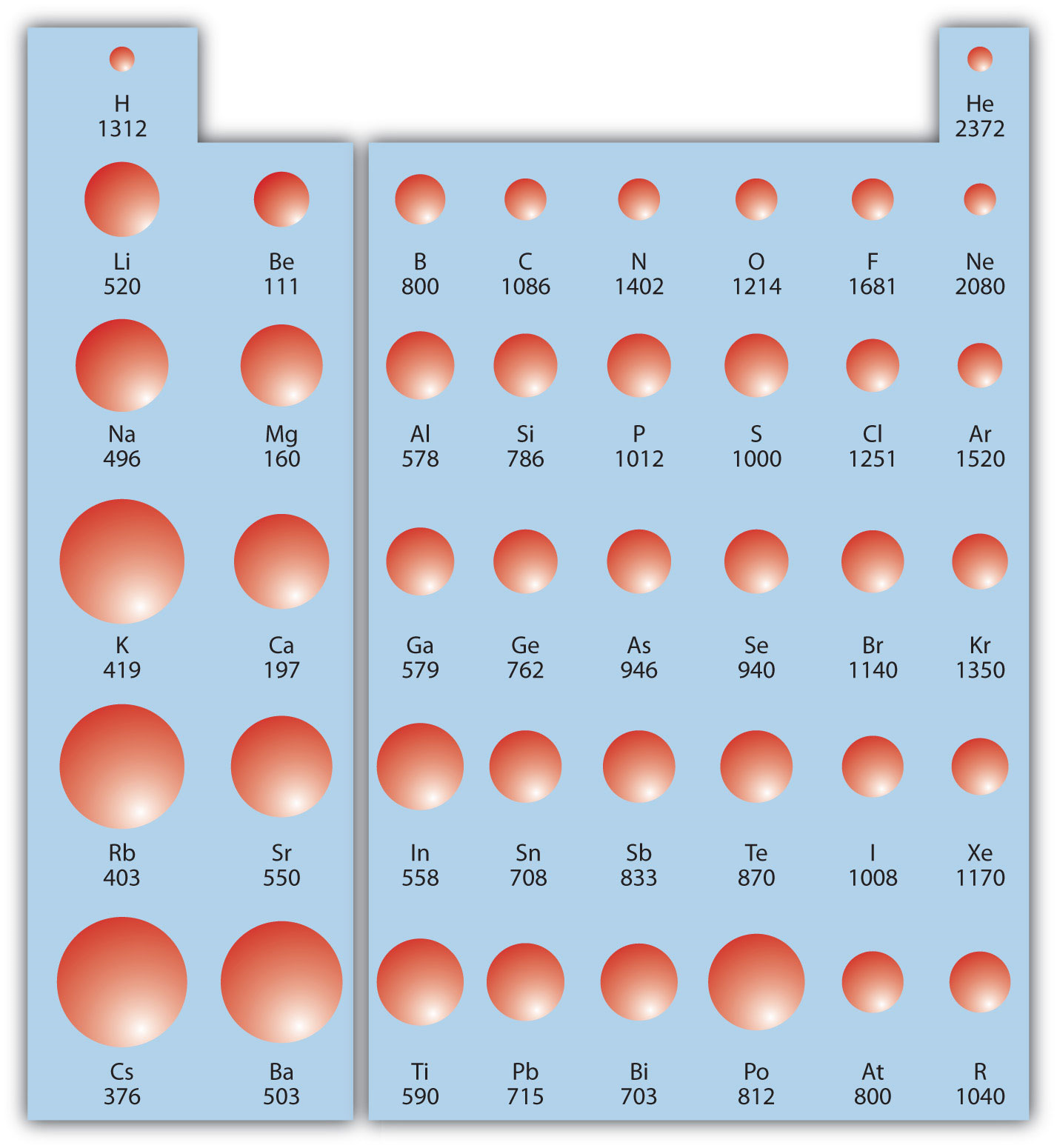
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic

The Parts of the Periodic Table

Periodic Variations in Element Properties General Chemistry
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic

Ionization Energy the amount of energy required to remove an electron
The First Molar Ionization Energy Applies To The Neutral Atoms.
The First Chemical Element Is Cesium And The Last One Is Helium.
Web But If You Want To See The Ionization Energy Of All The 118 Elements, Then Visit:
As Described Above, Ionization Energies Are Dependent Upon The Atomic Radius.
Related Post:
