Kingdoms And Domains Chart
Kingdoms And Domains Chart - These domains are based primarily on the presence or absence of a nucleus. Web the three domains of life are bacteria, archaea and eukaryota. Within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include. As we move down the levels of the classification of life, kingdoms are below domains. Web the most general category in taxonomic classification is domain, which is the point of origin for all species; In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms in the classification of organisms. Web organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life. They are present in the soil, water, and air. Kingdom archaea also has just one kingdom: Web scientists classify organisms into six kingdoms. Organisms are placed into these categories based on similarities or common characteristics. Classification of the human species. Web organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life. The six different animal kingdoms. Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make food, and the number of cells that make up their bodies. Plantae, animalia, fungi, protoctista and prokaryotae. The classification of humans is given in the chart as an example. They are present in the soil, water, and air. Web there are. Web domains & kingdoms section 17.3 domain bacteria e. The six kingdoms of life. All living organisms can be placed in one of six different animal kingdom. The six different animal kingdoms. They are present in the soil, water, and air. Many mnemonic devices can be used to remember the order of the taxonomic hierarchy, such as “dear king philip came over for good. Dominium), introduced by moore in 1974. Web the six kingdoms are: Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability to make food, and the number of cells that. Web domains and kingdoms | 174 plays | quizizz. For example, a species is a subdivision of a genus. Table 1 identifies the scientists who introduced the kingdoms and the dates the kingdoms were introduced. These included kingdoms such as animals, plants, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. Web the six kingdoms are: Plantae, animalia, fungi, protoctista and prokaryotae. The plant kingdom consists of 14. The six different animal kingdoms. The first two kingdoms are easy to remember. For a long time, all life was separated into five or six kingdoms. All living organisms can be placed in one of six different animal kingdom. Web the five kingdoms are: Each phylum is grouped into a kingdom, which is grouped into a domain. These included kingdoms such as animals, plants, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. Web today organisms are grouped into three domains and six kingdoms based on their cell type, ability. Plantae, animalia, fungi, protoctista and prokaryotae. This chart shows the taxa of the linnaean classification system. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. All living organisms can be placed in one of six different animal kingdom. Within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include. Web the most general category in taxonomic classification is domain, which is the point of origin for all species; Web domains and kingdoms | 174 plays | quizizz. Web living organisms can be classified into three domains: Kingdom, phylum or division, class, order, family, genus, and species. These domains are based primarily on the presence or absence of a nucleus. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown. The six different animal kingdoms. Web in biological taxonomy, a domain ( / dəˈmeɪn / or / doʊˈmeɪn /) ( latin: Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla. Groups organisms according to body plan eg backbone. This domain is characterized by ancient bacteria that can live in extreme environments, such as near volcanoes. Web scientists classify organisms into six kingdoms. The plant kingdom consists of 14. Domain bacteria has just one kingdom: However, archaebacteria are the oldest known living organisms. The first two kingdoms are easy to remember. Web the hierarchy of biological classification 's eight major taxonomic ranks. The classification of humans is given in the chart as an example. Web organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life. As we move down the levels of the classification of life, kingdoms are below domains. Within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include. The first domain is bacteria. Web there are seven main taxonomic ranks: Web domains and kingdoms | 174 plays | quizizz. Web he also developed a classification system called the taxonomic hierarchy, which today has eight ranks from general to specific:
Three Domain and six kingdom Classification by Carl Woese Biology

Ms. Mora's Biology Blog DOMAINS AND KINGDOMS (DOMINIOS Y REINOS)
PPT Kingdoms, Classification, and Plants PowerPoint Presentation
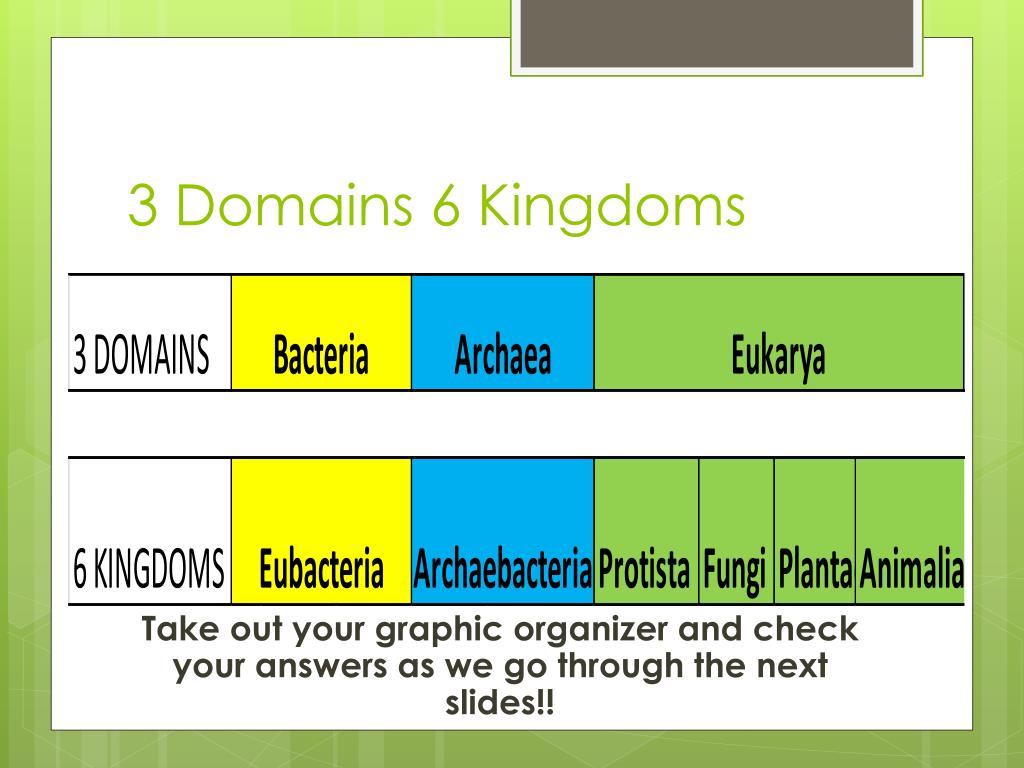
PPT Domains and Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
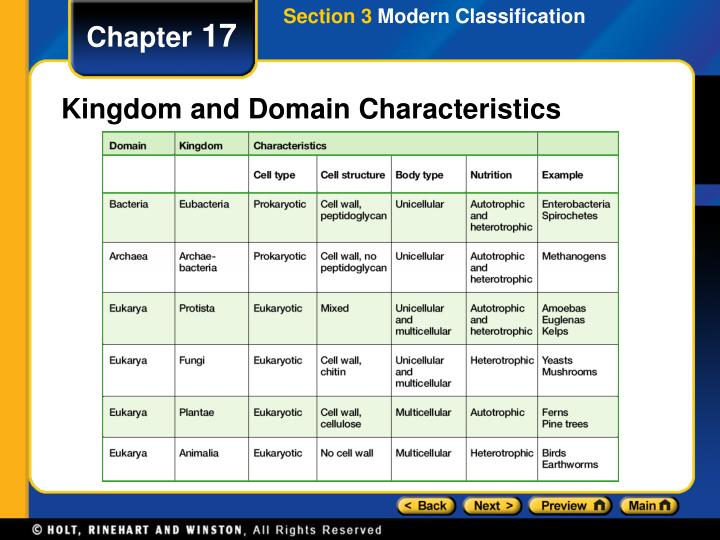
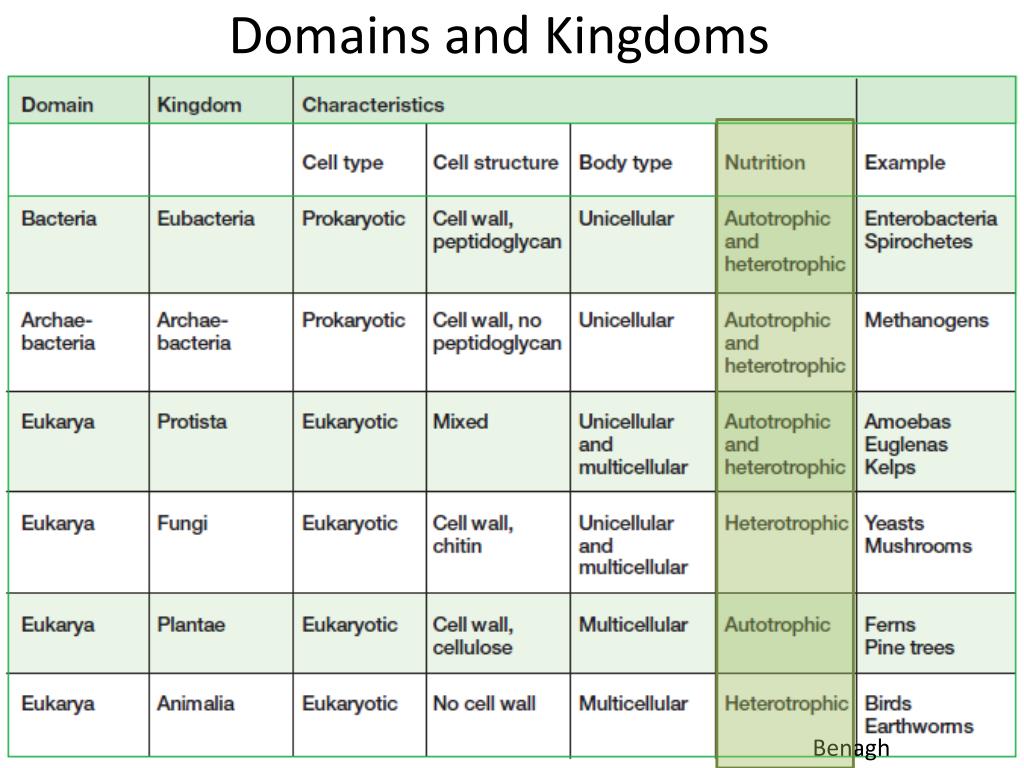
️ Kingdom and domain characteristics. Mnemonic taxonomy / biology
Domains/Kingdoms 4K plays Quizizz
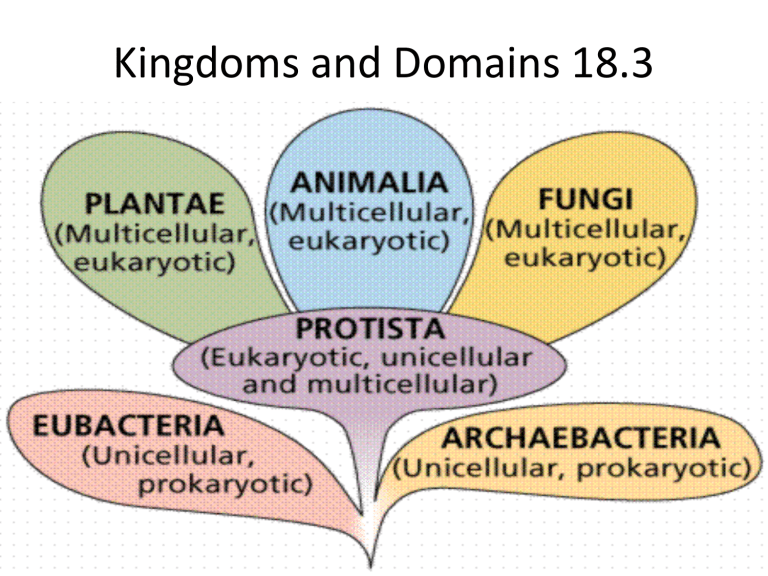
Kingdoms and Domains 18.3

️ Kingdom and domain characteristics. Mnemonic taxonomy / biology
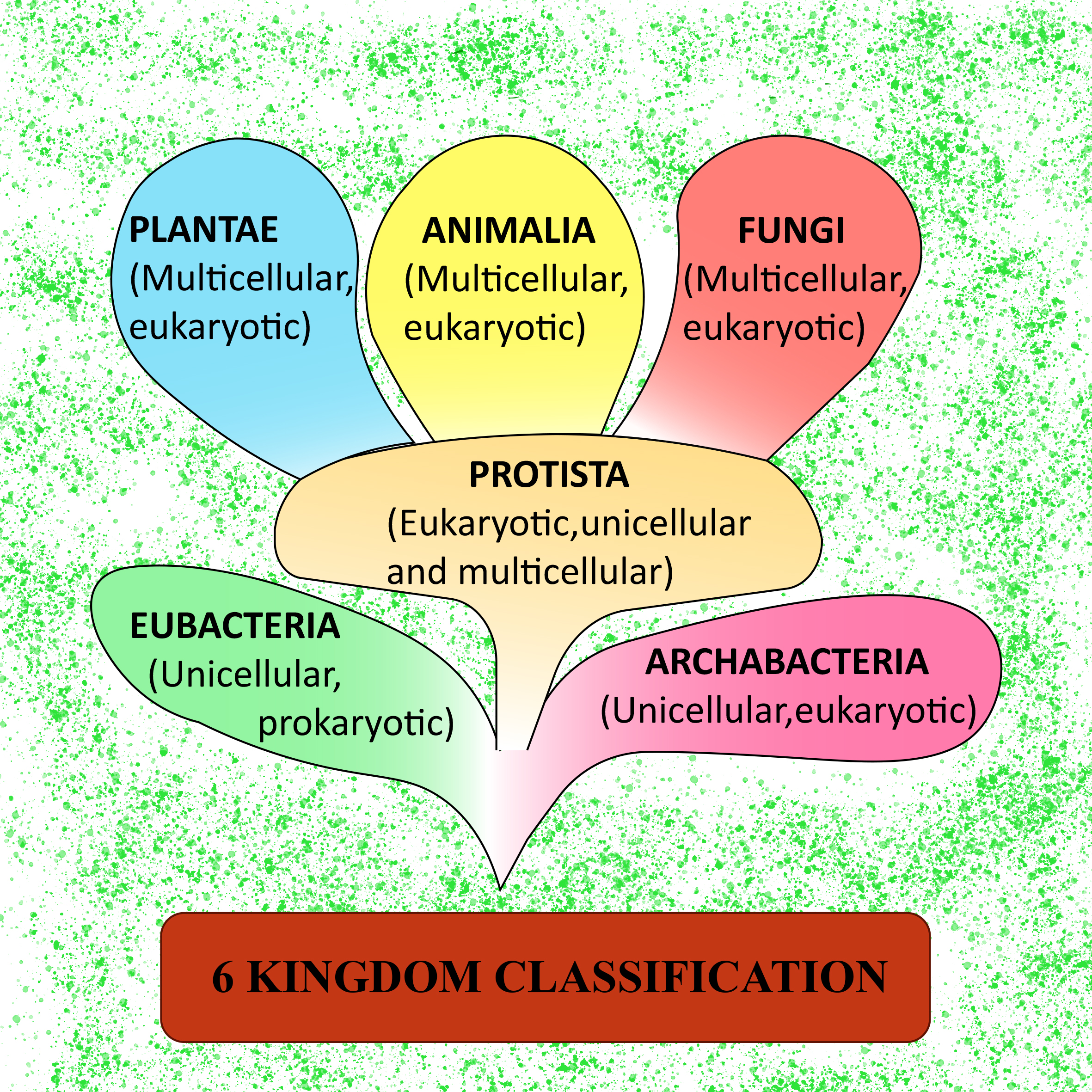
Six Kingdom Classification Was Suggested By Class 11 Biology Cbse Riset
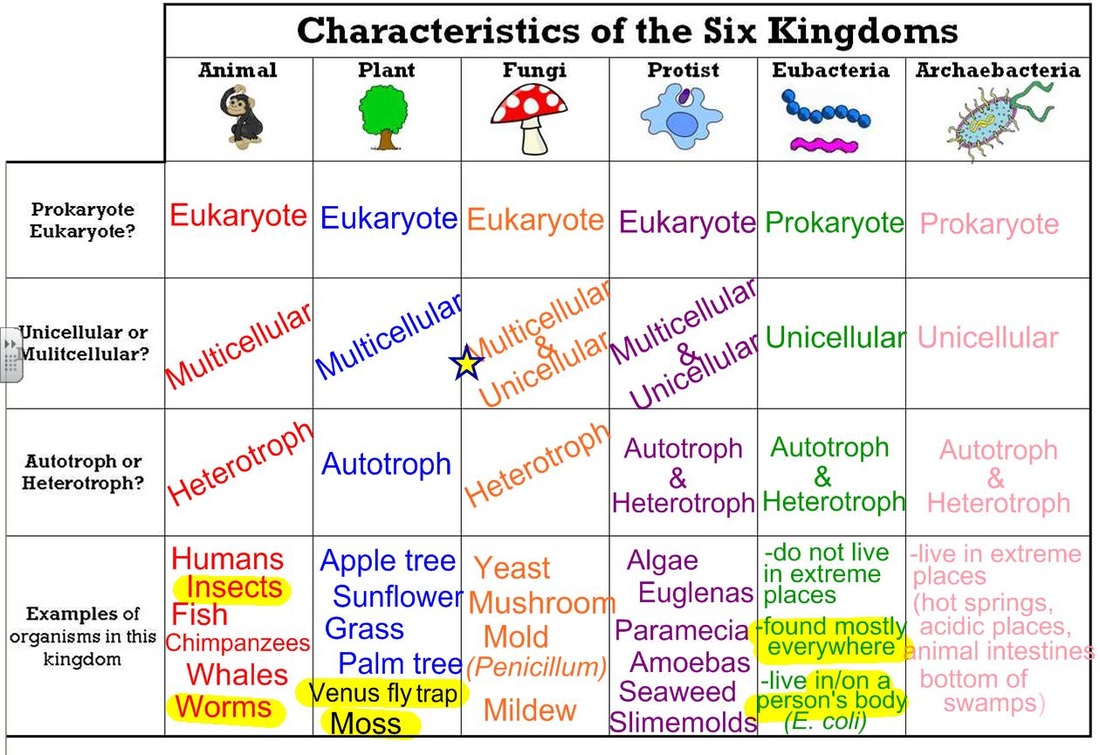
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
Web The Three Domains Of Life Are Bacteria, Archaea And Eukaryota.
In Biology, A Kingdom Is The Second Highest Taxonomic Rank, Just Below Domain.
Classification Of The Human Species.
Web The Taxa In Hierarchical Order:
Related Post:
