Laplace Chart
Laplace Chart - A table of commonly used laplace transforms. Here differential equation of time domain form is first transformed to algebraic equation of frequency domain form. ( 4 t) − 9 sin. Laplacetransform [ f [ t1,., t n], { t1,., t n }, { s1,., s n }] gives the multidimensional laplace transform of f [ t1,., t n]. This list is not a complete listing of laplace transforms and only contains some of the more commonly used laplace transforms and formulas. {d} {t}\right.}\right\rbrace}_ { { {t}= {0}}} s1. Web s.boyd ee102 table of laplace transforms rememberthatweconsiderallfunctions(signals)asdeflnedonlyont‚0. T ≥ 0 time delay 3 f(at) 1 a f(s a); I generally spend a couple of days giving a rough overview of the omitted chapters: G(t) = 4cos(4t)−9sin(4t) +2cos(10t) g ( t) = 4 cos. Web tables of laplace transforms. Web table of elementary laplace transforms. Cosh(t) = et +e−t 2 sinh(t) = et−e−t 2 cosh. U(t — 2tr) sin t 18. The laplace equation is given by: Educator.com has been visited by 10k+ users in the past month ∇^2u(x,y,z) = 0, where u(x,y,z) is the scalar function and ∇^2 is the laplace operator. U(t — 2tr) sin t 18. Properties of laplace transforms number time function laplace transform property 1 αf1(t)+βf2(t) αf1(s)+βf2(s) superposition 2 f(t− t)us(t− t) f(s)e−st; ( 4 t) + 2 cos. If we transform both sides of a differential equation, the resulting equation is often something we can solve with algebraic methods. Web table of laplace transforms f(t) l[f(t)] = f(s) 1 1 s (1) eatf(t) f(s a) (2) u(t a) e as s (3) f(t a)u(t a) e asf(s) (4) (t) 1 (5) (t stt 0) e 0 (6) tnf(t). Web example 1 find the laplace transforms of the given functions. ∇^2u(x,y,z) = 0, where u(x,y,z) is the scalar function and ∇^2 is the laplace operator. ( 10 t) h(t) = 3sinh(2t) +3sin(2t) h ( t) = 3 sinh. Web if we want to take the laplace transform of the unit step function that goes to 1 at pi, t. {d} {t}\right.}\right\rbrace}_ { { {t}= {0}}} s1. ∇^2u(x,y,z) = 0, where u(x,y,z) is the scalar function and ∇^2 is the laplace operator. Visit byju’s to learn the definition, properties, inverse laplace transforms and examples. (sin at) * (cos cot) state the laplace transforms of a few simple functions from memory. The laplace equation is given by: Web table of laplace transforms (continued) a b in t f(t) (y 0.5772) eat) cos cot) cosh at) — sin cot si(t) 15. \displaystyle\frac {1} { {s}} {\left\lbrace\int g { {\left ( {t}\right)}}\ {\left. I generally spend a couple of days giving a rough overview of the omitted chapters: Web laplacetransform [ f [ t], t,] gives the numeric laplace. This list is not a complete listing of laplace transforms and only contains some of the more commonly used laplace transforms and formulas. Get the free laplace transform calculator widget for your website, blog, wordpress, blogger, or igoogle. In the following sections we see how to use the table of laplace transformations to solve problems. T cos t + sin. 12t*e arctan arccot s 16. ( t) = e t − e − t 2. {d} {t}\right.}\right\rbrace}_ { { {t}= {0}}} s1. What are the steps of solving an ode by the laplace transform? Recall the definition of hyperbolic functions. Properties of laplace transforms number time function laplace transform property 1 αf1(t)+βf2(t) αf1(s)+βf2(s) superposition 2 f(t− t)us(t− t) f(s)e−st; T ≥ 0 time delay 3 f(at) 1 a f(s a); Introduction to the laplace transform. Web table of laplace transforms f(t) l[f(t)] = f(s) 1 1 s (1) eatf(t) f(s a) (2) u(t a) e as s (3) f(t a)u(t. This list is not a complete listing of laplace transforms and only contains some of the more commonly used laplace transforms and formulas. Web table of laplace transforms f(t) l[f(t)] = f(s) 1 1 s (1) eatf(t) f(s a) (2) u(t a) e as s (3) f(t a)u(t a) e asf(s) (4) (t) 1 (5) (t stt 0) e 0. Web example 1 find the laplace transforms of the given functions. C is pi in this case, so minus pi s times the laplace transform of. This list is not a complete listing of laplace transforms and only contains some of the more commonly used laplace transforms and formulas. 12t*e arctan arccot s 16. If we transform both sides of a differential equation, the resulting equation is often something we can solve with algebraic methods. Web table of elementary laplace transforms. Web s.boyd ee102 table of laplace transforms rememberthatweconsiderallfunctions(signals)asdeflnedonlyont‚0. F (t) = 6e−5t+e3t +5t3 −9 f ( t) = 6 e − 5 t + e 3 t + 5 t 3 − 9. Web laplace transform is the integral transform of the given derivative function with real variable t to convert into a complex function with variable s. Educator.com has been visited by 10k+ users in the past month ( t) = e t + e − t 2 sinh. Web laplace transforms and fourier transforms are probably the main two kinds of transforms that are used. Web if we want to take the laplace transform of the unit step function that goes to 1 at pi, t times the sine function shifted by pi to the right, we know that this is going to be equal to e to the minus cs. Basic examples (4) compute the laplace transform of a function: Series solutions (chapter 4) and difference equations (chapter 7). The brief table of laplace transforms in the appendix will be adequate for our purposes.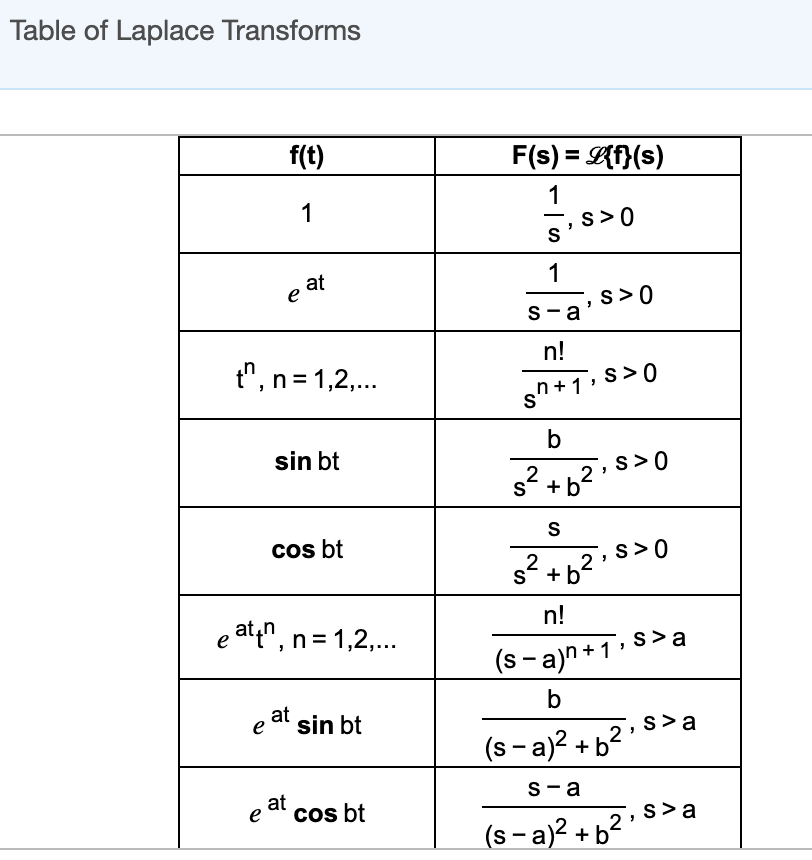
Solved 7.3.10 Use the tables of Laplace

laplace transform table Buscar con Google Laplace, Laplace
Solved Access to Laplace Chart Laplace Transform Chart.pdf
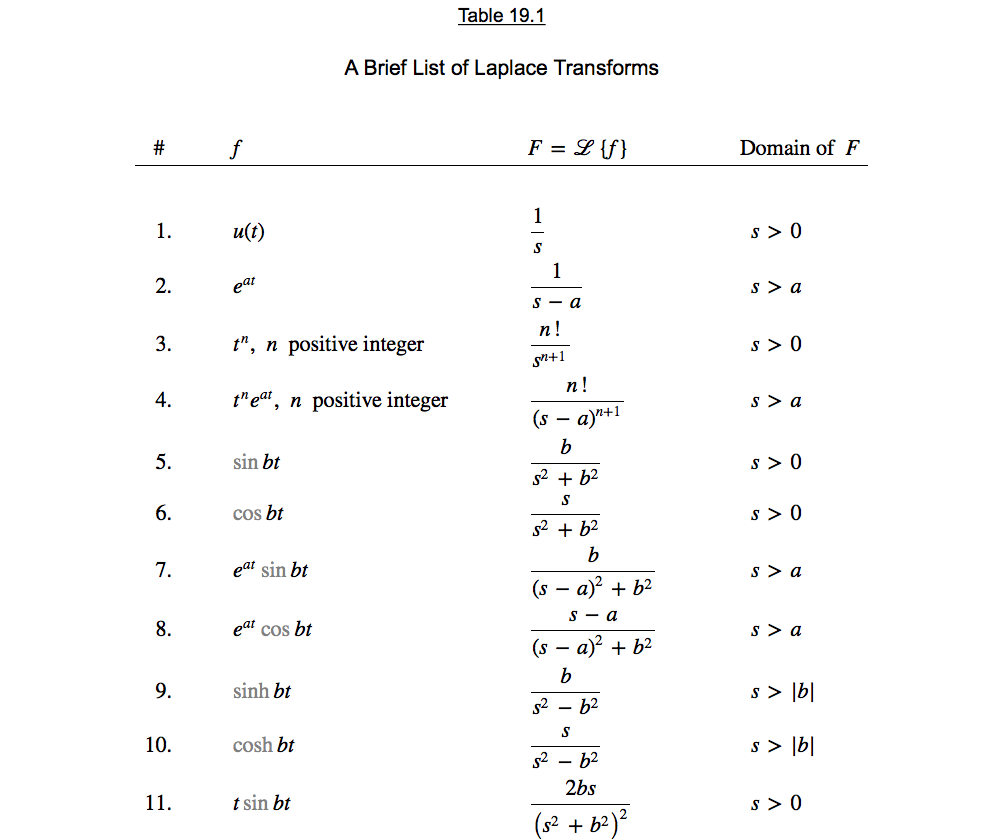
Solved Table 19.1 A Brief List of Laplace Transforms u(t) at
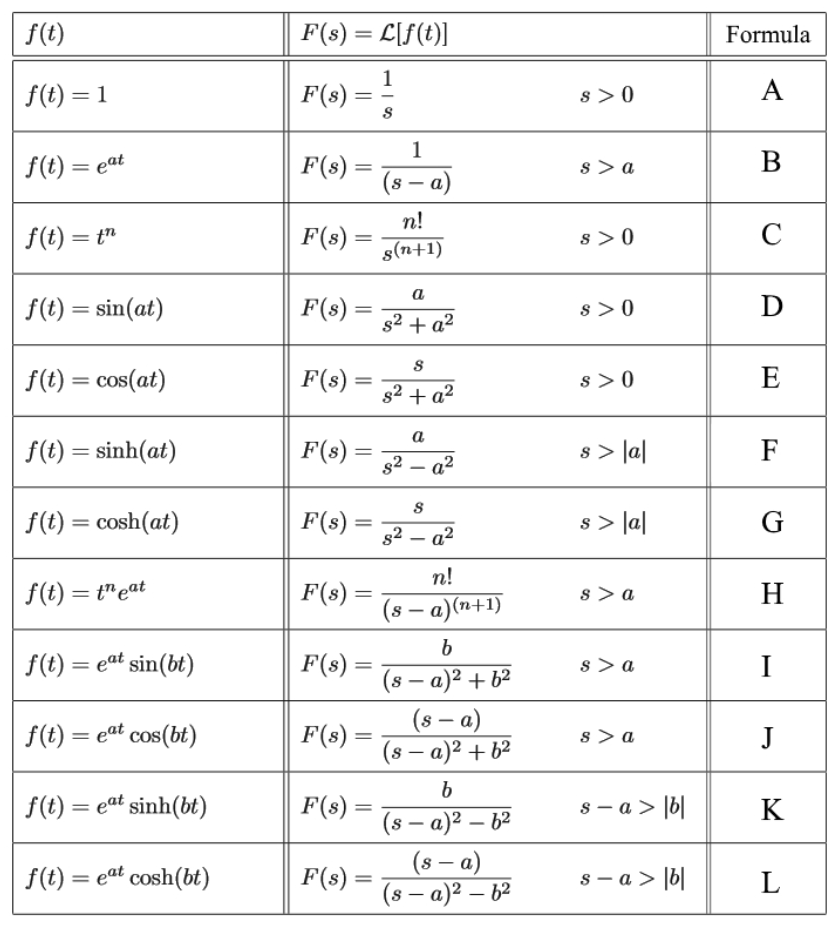
Calculating laplace transforms StudyPug

Solved 2. (2 points each) Determine the Laplace transform of
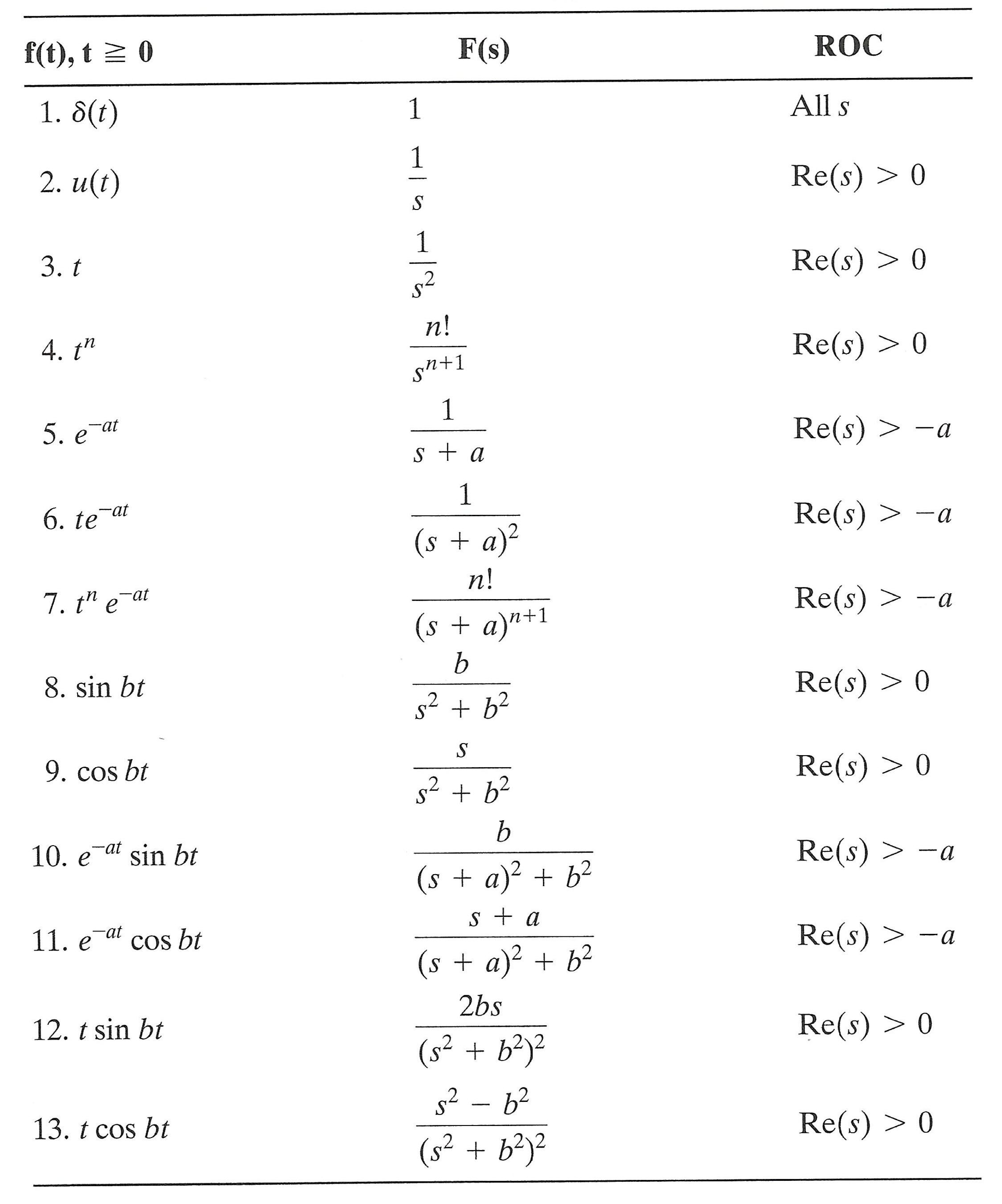
Solved Use Laplace transforms to solve the initial value
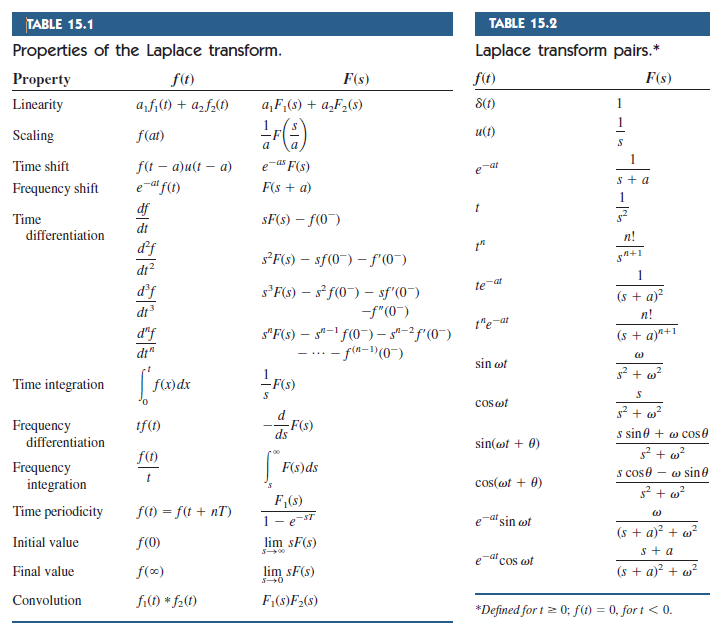
Solved Determine the Laplace transform of the followng
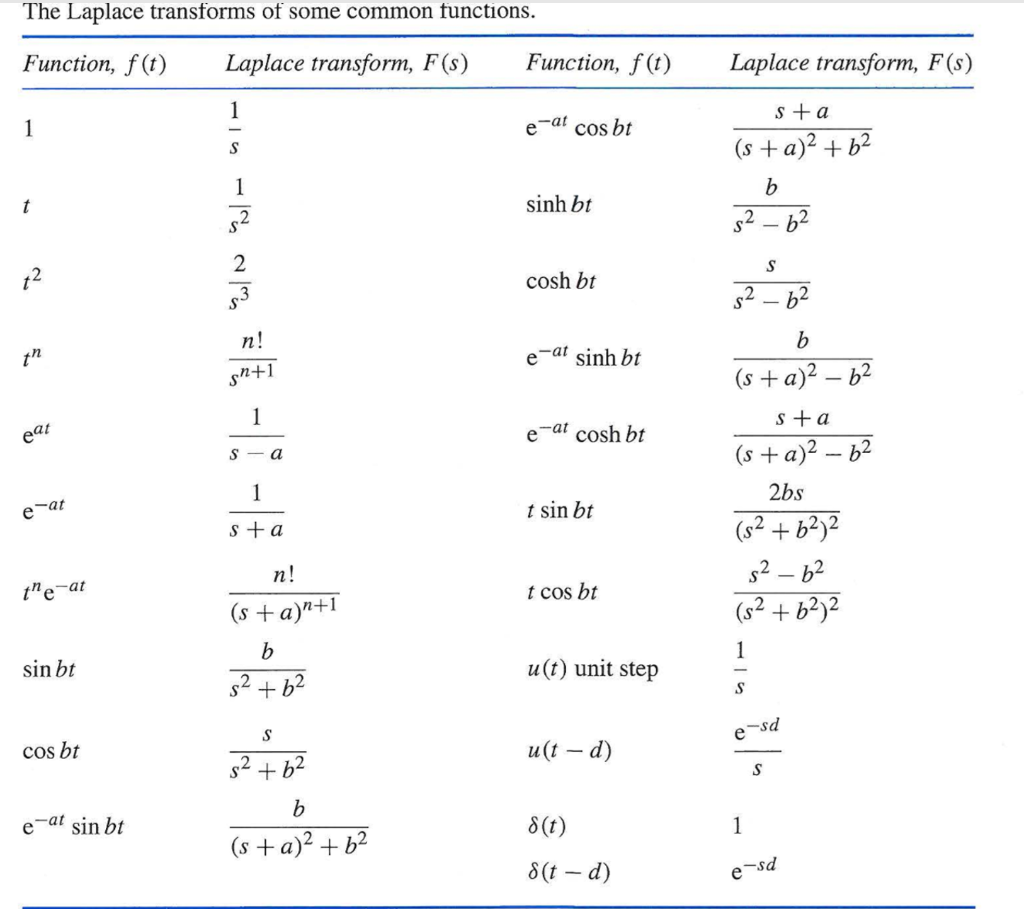
Solved 4 The Laplace transforms of some common functions.

Laplace table Laplace transform, Laplace, Physics and mathematics
The Solution Of The Laplace Equation U Xx +U Yy =0,0<X<A,0 Y B,Satisfyingtheboundaryconditionsu(X,0) = U(X,B)=0For0<X<Aand U(0,Y)=0 And U(A,Y)=F(Y)For0 Y B Has The General Form U(X,Y)= X1 N=1 C N Sinh N⇡X B Sin N⇡Y B Where C N = 2 Bsinh(N⇡A B) Z B 0 F(Y)Sin N⇡Y B Dy.
Web Table Of Laplace Transforms F(T) L[F(T)] = F(S) 1 1 S (1) Eatf(T) F(S A) (2) U(T A) E As S (3) F(T A)U(T A) E Asf(S) (4) (T) 1 (5) (T Stt 0) E 0 (6) Tnf(T) ( 1)N Dnf(S) Dsn (7) F0(T) Sf(S) F(0) (8) Fn(T) Snf(S) S(N 1)F(0) (Fn 1)(0) (9) Z T 0 F(X)G(T X)Dx F(S)G(S) (10) Tn (N= 0;1;2;:::) N!
{D} {T}\Right.}\Right\Rbrace}_ { { {T}= {0}}} S1.
In The Following Sections We See How To Use The Table Of Laplace Transformations To Solve Problems.
Related Post:
