Meiosis Vs Mitosis Chart
Meiosis Vs Mitosis Chart - They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. While mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. Web there are two types of cell division: The purpose of mitosis is cell regeneration, growth, and asexual reproduction,while the purpose of meiosis is the production of gametes for sexual. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by which egg and sperm cells are formed. Mitosis happens when you grow. On the left side of the diagram, you can see the key features of mitosis, on the right are the key features of meiosis, and where the two circles overlap is where their similarities are listed. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain only half as much dna. Most cells in the body regularly go through mitosis, but some do so more often than others. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Web meiosis versus mitosis comparison chart; Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. Introduction mitosis is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs. Most cells in the body regularly go through mitosis, but some do so more often than others. Mitosis is the process by. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain only half as much dna. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. While mitosis yields two daughter. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. The goal of mitosis is to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. While mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces. Introduction mitosis is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs. A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from. Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. Web both mitosis and meiosis result in eukaryotic cell division. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation.. Introduction mitosis is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs. Web mitosis and meiosis are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. Web there are two types of cell division: Mitosis is the process by. The purpose of mitosis is cell regeneration, growth, and asexual reproduction,while the purpose of meiosis is the production of gametes for sexual. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division and. Web mitosis produces two genetically identical “daughter” cells from a single “parent” cell, whereas meiosis produces cells that are genetically unique from the parent and contain only half as much dna. The purpose of mitosis is cell. Mitosis happens when you grow. Web below is a mitosis and meiosis venn diagram that summarizes all the key mitosis vs meiosis similarities and differences. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. Mitosis is the process by which body cells divide and create copies of themselves for growth. Web both mitosis and meiosis result in eukaryotic cell division. In meiosis, the new cells have half the genetic material of the parent cell and is the process by which egg and sperm cells are formed. Web meiosis versus mitosis comparison chart; Web mitosis and meiosis are both forms of division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division and. Web mitosis and meiosis are two different types of cell division. While mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells. Mitosis is the process by which body cells divide and create copies of themselves for growth and repair. Meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced. Mitosis happens when you grow. Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. They share some similarities, but also exhibit distinct differences that lead to very different outcomes. Web there are two types of cell division: The primary difference between these divisions is the differing goals of each process. On the left side of the diagram, you can see the key features of mitosis, on the right are the key features of meiosis, and where the two circles overlap is where their similarities are listed.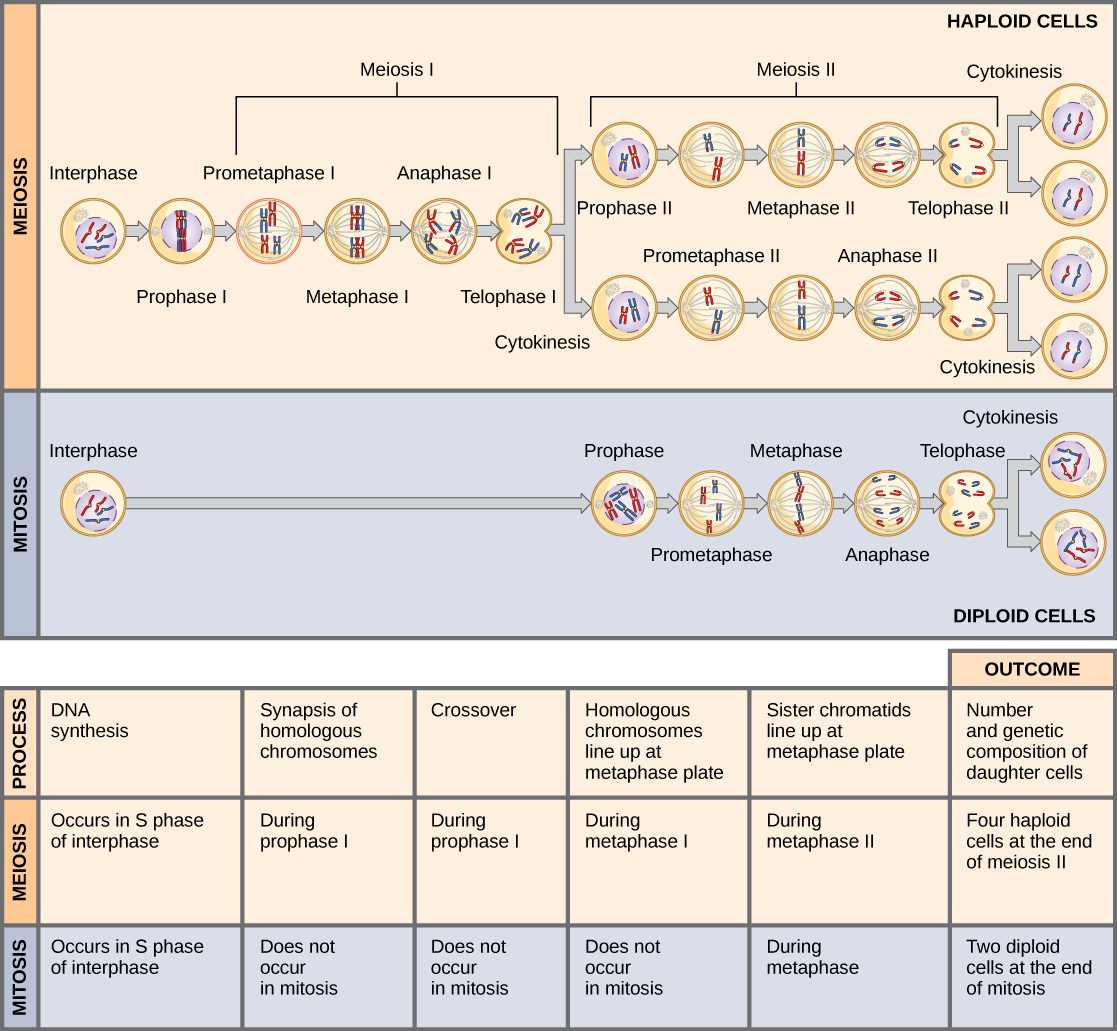
Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis Principles of Biology
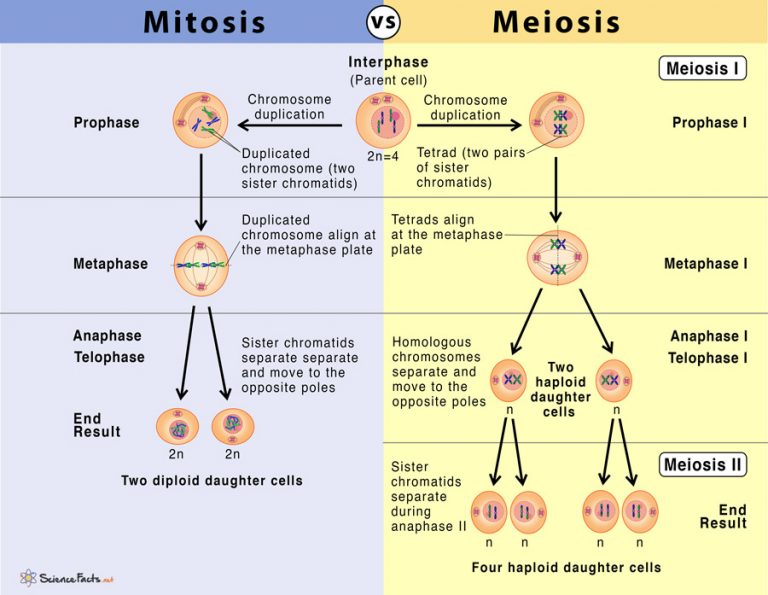
Mitosis vs Meiosis 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities

Meiosis vs. Mitosis Comparison SchoolWorkHelper

cell biology Mitosis versus Meiosis I What's the difference

Annie's Science Blog Meiosis vs. Mitosis

Chart Of Meiosis Biological Science Picture Directory
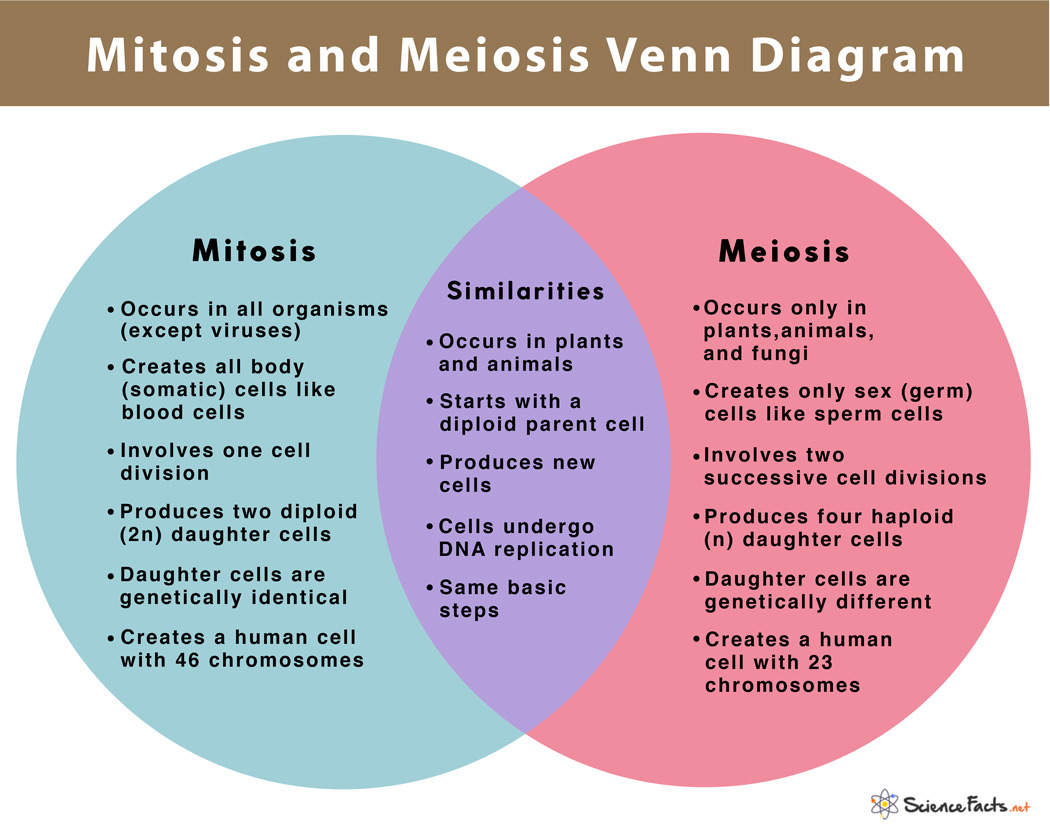
Mitosis vs Meiosis 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities
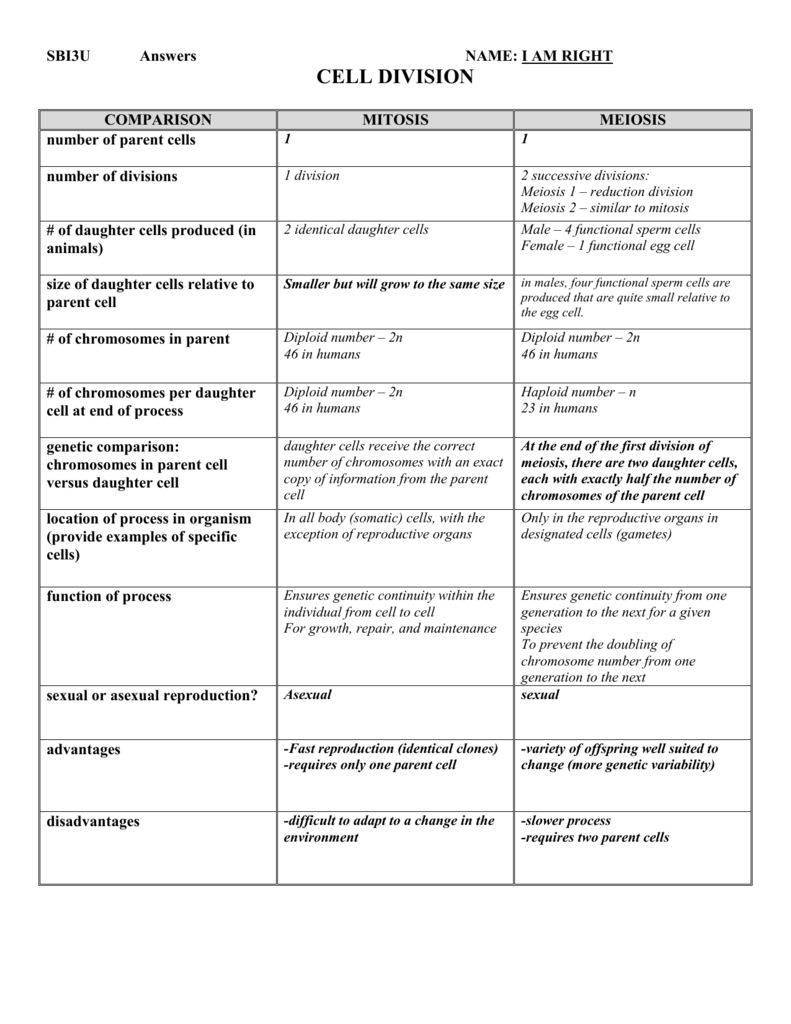
Mitosis vs Meiosis Chart

17 Best images about Cell Division School Mitosis, A m and Pictures

PPT Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis PowerPoint Presentation ID237753
Web Science > Ap®︎/College Biology > Heredity > Meiosis And Genetic Diversity Meiosis Google Classroom How Meiosis Reduces Chromosome Number By Half:
Crossing Over, Meiosis I, Meiosis Ii, And Genetic Variation.
A Type Of Cellular Reproduction In Which The Number Of Chromosomes Are Reduced By Half Through The Separation Of Homologous Chromosomes, Producing Two Haploid Cells.
Mitosis Occurs In Somatic Cells And Results In Two Identical Daughter Cells With A Diploid (2N) Number Of Chromosomes.
Related Post: