Osha Minimum Approach Distance Chart
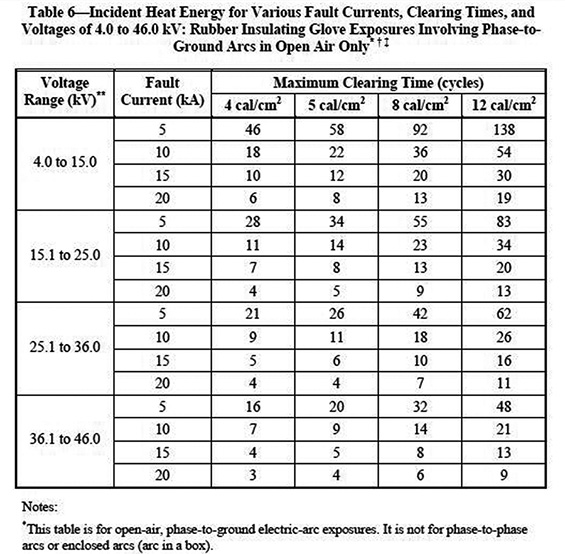
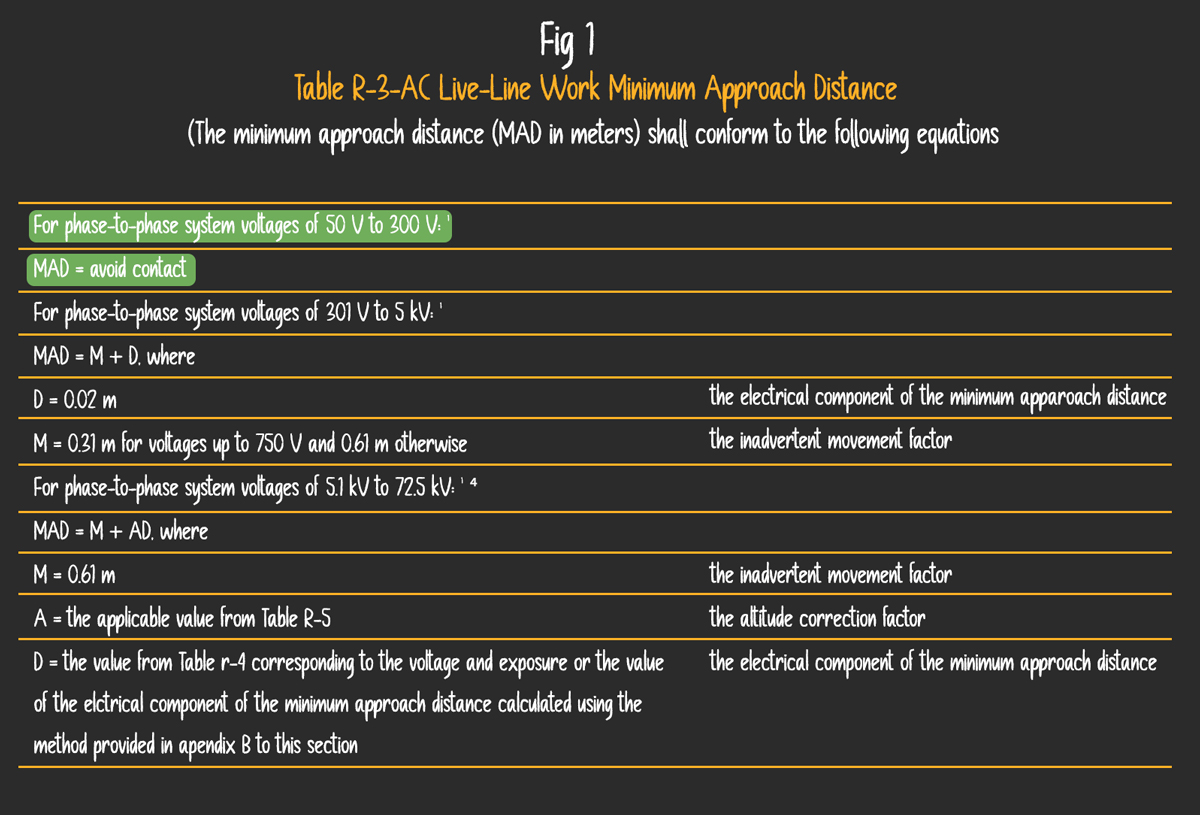
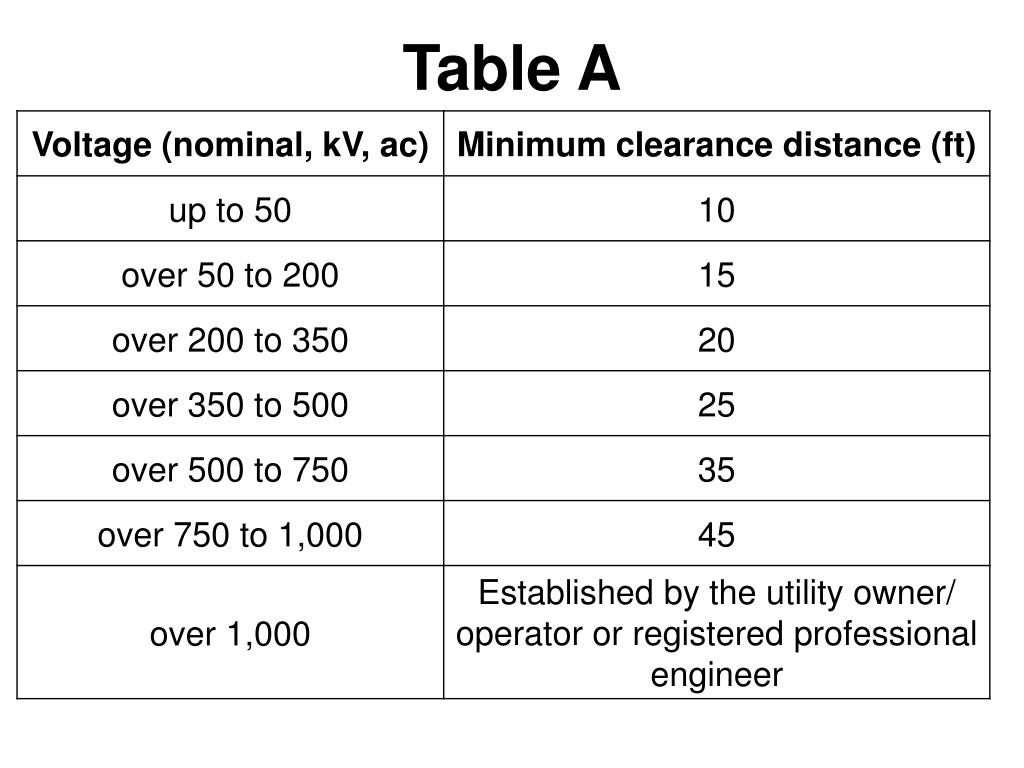
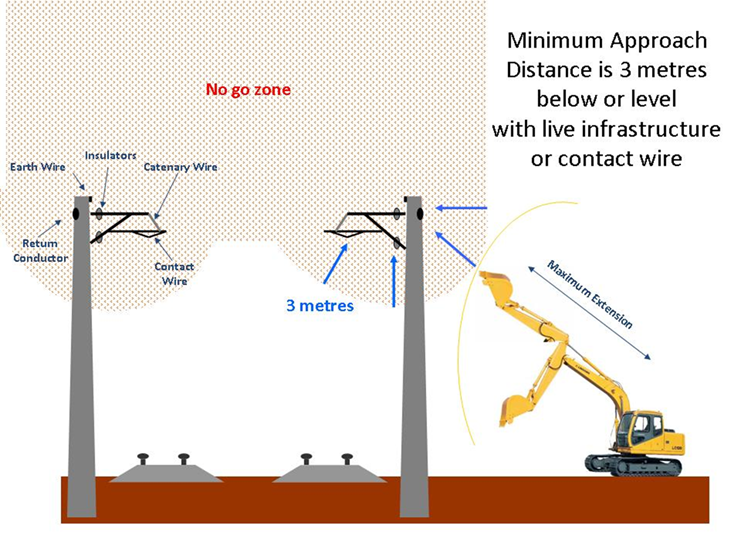
Osha Minimum Approach Distance Chart - Web osha table a minimum approach distances* *used only after aps has clarified specific voltage. Minimum approach distances and insulation. Web comply with osha, it must be sufficient to enable the employee to recognize the hazard and take reasonable measures to avoid or adequately control it. Select the method of measurement. Web january 31 begins osha's enforcement of minimum approach distances for voltages of 72.6 kilovolts and higher. (a) the employer shall establish minimum approach distances using one of the following methods: The minimum approach distance (mad; Enter maximum transient overvoltage (per unit)( 1): Web if the work is performed at elevations greater than 3,000 ft (900m) above mean sea level, the minimum approach distance must be determined by multiplying the distances by the correction factor corresponding to the altitude at which the work is performed. Posted in worksite safety, osha articles. Minimum approach distances and insulation. Web ameren’s minimum approach distance. Posted in worksite safety, osha articles. Web comply with osha, it must be sufficient to enable the employee to recognize the hazard and take reasonable measures to avoid or adequately control it. Over 15kv, not over 37kv: Web use table a to determine the crane’s minimum approach distance (mad) to the power line. Web ameren’s minimum approach distance. In meters) shall conform to the following equations. Required encroachment prevention precautions— see osha 1408(b) you must do all of the following: Written by matt edmonds, cusp, cit, chst, and pam tompkins, csp, cusp on april 15, 2021. Web the minimum approach distances specified in this section corresponding to the voltages to which the qualified employee will be exposed and the skills and techniques necessary to maintain those distances, Minimum approach distances should be increased by 3 percent for every 1000 feet of increased altitude above 300 feet. Minimum approach distances for voltages for 50 v to 362.0. 1910.269(a)(2)(ii)(c) 1926.950(b)(2)(iii) training new added skills and techniques necessary to maintain minimum approach distances (mad) employees must know mad distances. The minimum approach distance (mad; 1910.269 (l) (2) on minimum approach distances (mad) altitude adjustments. Web if the work is performed at elevations greater than 3,000 ft (900m) above mean sea level, the minimum approach distance must be determined by. Web ameren’s minimum approach distance. Over 2kv, not over 15kv: Over 87.5kv, not over 121kv: Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor. Minimum approach distances for voltages for 50 v to 362.0 kv. Web 1 employers may use the minimum approach distances in this table provided the worksite is at an elevation of 900 meters (3,000 feet) or less. Minimum approach distances should be increased by 3 percent for every 1000 feet of increased altitude above 300 feet. Over 37kv, not over. Select the method of measurement. Web minimum approach distance 300v and less: The minimum approach distance (mad; Web comply with osha, it must be sufficient to enable the employee to recognize the hazard and take reasonable measures to avoid or adequately control it. Web osha table a minimum approach distances* *used only after aps has clarified specific voltage. 1910.269 (l) (2) on minimum approach distances (mad) altitude adjustments. Web for example, if the conductors are energized at 13.2 kv phase to phase, the minimum approach distance is 2 feet 3 inches and the worker’s arm reach is 3 feet, the worker must position their body 5 feet 3 inches from the energized conductor or device until they have. 1910.269(a)(2)(ii)(c) 1926.950(b)(2)(iii) training new added skills and techniques necessary to maintain minimum approach distances (mad) employees must know mad distances. Web comply with osha, it must be sufficient to enable the employee to recognize the hazard and take reasonable measures to avoid or adequately control it. In meters) shall conform to the following equations. Web use table a to determine. Over 300v, not over 750v: Minimum approach distances and insulation. Web minimum approach distance 300v and less: Web if employees will be working at elevations greater than 900 meters (3,000 feet) above mean sea level, the employer shall determine minimum approach distances by multiplying the distances in this table by the correction factor in table r. Over 87.5kv, not over. Web the minimum approach distances specified in this section corresponding to the voltages to which the qualified employee will be exposed and the skills and techniques necessary to maintain those distances, Web strength of an air gap. Web ameren’s minimum approach distance. Select the method of measurement. Written by matt edmonds, cusp, cit, chst, and pam tompkins, csp, cusp on april 15, 2021. Minimum approach distances for voltages for 50 v to 362.0 kv. Web if the work is performed at elevations greater than 3,000 ft (900m) above mean sea level, the minimum approach distance must be determined by multiplying the distances by the correction factor corresponding to the altitude at which the work is performed. Minimum approach distances for voltages for 50 v to 362.0 kv. Over 2kv, not over 15kv: Over 37kv, not over 87.5kv: Over 300v, not over 750v: The minimum approach distance (mad; Over 15kv, not over 37kv: Web 1 employers may use the minimum approach distances in this table provided the worksite is at an elevation of 900 meters (3,000 feet) or less. (a) the employer shall establish minimum approach distances using one of the following methods: If employees will be working at elevations greater than 900 meters (3,000 feet) above mean sea level, the employer shall determine minimum approach distances by multiplying the distances in this table by.)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
Gallery of ppt osha crane rule cfr 1926 subpart cc powerpoint osha
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum

OSHA Minimum Approach Distances Fact Sheet State and Federal Poster
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum

Arsenic content in different plant parts of tested aromatic rice
What is the OSHA? Occupational Safety & Health Association
Gallery of ppt osha crane rule cfr 1926 subpart cc powerpoint osha
Electrical Safety Department for Infrastructure and Transport South
)
California Code of Regulations, Title 8, Section 2940.2. Minimum
Enter Maximum Transient Overvoltage (Per Unit)( 1):
Posted In Worksite Safety, Osha Articles.
Web Osha Table A Minimum Approach Distances* *Used Only After Aps Has Clarified Specific Voltage.
1910.269(A)(2)(Ii)(C) 1926.950(B)(2)(Iii) Training New Added Skills And Techniques Necessary To Maintain Minimum Approach Distances (Mad) Employees Must Know Mad Distances.
Related Post: