Overtone Series Chart
Overtone Series Chart - Web briefly, the harmonic series, also referred to as the overtone series, occurs whenever you play a pitch in your instrument. The 'fundamental frequency' is the lowest partial present in a complex waveform. There are 2 vibrations for each 1 of the fundamental. Micah everett university of mississippi olemiss.edu/lowbrass. A 'harmonic' is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, while an 'overtone' refers. Practically speaking, it helps define an instrument’s timbre. 330 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 6th overtone: 3 × f = 1320 hz: Web this chart shows the fundamental and first 15 overtones in the middle c overtone series. Adjacent note (where you move from one note on the overtone series to the next one), nonadjacent or “leap” exercises (where you jump over one or more ots note), and mixed exercises with both adjacent and. Web the overtones produced from a single fundamental pitch are predictable. Web the initial (bottom) pitch is called the fundamental. A 'partial' is any single frequency of a complex waveform. In the example below, c2 is the fundamental, c3 is the first overtone, g3 is the second overtone, and so on. Web overtone series chart for bbb tuba. 165 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 3rd overtone: Pitched musical instruments are often based on an acoustic resonator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous modes simultaneously. Web briefly, the harmonic series, also referred to as the overtone series, occurs whenever you play a pitch in your instrument. The fundamental of a2 is 110hz.. The fundamental of a2 is 110hz. The series begins with an octave, followed by a fifth and then back to the next octave. 165 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 3rd overtone: 330 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 6th overtone: Web the overtone series is a series of intervals, or a harmonic series, above a given pitch. The overtones go on and on, and up and up, and get quieter and quieter. There are 2 vibrations for each 1 of the fundamental. 495 hz major 2nd (+4 cents) 4 × f = 1760 hz: A 'partial' is any single frequency of a complex waveform. In the example below, c2 is the fundamental, c3 is the first overtone, g3 is the second overtone, and so on. Pitched musical instruments are often based on an acoustic resonator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous modes simultaneously. This 1st overtone is ringing at a 2:1 ratio. Adjacent note (where you move. In the example below, c2 is the fundamental, c3 is the first overtone, g3 is the second overtone, and so on. When you play a c, what you are hearing is a collection of overtones associated to this pitch and this is applicable to any sound you hear coming from an instrument or otherwise. In the diagram below, the fundamental. A 'harmonic' is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, while an 'overtone' refers. The “c” fundamental, together with a series of overtones, including c itself (repeated several times as an overtone), plus the notes e and g. This 1st overtone is ringing at a 2:1 ratio. We call the lowest pitch the fundamental, and every tone above it is. The series begins with an octave, followed by a fifth and then back to the next octave. Web the overtone series is a series of intervals, or a harmonic series, above a given pitch. In the example below, c2 is the fundamental, c3 is the first overtone, g3 is the second overtone, and so on. Web briefly, the harmonic series,. 165 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 3rd overtone: 4 × f = 1760 hz: Web a partial is what we call each note in the overtone set, including the fundamental. Micah everett university of mississippi olemiss.edu/lowbrass. The pitches above it are that pitch's overtones. When you play a c chord, here’s what the music modules in your brain actually pick up and process (fundamental and strongest overtones): The harmonic (or overtone) series | horn matters | a french horn and brass site and resource | john ericson and bruce hembd. There are also sounds with inharmonic overtones. Web have a look at table 35. The fundamental of a2 is 110hz. Adjacent note (where you move from one note on the overtone series to the next one), nonadjacent or “leap” exercises (where you jump over one or more ots note), and mixed exercises with both adjacent and. We call the lowest pitch the fundamental, and every tone above it is considered an overtone. Web overtone series chart for tenor and bass trombones. The harmonic (or overtone) series | horn matters | a french horn and brass site and resource | john ericson and bruce hembd. What are overtones in music? Web the overtone series (or harmonic series) if you have the right equipment, you can identify and measure all the overtones present when you pluck a single guitar string and produce middle c. Web a harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a fundamental frequency. 330 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 6th overtone: Web the initial (bottom) pitch is called the fundamental. 4 × f = 1760 hz: The series begins with an octave, followed by a fifth and then back to the next octave. Web the overtone series is a series of intervals, or a harmonic series, above a given pitch. In the example below, c2 is the fundamental, c3 is the first overtone, g3 is the second overtone, and so on. 165 hz perfect fifth (+2 cents) 3rd overtone: Web the overtones produced from a single fundamental pitch are predictable.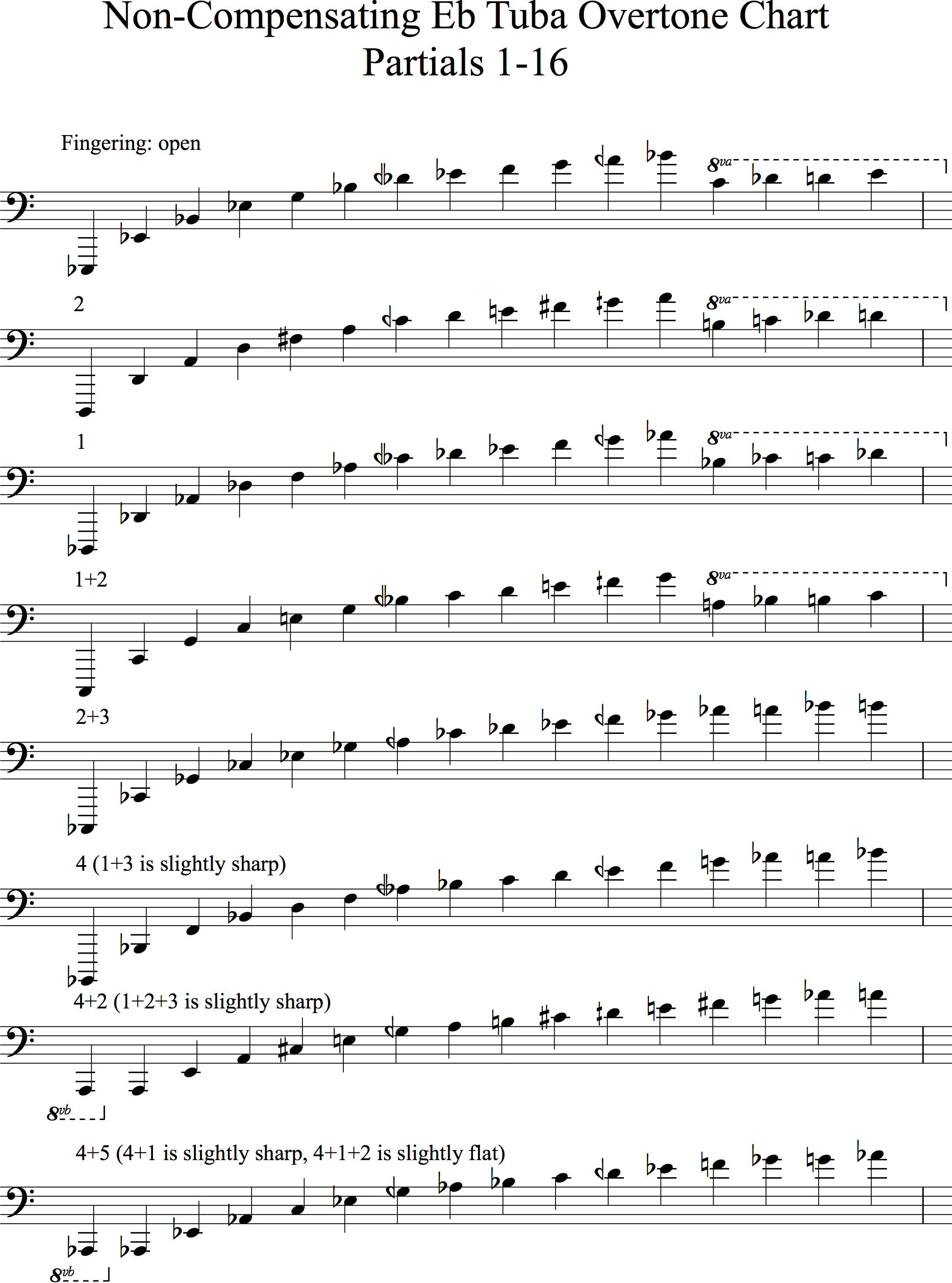
Range/Harmonic Series The Composer's Guide to the Tuba

The Science of Music Performance Harmonic Overtone Series Lesson Plan

harmonics Why do we scale/shift up an octave in the overtone series

10. The Overtone Series and Dissonance YouTube

46The Overtone Series Music Student 101

Park Arts / The origin of Intervals and Scales
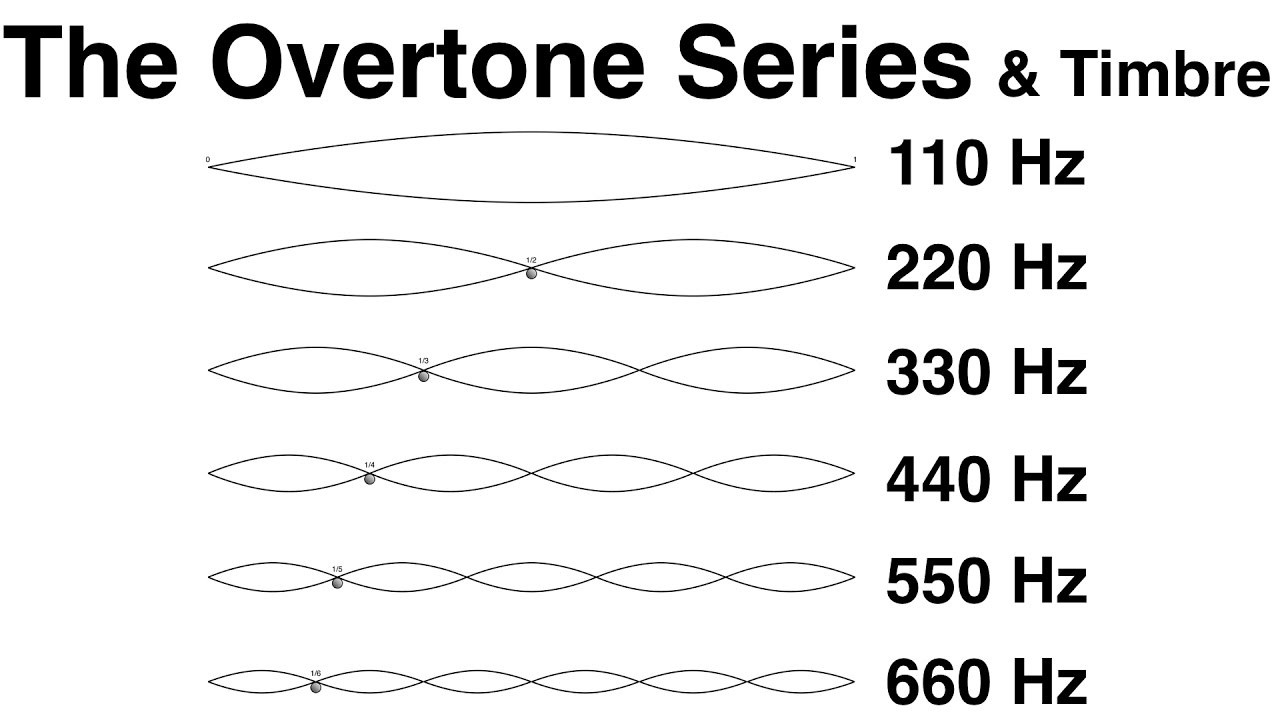
9. The Overtone Series and Timbre YouTube

Range/Harmonic Series The Composer's Guide to the Tuba
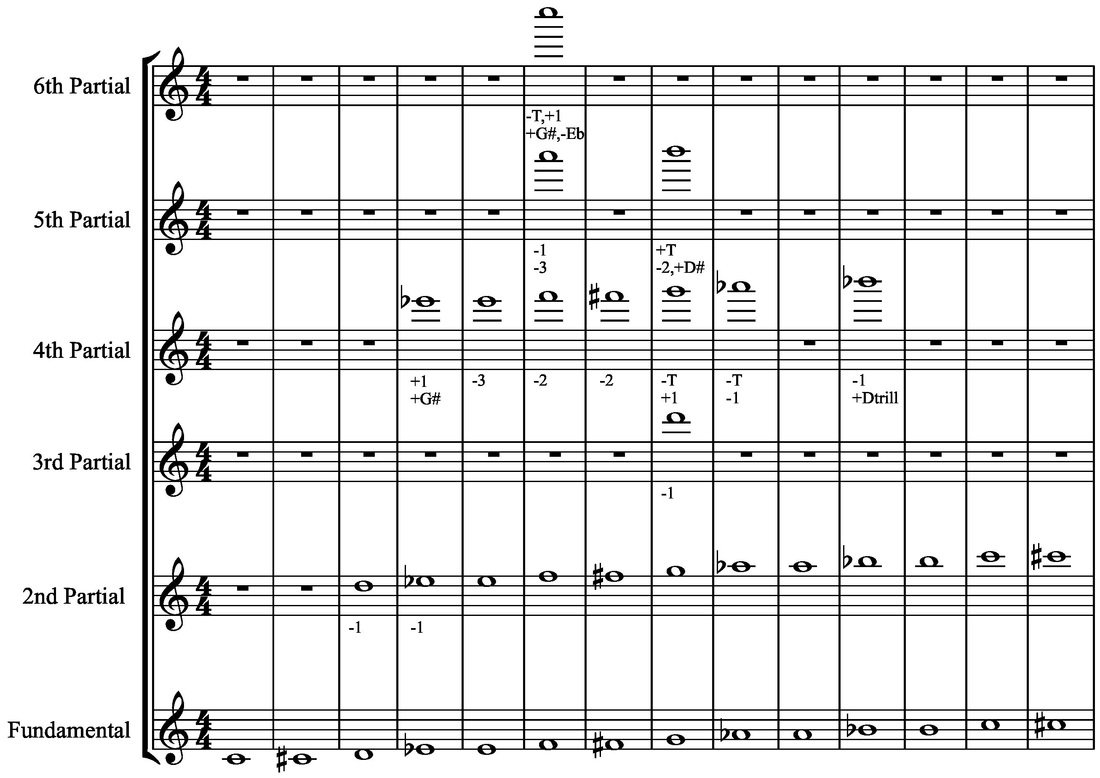
How Does it Affect Me? Overtone Series

Harmonics, Waveforms, and the Overtone Series — Leilehua Lanzilotti
Web Overtone Series Chart For Bbb Tuba.
Web Have A Look At Table 35 Below.
Web The Overtone Series Is A Series Of Intervals, Or A Harmonic Series, Above A Given Pitch.
This Function Calculates The Overtones As The Tone A Double The Frequency Of The Fundamental Pitch, + 1/2 The Frequency, + 1/3, +1/4, And So On.
Related Post: