Polyvagal Theory Chart
Polyvagal Theory Chart - 2) and boosting ones that encourage feelings of safety can benefit our psychological wellbeing, potentially helping individuals who have experienced trauma. Created and developed by stephen porges, phd, the theory describes the physiological/psychological states which underlie our daily behavior as well as challenges related to our wellness and mental health. It further proposes that physiological state limits the. Web in polyvagal theory, dr. The polyvagal theory ( poly meaning “many,” and vagal meaning “wandering”) explores the different parts of the nervous system and the body’s responses to stress. The theory was introduced in 1994 by stephen porges. Web the vagus nerve, referred to as the wandering nerve in latin, is one of the longest nerves and is a cranial nerve that originates in the brainstem and innervates the muscles of the throat, circulation, respiration, digestion, and elimination. This theory considers how the vagus nerve—the longest nerve in the autonomic nervous system running from the brain stem. Web the polyvagal theory proposes that the evolution of the mammalian autonomic nervous system provides the neurophysiological substrates for adaptive behavioral strategies. An approach to understanding trauma this theory highlights the nervous systems importance in how we perceive trauma. The vagus is divided into two parts: Porges describes the process in which our neural circuits read cues of danger in our environment as neuroception. Web according to the polyvagal theory, lowering “autonomic states that support threat reactions” (porges, 2022, p. Web the polyvagal theory proposes that the evolution of the mammalian autonomic nervous system provides the neurophysiological substrates for. The vagus is divided into two parts: Porges describes the process in which our neural circuits read cues of danger in our environment as neuroception. Created and developed by stephen porges, phd, the theory describes the physiological/psychological states which underlie our daily behavior as well as challenges related to our wellness and mental health. When clients are stuck in the. An approach to understanding trauma this theory highlights the nervous systems importance in how we perceive trauma. The vagus is divided into two parts: It further proposes that physiological state limits the. Web in polyvagal theory, dr. Web from the brain stem at the base of the skull, the vagus travels in two directions: Posted june 9, 2022 | reviewed by lybi ma Downward through the lungs, heart, diaphragm, and stomach and upward to connect with nerves in the neck, throat, eyes, and ears. When clients are stuck in the cognitive experience of their story, an explanation of polyvagal theory helps to bring their attention to the autonomic experience― to bring the. It further. Web in polyvagal theory, dr. Web from the brain stem at the base of the skull, the vagus travels in two directions: Web the polyvagal theory proposes that the evolution of the mammalian autonomic nervous system provides the neurophysiological substrates for adaptive behavioral strategies. Created and developed by stephen porges, phd, the theory describes the physiological/psychological states which underlie our. Web the polyvagal theory proposes that the evolution of the mammalian autonomic nervous system provides the neurophysiological substrates for adaptive behavioral strategies. 2) and boosting ones that encourage feelings of safety can benefit our psychological wellbeing, potentially helping individuals who have experienced trauma. Web the vagus nerve, referred to as the wandering nerve in latin, is one of the longest. The vagus is divided into two parts: The ventral vagal pathway and the dorsal vagal pathway. This theory considers how the vagus nerve—the longest nerve in the autonomic nervous system running from the brain stem. It further proposes that physiological state limits the. Through this process of neuroception, we are experiencing the world in a way in which we are. An approach to understanding trauma this theory highlights the nervous systems importance in how we perceive trauma. When clients are stuck in the cognitive experience of their story, an explanation of polyvagal theory helps to bring their attention to the autonomic experience― to bring the. It further proposes that physiological state limits the. The theory was introduced in 1994 by. Web (december 2021) the vagus nerve polyvagal theory ( pvt) is a collection of proposed evolutionary, neuroscientific, and psychological constructs pertaining to the role of the vagus nerve in emotion regulation, social connection and fear response. Web according to the polyvagal theory, lowering “autonomic states that support threat reactions” (porges, 2022, p. Porges describes the process in which our neural. Web the vagus nerve, referred to as the wandering nerve in latin, is one of the longest nerves and is a cranial nerve that originates in the brainstem and innervates the muscles of the throat, circulation, respiration, digestion, and elimination. Web in polyvagal theory, dr. An approach to understanding trauma this theory highlights the nervous systems importance in how we. Web (december 2021) the vagus nerve polyvagal theory ( pvt) is a collection of proposed evolutionary, neuroscientific, and psychological constructs pertaining to the role of the vagus nerve in emotion regulation, social connection and fear response. Web the polyvagal theory proposes that the evolution of the mammalian autonomic nervous system provides the neurophysiological substrates for adaptive behavioral strategies. Web in polyvagal theory, dr. Posted june 9, 2022 | reviewed by lybi ma An approach to understanding trauma this theory highlights the nervous systems importance in how we perceive trauma. It further proposes that physiological state limits the. Web according to the polyvagal theory, lowering “autonomic states that support threat reactions” (porges, 2022, p. 2) and boosting ones that encourage feelings of safety can benefit our psychological wellbeing, potentially helping individuals who have experienced trauma. Web the vagus nerve, referred to as the wandering nerve in latin, is one of the longest nerves and is a cranial nerve that originates in the brainstem and innervates the muscles of the throat, circulation, respiration, digestion, and elimination. The polyvagal theory ( poly meaning “many,” and vagal meaning “wandering”) explores the different parts of the nervous system and the body’s responses to stress. This theory considers how the vagus nerve—the longest nerve in the autonomic nervous system running from the brain stem. The vagus is divided into two parts: Through this process of neuroception, we are experiencing the world in a way in which we are involuntarily scanning situations and people to determine if they are safe or dangerous. The theory was introduced in 1994 by stephen porges. Web from the brain stem at the base of the skull, the vagus travels in two directions: Porges describes the process in which our neural circuits read cues of danger in our environment as neuroception.
The Polyvagal Theory Chart Mentor Books West
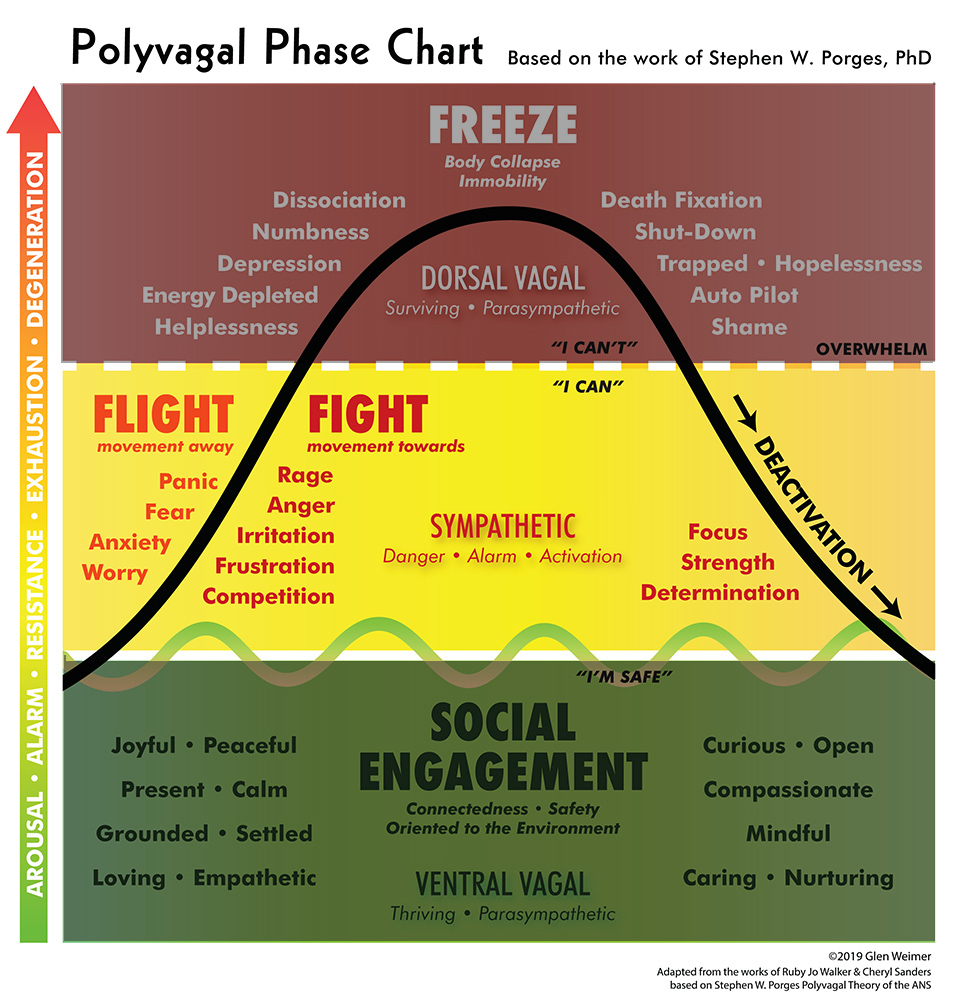
polyvagalWave_chart_02vb Glen Weimer Holodynamic Bodywork
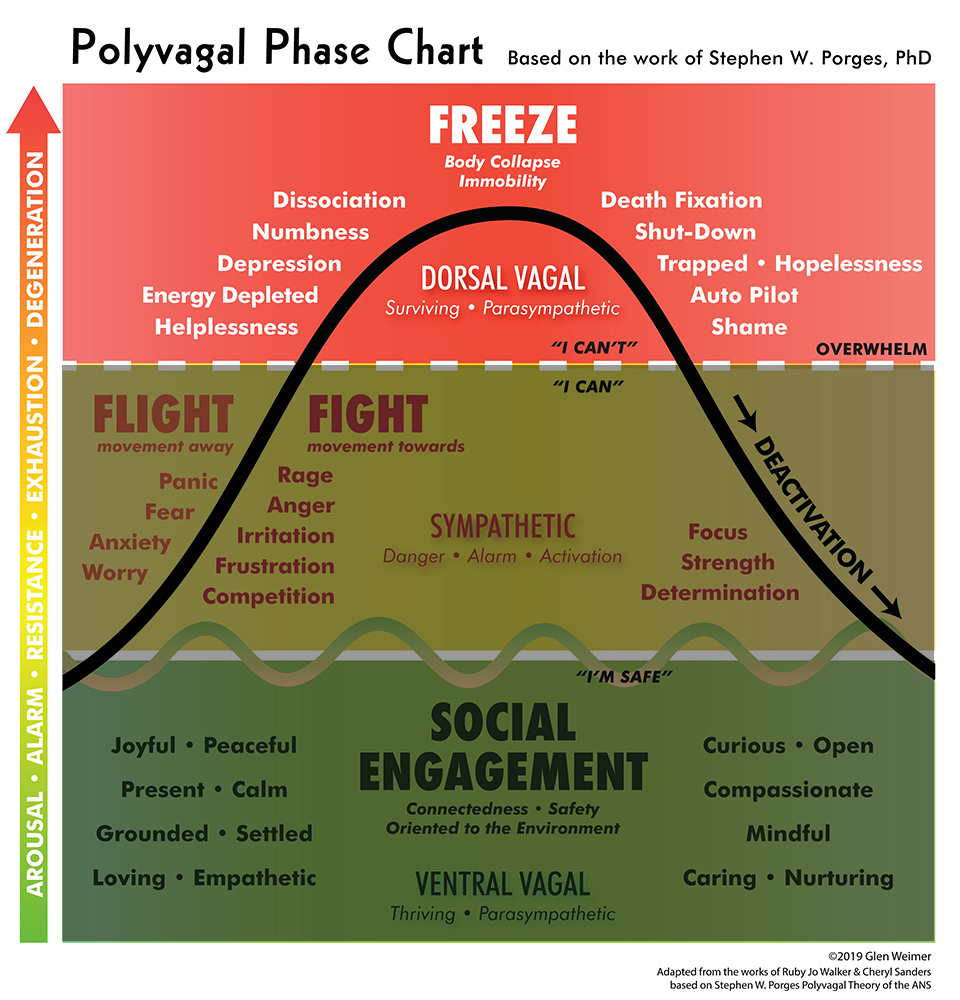
polyvagalWave_chart_03vb Glen Weimer Holodynamic Bodywork

What the polyvagal theory is and how it works Sacred Path Holistic
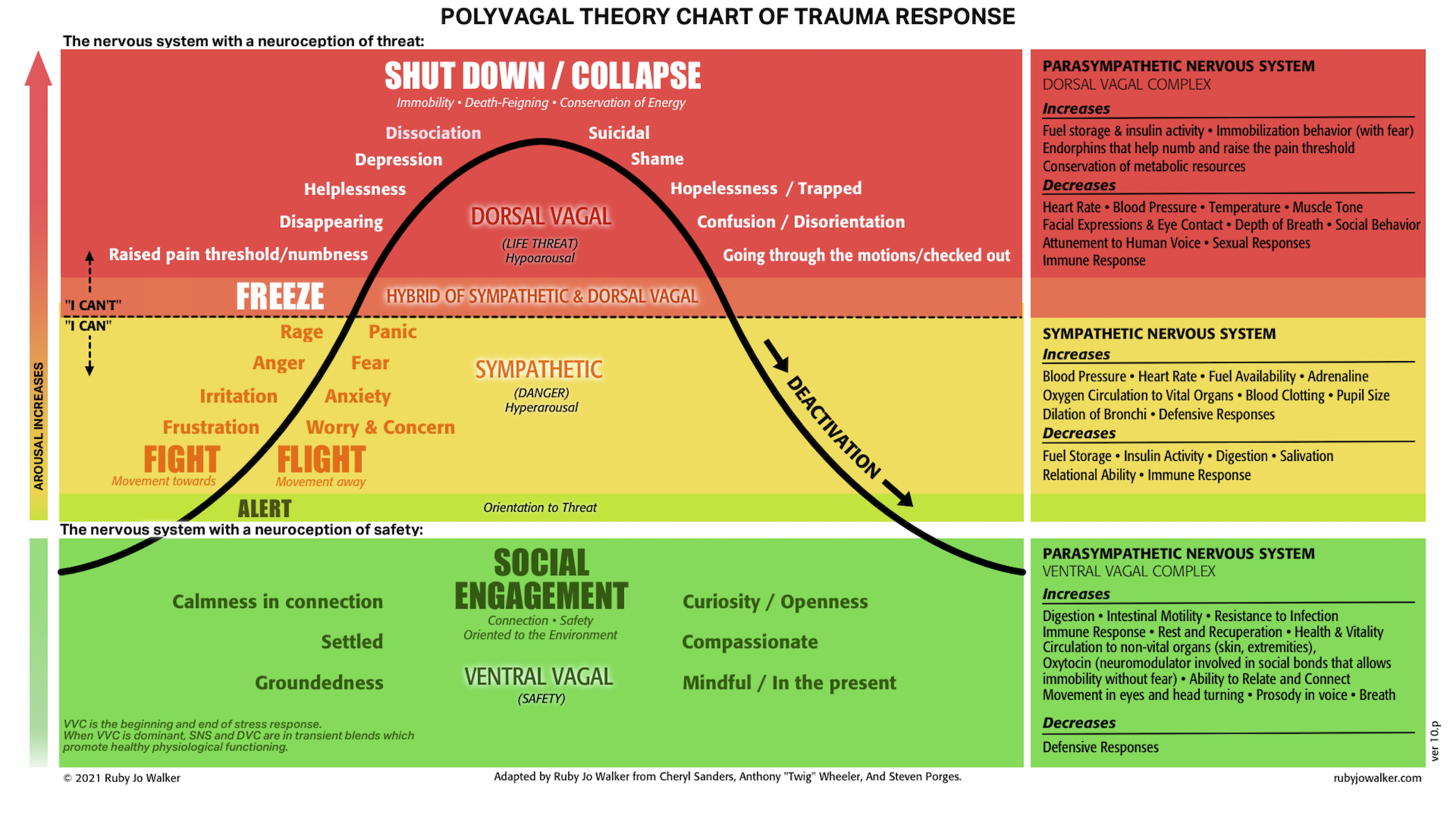
Polyvagal Theory Psychotherapist in Brighton & Hove, Sussex

How to Map Your Own Nervous Sytem The Polyvagal Theory The Movement

polyvagal+chart++Autonomic+nervous+system TOWARDS LIFEKNOWLEDGE
![]()
Polyvagal Theory Mindfully Well Counselling Cork

Polyvagal Curve 2 x Téléchargements numériques Journey to Etsy Canada
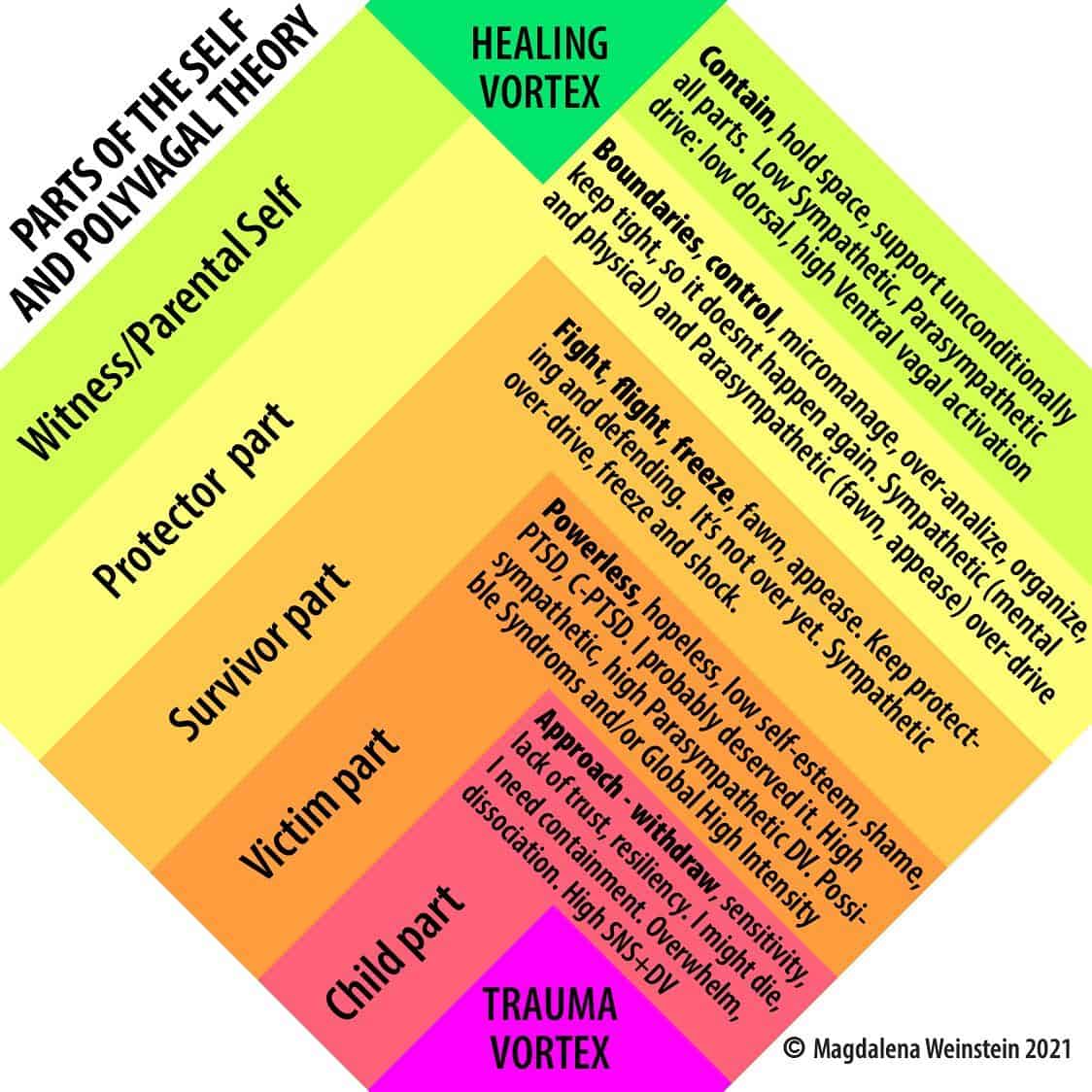
Polyvagal Chart By Magdelena Weinstein TRE® Scotland
Downward Through The Lungs, Heart, Diaphragm, And Stomach And Upward To Connect With Nerves In The Neck, Throat, Eyes, And Ears.
Created And Developed By Stephen Porges, Phd, The Theory Describes The Physiological/Psychological States Which Underlie Our Daily Behavior As Well As Challenges Related To Our Wellness And Mental Health.
When Clients Are Stuck In The Cognitive Experience Of Their Story, An Explanation Of Polyvagal Theory Helps To Bring Their Attention To The Autonomic Experience― To Bring The.
The Ventral Vagal Pathway And The Dorsal Vagal Pathway.
Related Post: