Radii Chart
Radii Chart - The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. In simpler terms, it can be defined as something similar to the radius of a circle, where the center of the circle is the nucleus and the outer edge of the circle is the outermost orbital of electron. Definitions of the atomic radius. The following web interface allows listing and comparison of ionic and crystal radii with different coordination and charge states. Atomic radii (empirical) atomic radii (absolute) atomic radii (density cutoff) covalent radii revisited (2008 values) covalent radii (molecular single bond) The covalent radius of an atom is the radius of an atom under the covalent bond with another atom (s) of a similar element. And metallic radii are the radii of the metallic atoms. Types of atomic radius with respect to the types of bond. Atomic radius in the periodic table of elements. [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. The following web interface allows listing and comparison of ionic and crystal radii with different coordination and charge states. Web at the end of this section is a chart with the estimated empirical atomic radius for each element. When the effective radii do not follow. Selected template will load here. Selected template will load here. Atomic radius in the periodic table of elements. Atomic radius is the radius of an atom which measures the distant from its nucleus to the electron. This action is not available. Previous table | next table (requires javascript enabled). Web atomic radius of elements (pm) 1: 1 å = 1 × 10 −10 m = 100 pm. Web the periodic table of the elements, showing relative atom sizes. The value for the atomic radius and the relative size of each element is presented in a familiar periodic table format. The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size. Web atomic radius is generally stated as being the total distance from an atom’s nucleus to the outermost orbital of electron. Crystalmaker 3d visualizer (free demo) periodic table graphics: Suggestions as to how the scope and content of the database can be extended are gratefully received. Web welcome to the database of ionic radii. [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. 1 å = 1 × 10 −10 m = 100 pm. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually, the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. This action is not available. Web mcdonald’s concentrated in cities. Atomic radius of all the elements of periodic table. Atomic radius in the periodic table of elements. Based on the type of bond, atomic radius is divided into three types as follows: C = πd c = 2πr d = diameter, c = circumference, and r = radius hope this helped :) It is the size of a metallic atom. Definitions of the atomic radius. Previous table | next table (requires javascript enabled). For instance, the radii generally decrease rightward along each period (row) of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases ; Selected template will load here. Affinity, impact, swot complete needs assessment &. Web at the end of this section is a chart with the estimated empirical atomic radius for. Types of atomic radius with respect to the types of bond. Atomic radius trends on the periodic table. Based on the type of bond, atomic radius is divided into three types as follows: Select from the following links to see visual periodicity representations for atomic radii, covalent radii, and van der waals radii. Ionic radii are also available. Web mcdonald’s concentrated in cities. Atomic radius is measured in picometers (pm). Going down a group, the main group elements tend to increase in atomic radius due to increased shielding and the addition of new shells to the. Web the periodic table of the elements, showing relative atom sizes. The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases. Previous table | next table (requires javascript enabled). Web at the end of this section is a chart with the estimated empirical atomic radius for each element. Sizes of atoms and ions. Web the relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. Atomic radius in the periodic table of elements. C = πd c = 2πr d = diameter, c = circumference, and r = radius hope this helped :) The second most is an area just outside chicago with 88. Crystalmaker 3d visualizer (free demo) periodic table graphics: In simpler terms, it can be defined as something similar to the radius of a circle, where the center of the circle is the nucleus and the outer edge of the circle is the outermost orbital of electron. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure 2.8.4). This makes sense because mcdonald’s was founded in southern california. [1], and pyykkö and atsumi [2]. Sizes of atoms and ions. When calculated, the atomic radius is defined as the radius of the spherical volume in which the electron can be observed with 90% probability. Calculate atomic radii are shown in figure 1.11.1 1.11. Web atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or can be determined experimentally. Atomic radii (empirical) atomic radii (absolute) atomic radii (density cutoff) covalent radii revisited (2008 values) covalent radii (molecular single bond) As we progress down a group in the periodic table, the number of electrons increases, and so does the number of shells that those electrons are organized into. Web mcdonald’s concentrated in cities. Web atomic radius chart. And metallic radii are the radii of the metallic atoms.
Periodic Table Atom Radii (pm or in 2021 Periodic table

Atoms

Elements, Atomic Radii and the Periodic Radii
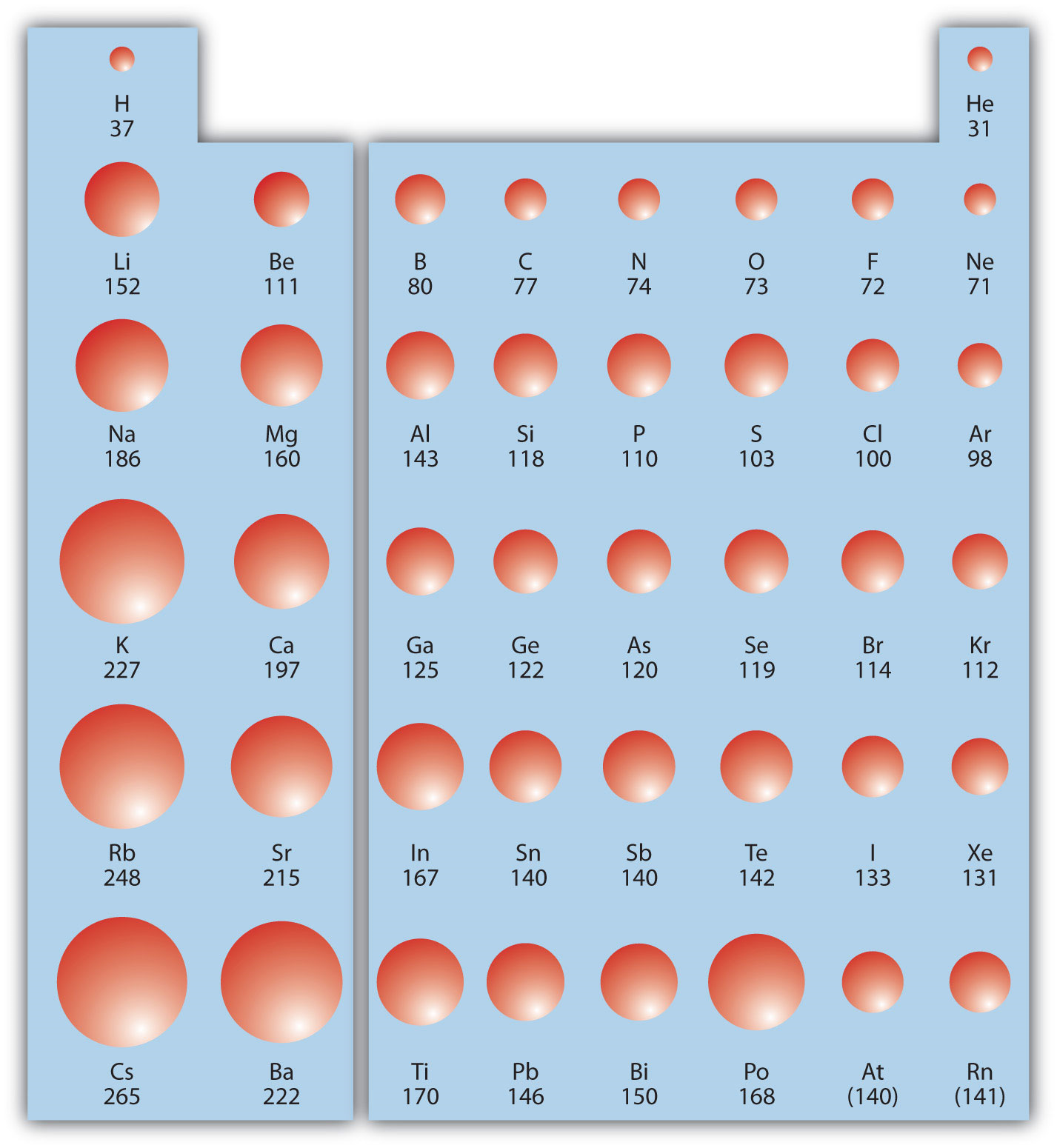
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic
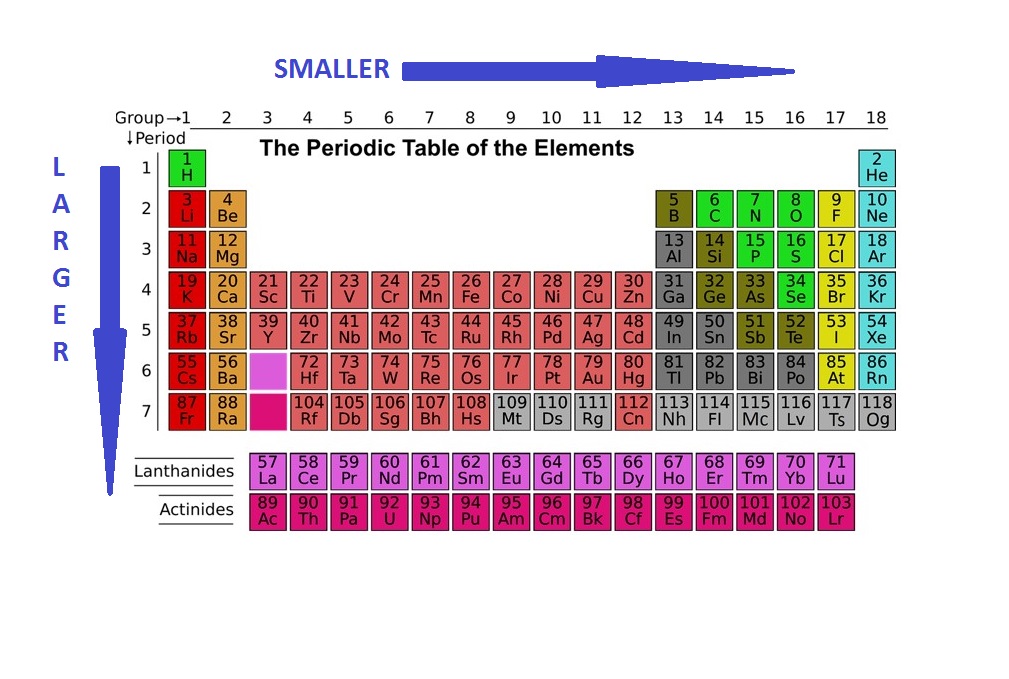
commodité retard Cruche atomic radius of the periodic table Orient Est
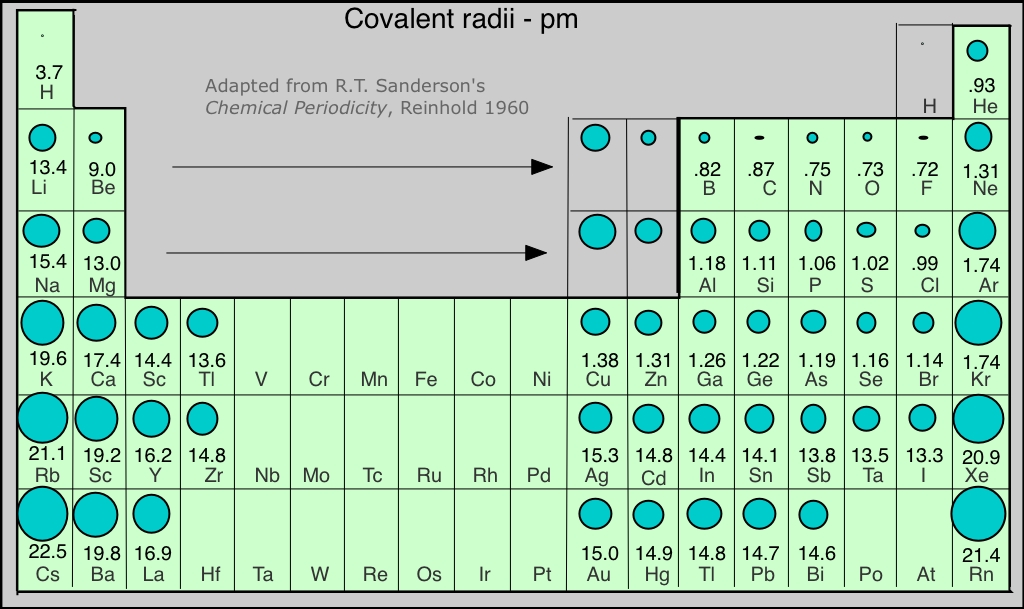
5.7 Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemistry LibreTexts
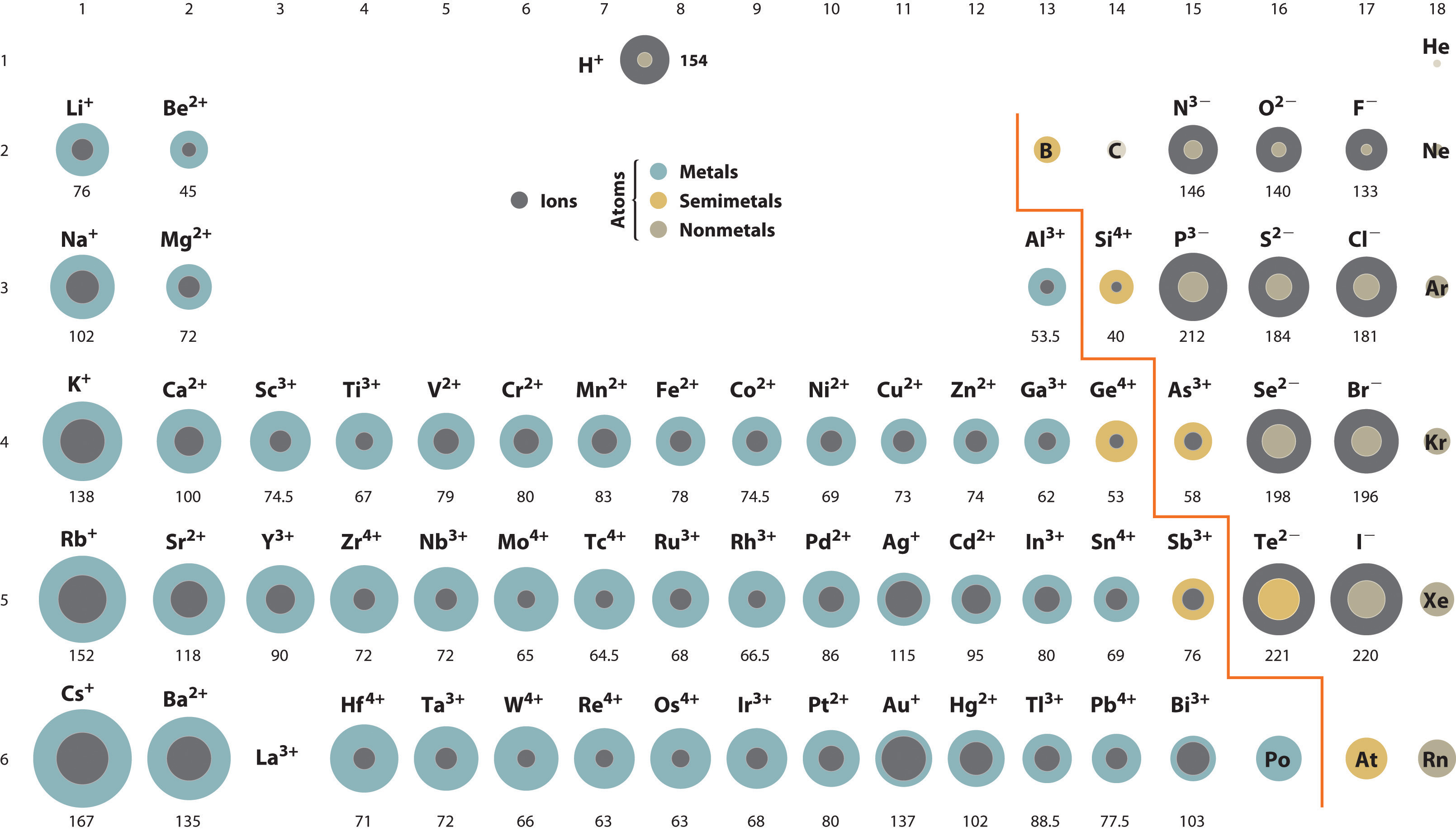
Sizes of Atoms and Ions
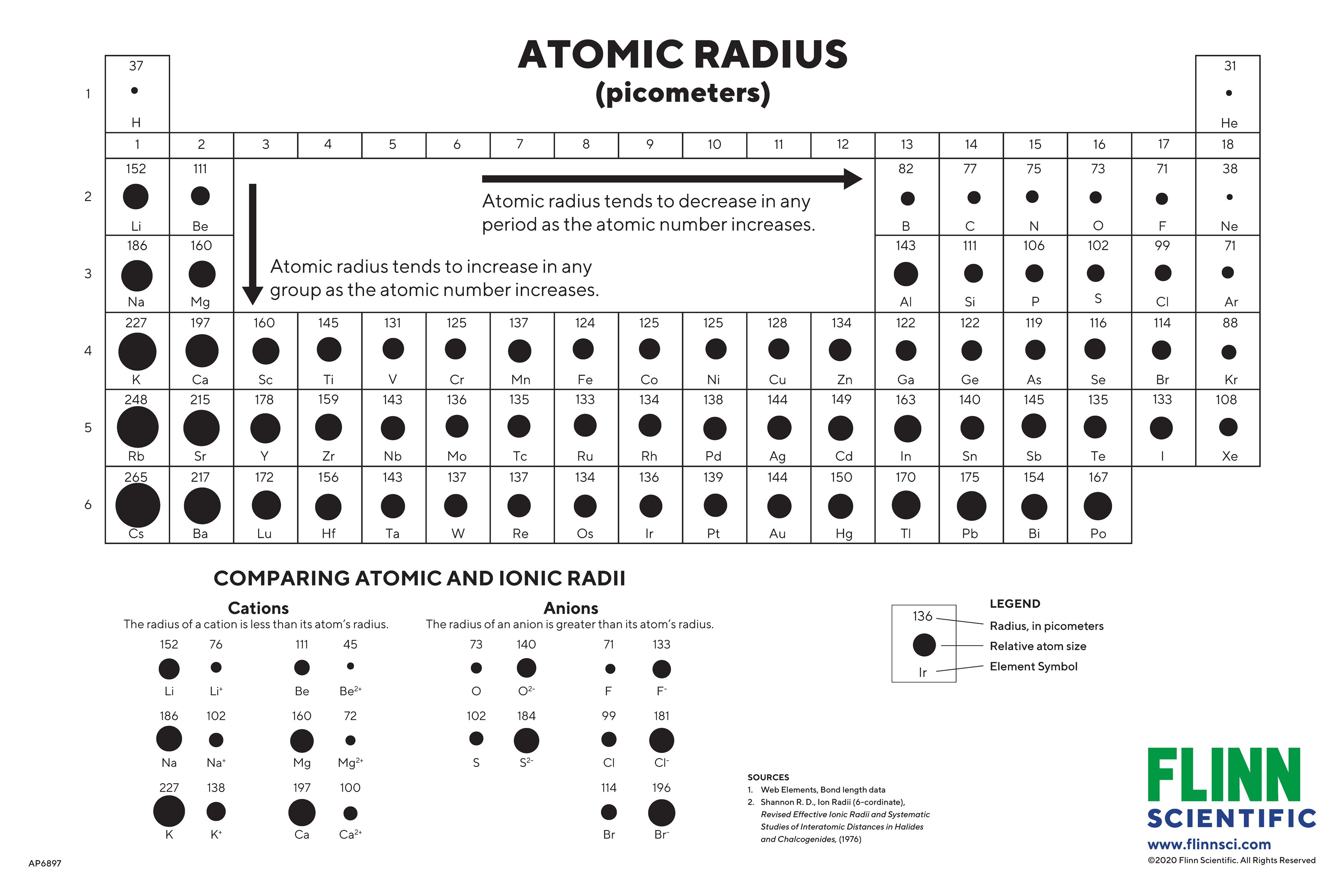
Atomic Radius Diagram
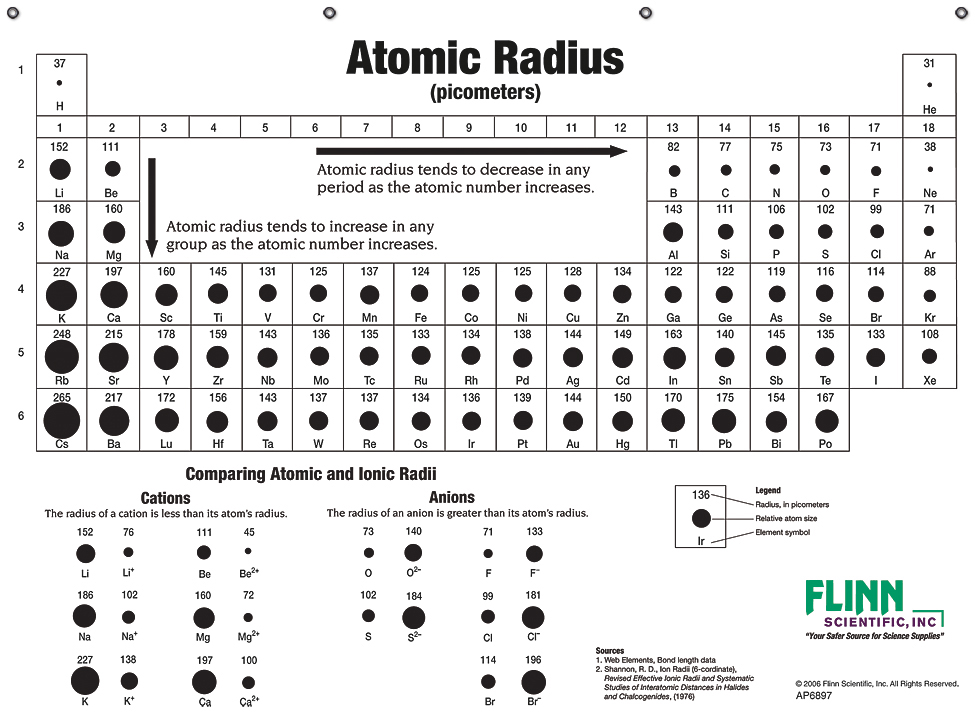
Atomic Sizes and Radii Chart

Figure 2 from Atomic and Ionic Radii of Elements 196. Semantic Scholar
Web Atomic Radius Of Elements (Pm) 1:
Based On The Type Of Bond, Atomic Radius Is Divided Into Three Types As Follows:
The Values Of Table 3 Show The Covalent Radii From The Two Recent Original Determinations By Cordero Et Al.
Web The Periodic Table Of The Elements, Showing Relative Atom Sizes.
Related Post: