Sacral Torsion Chart
Sacral Torsion Chart - Herein, we present issues, challenges and solutions related to the management of sacral fractures. Web step 1 the patient is positioned in the right lateral recumbent position with the operator standing in front and monitoring the lumbosacral junction. The sacrum is typically wider and shorter in. Read ratings & reviewsshop best sellersshop our huge selection Web the author holds that sacral torsion is often caused by a simple piriformis strength asymmetry and that sacral shear is often caused by either sacral torsion and/or anterior tilt of the sacrum, which is either caused or. Web if the test is negative (improved symmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral flexion dysfunction or an anterior sacral torsion. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. Web what is sacral torsion? Web hvla for anterior and posterior sacral torsions sacral clinical presentations presentations commonly associated with sacral somatic dysfunction and/or benefiting from correction of that dysfunction: The pain may radiate down the leg to the knee or at times, to the ankle or foot. Read ratings & reviewsshop best sellersshop our huge selection The sacrum is typically wider and shorter in. The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. Web what is sacral torsion? Web what is sacral torsion? The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. Web the author holds that sacral torsion is often caused by a simple piriformis strength asymmetry and that sacral shear is often caused by either sacral torsion and/or anterior tilt of the sacrum, which is either caused or. Web if the test. The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of somatic dysfunction (torsions, unilateral shears or. Web what is sacral torsion? Herein, we present issues, challenges and solutions related to. Web if the test is negative (improved symmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral flexion dysfunction or an anterior sacral torsion. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. Web the author holds. The sacrum is typically wider and shorter in. Web hvla for anterior and posterior sacral torsions sacral clinical presentations presentations commonly associated with sacral somatic dysfunction and/or benefiting from correction of that dysfunction: Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of. Web hvla for anterior and posterior sacral torsions sacral clinical presentations presentations commonly associated with sacral somatic dysfunction and/or benefiting from correction of that dysfunction: Web step 1 the patient is positioned in the right lateral recumbent position with the operator standing in front and monitoring the lumbosacral junction. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this. The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. Web the author holds that sacral torsion is often caused by a simple piriformis strength asymmetry and that sacral shear is often caused by either sacral torsion and/or anterior tilt of the sacrum, which is either caused or. Web if the test is negative (improved symmetry of. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. Herein, we present issues, challenges and solutions related to the management of sacral fractures. Web hvla for anterior and posterior sacral torsions sacral clinical presentations presentations commonly associated with sacral somatic dysfunction and/or benefiting from correction of that dysfunction:. The pain may radiate down the leg to the knee or at times, to the ankle or foot. Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of somatic dysfunction (torsions, unilateral shears or. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a condition in which. Web step 1 the patient is positioned in the right lateral recumbent position with the operator standing in front and monitoring the lumbosacral junction. Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of somatic dysfunction (torsions, unilateral shears or. The primary motion. Herein, we present issues, challenges and solutions related to the management of sacral fractures. Web what is sacral torsion? Web if the test is negative (improved symmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral flexion dysfunction or an anterior sacral torsion. The sacrum is typically wider and shorter in. Web the author holds that sacral torsion is often caused by a simple piriformis strength asymmetry and that sacral shear is often caused by either sacral torsion and/or anterior tilt of the sacrum, which is either caused or. Web step 1 the patient is positioned in the right lateral recumbent position with the operator standing in front and monitoring the lumbosacral junction. The primary motion is left or right rotation, occurring in the transverse plane. Web hvla for anterior and posterior sacral torsions sacral clinical presentations presentations commonly associated with sacral somatic dysfunction and/or benefiting from correction of that dysfunction: Once tart is found the specific diagnosis is distinguished by landmarks (sacral sulcus and inferior lateral angle of the sacrum and ila) to determine the type of somatic dysfunction (torsions, unilateral shears or. Web sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a condition in which pain originates at the si joint and typically concentrates on one side of the low back.
Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Inferior Lateral Angle Of Sacrum Palpation
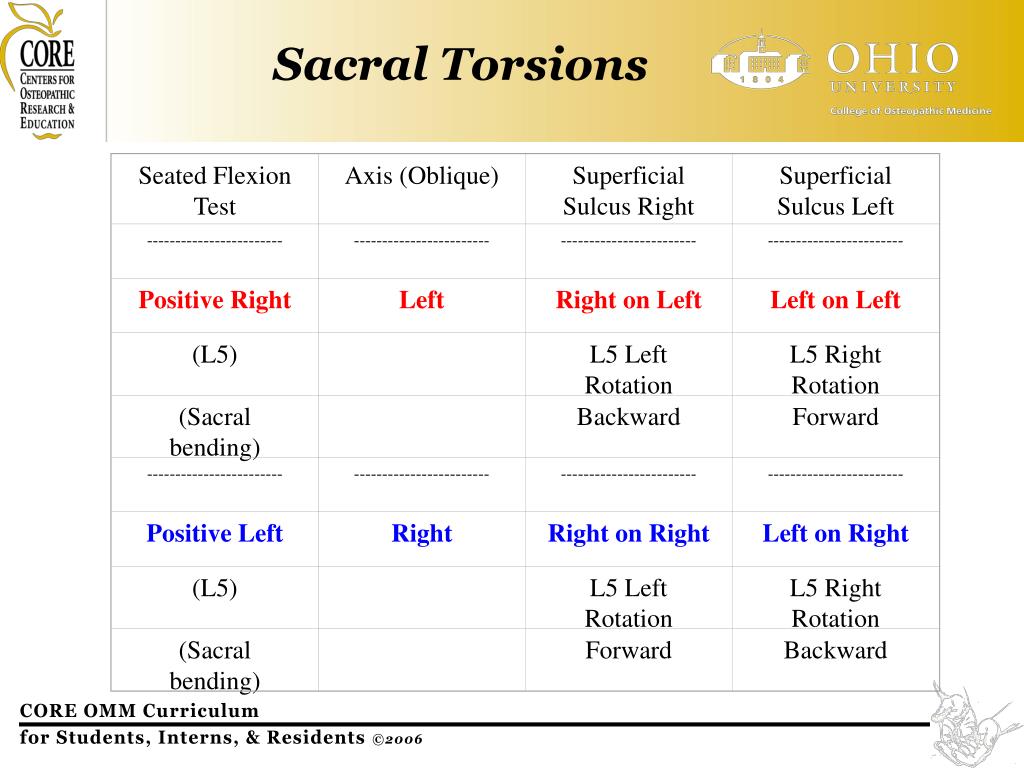
PPT CORE OMM Curriculum Board Review PowerPoint Presentation, free

The Sacroiliac Joint Sacral Nutation and Counternutation YouTube

Sacral Torsion Sacroiliac Easy Treatment YouTube

What is Sacral Torsion? Erik Dalton Blog

Sacral Torsion Linda K Sienkiewicz

Sacral Torsion Diagnosis YouTube

What is Sacral Torsion? Erik Dalton Blog

Sacrum Hesch_edited2 Physical therapy student, Assessment, Muscle
Read Ratings & Reviewsshop Best Sellersshop Our Huge Selection
If The Test Is Positive (Worsened Asymmetry Of The Bases), This Indicates A Sacral Extension Dysfunction Or A Posterior Sacral Torsion.
The Pain May Radiate Down The Leg To The Knee Or At Times, To The Ankle Or Foot.
Related Post: