Sacrum Diagnosis Chart
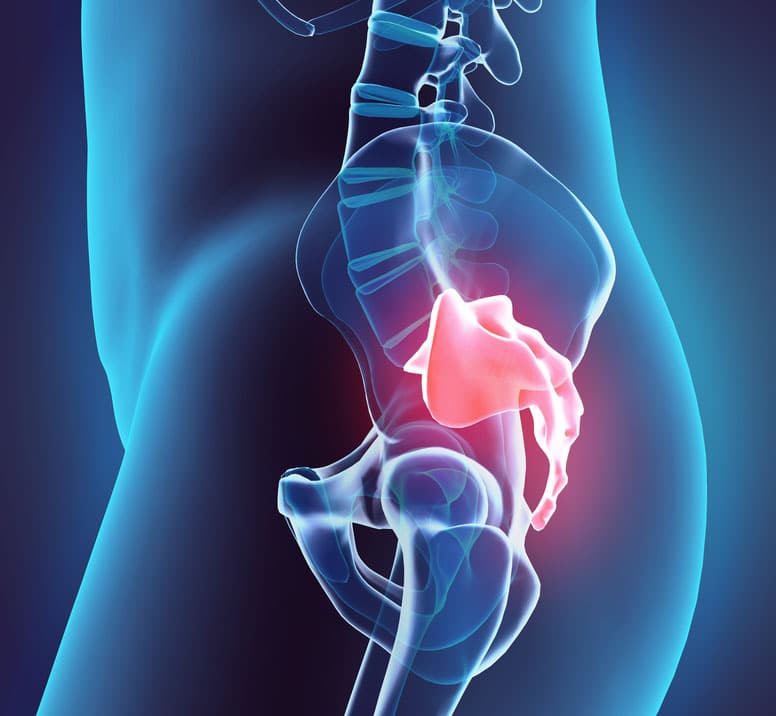
Sacrum Diagnosis Chart - R unilateral flexion + on r: Inflammation of one or both of your sacroiliac joints. Metastatic lesions, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma are far more common than primary sacral tumors. Web magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are the preferred imaging modalities for evaluating sacral masses. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Csf is a clear fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. Web the two core tests that are often recommended to diagnose the position of the sacrum are the sphinx test and seated flexion test.⁶ ⁷ the following landmarks are typically recommended to be palpated and assessed: When the sacroiliac joints become inflamed or irritated, it can cause lower back pain and stiffness. This pictorial review will highlight imaging features of common sacral tumors with pathologic correlation. Web review the following diagnostic and treatment techniques related to sacral somatic dysfunction: Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and. Inflammation of one or both of your sacroiliac joints. Radiographic alternations caused by sacral tumours are notoriously subtle. Anterior and superior b/l + n/a: Plain radiographs, although limited in evaluation of the sacrum, should be carefully examined when abnormalities of the sacrum are. Radiographic alternations caused by sacral tumours are notoriously subtle. Web how do we decide what diagnosis is? Web the sacral region (sacrum) is at the bottom of the spine and lies between the fifth segment of the lumbar spine (l5) and the coccyx (tailbone). Sacroiliitis can cause pain and stiffness in the buttocks or lower back, and. Vertebrae in the. Ror lor left flexed left extended. R unilateral flexion + on r: This robust bone can endure a lot of pressure and motion. Web what is it? This is known as sacroiliitis. The sacrum is a bone at the back of the pelvis between the hip bones. Anterior and superior b/l + n/a: Web what is it? Superior r innominate shear + on r: What is a tarlov cyst? The sacrum is a structure that is imaged by both general and subspecialty radiologists. Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. Web how do we decide what diagnosis is? With primary malignant tumors of the sacrum, mayo clinic orthopedic oncologists must thoroughly and thoughtfully counsel patients regarding the difficult complications inherent to aggressive removal of this type of. The skeleton is the third most common site of metastasis after the lungs and liver [ 1 ], with the spinal column most frequently involved [ 1 ]. These joints sit where the lower spine and pelvis meet. With primary malignant tumors of the sacrum, mayo clinic orthopedic oncologists must thoroughly and thoughtfully counsel patients regarding the difficult complications inherent. It causes pain in your lower back, butt (your buttock muscles) or legs. It can cause sharp, stabbing pain that starts in the hips and pelvis and radiates into the lower back and down the thighs. Primary benign and malignant tumors of the sacrum are rare lesions that account for fewer than 7% of all intraspinal primary tumors [ 1,. This is known as sacroiliitis. Csf is a clear fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. S1 nerves affect the hips and the groin area. Sacroiliitis is painful inflammation in the joints where your spine connects to your pelvis (your sacroiliac joints). Inflammation of one or both of your sacroiliac joints. Web types of sacral spine injury. Positive seated flexion on left positive seated flexion on right. S2 nerves affect the backs of the thighs. S3 nerves affect the medial buttock area. Radiographic alternations caused by sacral tumours are notoriously subtle. The sacrum is a single bone comprised of five separate vertebrae. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. When the sacroiliac joints become inflamed or irritated, it can cause lower back pain and stiffness. S1 nerves affect the hips and the groin. Anterior and superior b/l + n/a: Pain is the main symptom of si joint dysfunction. In some cases, the pain may also radiate. Web review the following diagnostic and treatment techniques related to sacral somatic dysfunction: S1 nerves affect the hips and the groin area. Web anatomy & structure. Bilateral inferior lateral angles of the sacrum (ila) Ror lor left flexed left extended. Web volume 174, issue 2. A joint is a place in your body where two bones meet. Inferior r innominate shear + on r: S3 nerves affect the medial buttock area. What is a tarlov cyst? Plain radiographs, although limited in evaluation of the sacrum, should be carefully examined when abnormalities of the sacrum are. Inflammation of one or both of your sacroiliac joints. With primary malignant tumors of the sacrum, mayo clinic orthopedic oncologists must thoroughly and thoughtfully counsel patients regarding the difficult complications inherent to aggressive removal of this type of cancer.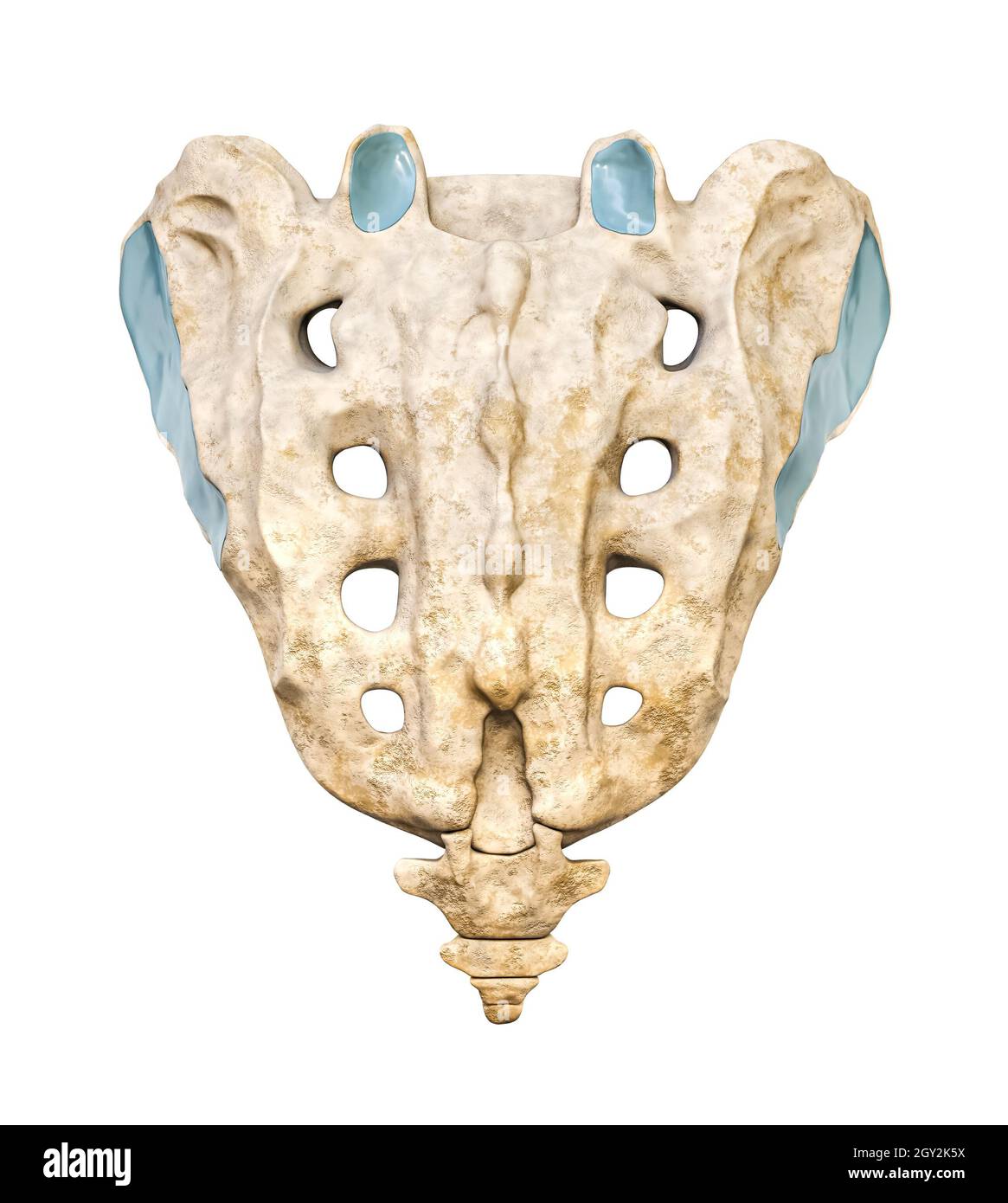
Sacrum bone anatomy Cut Out Stock Images & Pictures Alamy
Sacral Stress Fractures Raising Awareness as a Possible Differential

Schematic illustration demonstrating GCT of the sacrum. Midline tumor

Womens Medium Length Hairstyles 2015 Medical coding cheat sheet

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Osteopathic diagnosis of the sacrum. Positivity, Diagnosis, Negativity

Sacrum Hesch_edited2 Physical therapy student, Physical therapy

PreClinical Years fairyburger

️ Sacrum anatomy. Sacrum Anatomy, Area & Definition. 20190201

PPT OMM in the Treatment of Spring Sports Injuries PowerPoint
Web Types Of Sacral Spine Injury.
Vertebrae In The Vertebral Column.
Depending On The Type Of Sacral Injury Or Nerve Damage, Its Location Affects The Nerves In That Area And Leads To Lack Of Control And Pain:
The Sacrum Is A Bone At The Back Of The Pelvis Between The Hip Bones.
Related Post: