Stoichiometry Conversion Chart
Stoichiometry Conversion Chart - What units does the question ask? 2 na + mgbr 2 ——> mg + 2 nabr. Web the easiest way to do stoichiometric calculations involves using conversion factors. Apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a molar quantity and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. Web stoichiometric ratios, the ratios of the amounts of each substance used, are unique for each chemical reaction. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Web video stoichiometry conversions demonstrated example 1: The balanced equation of a reaction contains the stoichiometric ratios of the reactants and products; Web conversion table for problems below. A conversion factor is always equal to 1. A conversion factor is a ratio (or fraction) which represents the relationship between two different units. Web conversion table for problems below. Web video stoichiometry conversions demonstrated example 1: 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. 2 na + mgbr 2 ——> mg + 2 nabr. We need to balance the equation! How many moles of mg can be made from 5 moles of na given the chemical equation below? Web naoh ( a q) + h a 2 so a 4 ( a q) → h a 2 o ( l) + na a 2 so a 4 ( a q) how many grams of. In this case, we have 1 na atom and 3 h atoms on the reactant side and 2 na atoms and 2 h atoms on the product side. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. The balanced equation of a reaction contains the stoichiometric ratios. We need to balance the equation! 0.765l × 1.93molnaoh lsolution × 40.0gnaoh 1molnaoh = 59.1gnaoh. A conversion factor is a ratio (or fraction) which represents the relationship between two different units. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. Web this stoichiometry calculator helps to calculate the stoichiometric coefficients & relative amounts of. What information does the question supply us with? The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. Moles of a is converted to moles of b by multiplying by the molar ratio. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. Web apply a stoichiometric conversion factor to convert between the molar quantities of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. In this case, we have 1 na atom and 3 h atoms on the reactant side and 2 na atoms and 2 h atoms on the product side. The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above.. Web naoh ( a q) + h a 2 so a 4 ( a q) → h a 2 o ( l) + na a 2 so a 4 ( a q) how many grams of naoh are required to fully consume 3.10 grams of h a 2 so a 4 ? In this case, we have 1 na atom. Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. 0.765l × 1.93molnaoh lsolution × 40.0gnaoh 1molnaoh = 59.1gnaoh. Apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a molar quantity and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. In this case, we have 1 na atom and 3 h atoms on the reactant side and 2 na atoms and. Web the easiest way to do stoichiometric calculations involves using conversion factors. A conversion factor is a ratio (or fraction) which represents the relationship between two different units. In this case, we have 1 na atom and 3 h atoms on the reactant side and 2 na atoms and 2 h atoms on the product side. The balanced equation of. Web stoichiometric ratios, the ratios of the amounts of each substance used, are unique for each chemical reaction. A conversion factor is a ratio (or fraction) which represents the relationship between two different units. 2 na + mgbr 2 ——> mg + 2 nabr. This tutorial provides a brief overview of dimensional analysis, including conversion. Web flowchart of steps in. What units does the question ask? Grams of a is converted to moles by multiplying by the inverse of the molar mass. 1 kg = 1000 g = 2.20462 lb. 1 cm 3 = 1ml. 2 na + mgbr 2 ——> mg + 2 nabr. Web video stoichiometry conversions demonstrated example 1: Web flowchart of steps in stoichiometric calculations. Web the easiest way to do stoichiometric calculations involves using conversion factors. 1 lb = 16 oz = 453.6 g. Web conversion table for problems below. In this case, we have 1 na atom and 3 h atoms on the reactant side and 2 na atoms and 2 h atoms on the product side. 0.765l × 1.93molnaoh lsolution × 40.0gnaoh 1molnaoh = 59.1gnaoh. A conversion factor is always equal to 1. Apply multiple conversion factors to convert between a molar quantity and a particle count of two substances that participate in a chemical reaction. Web stoichiometric ratios, the ratios of the amounts of each substance used, are unique for each chemical reaction. The balanced equation of a reaction contains the stoichiometric ratios of the reactants and products;
Stoichiometry Chart YouTube
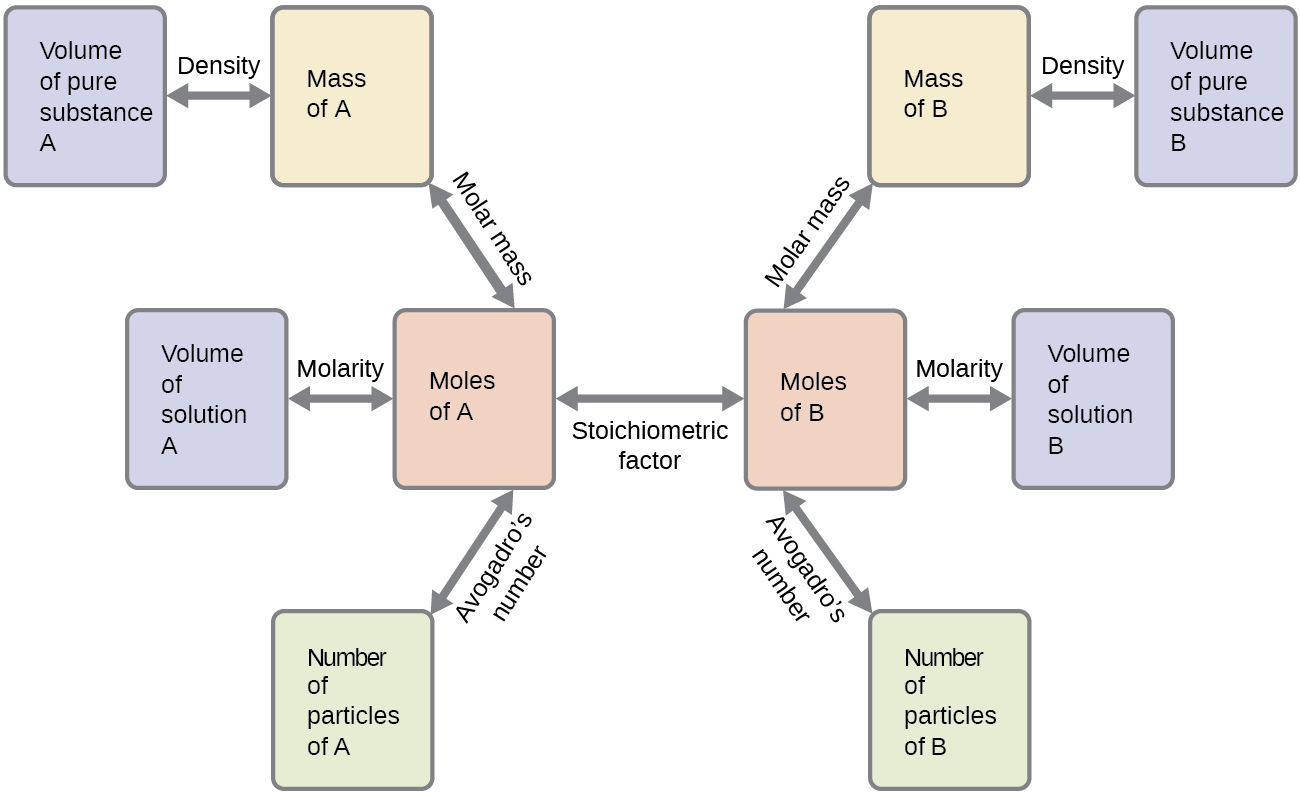
Stoichiometry Chemistry Activities
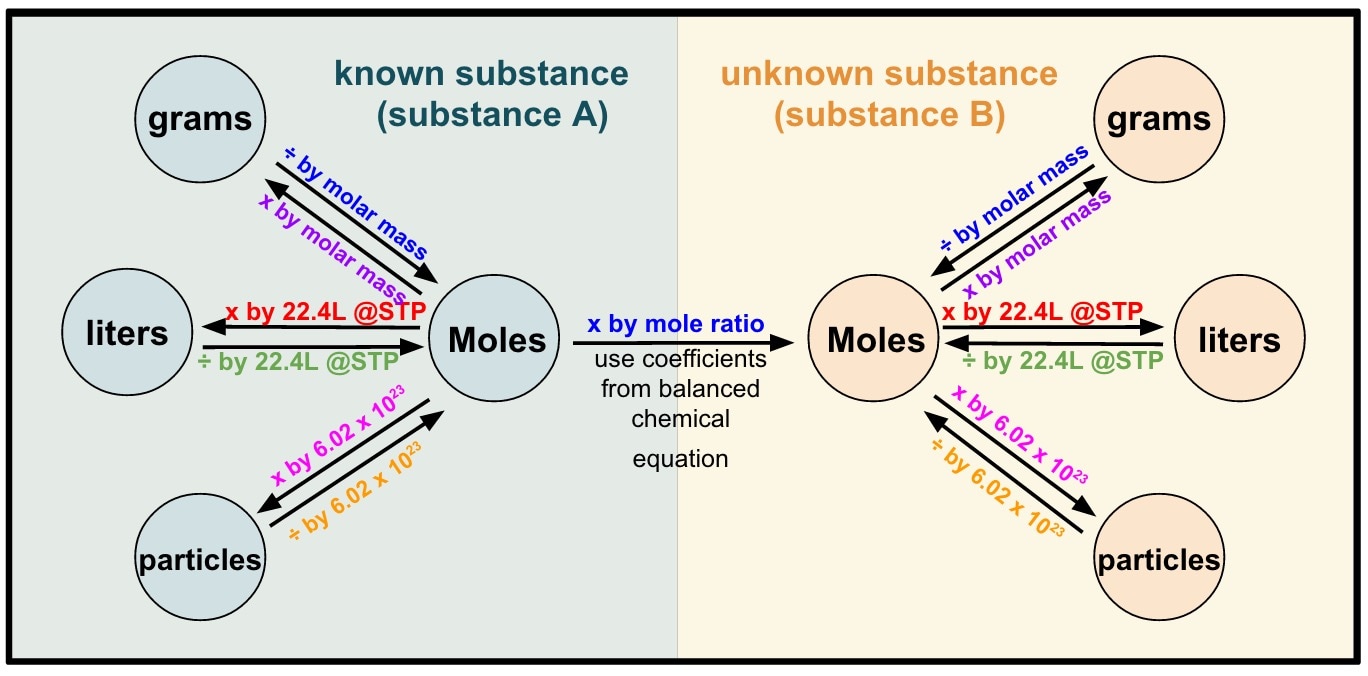
Stoichiometry Review Mr. Siemianowski Eisenhower High School
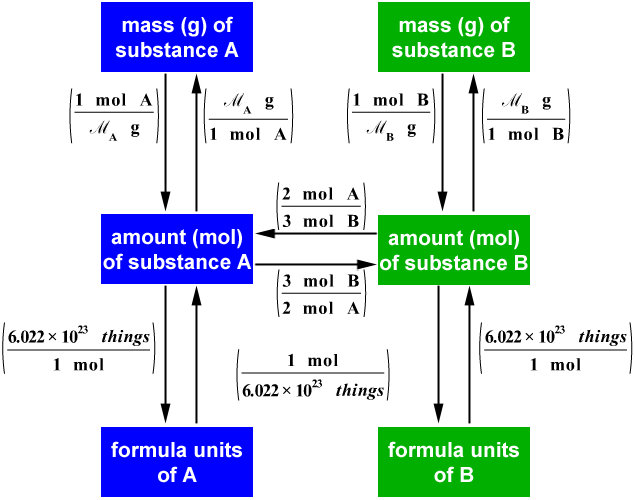
J² + H = Element 119 Kariodisonium Stoichiometry Calculations

Using Stoichiometry in Conversions Scientific Tutor

Erin'sChemBlog Stoichiometry

Extended Reaction Stoichiometry Road Map — Examples Expii

Using Stoichiometry in Conversions Scientific Tutor

A map of unit conversions and chemical reactions Wade Lanning
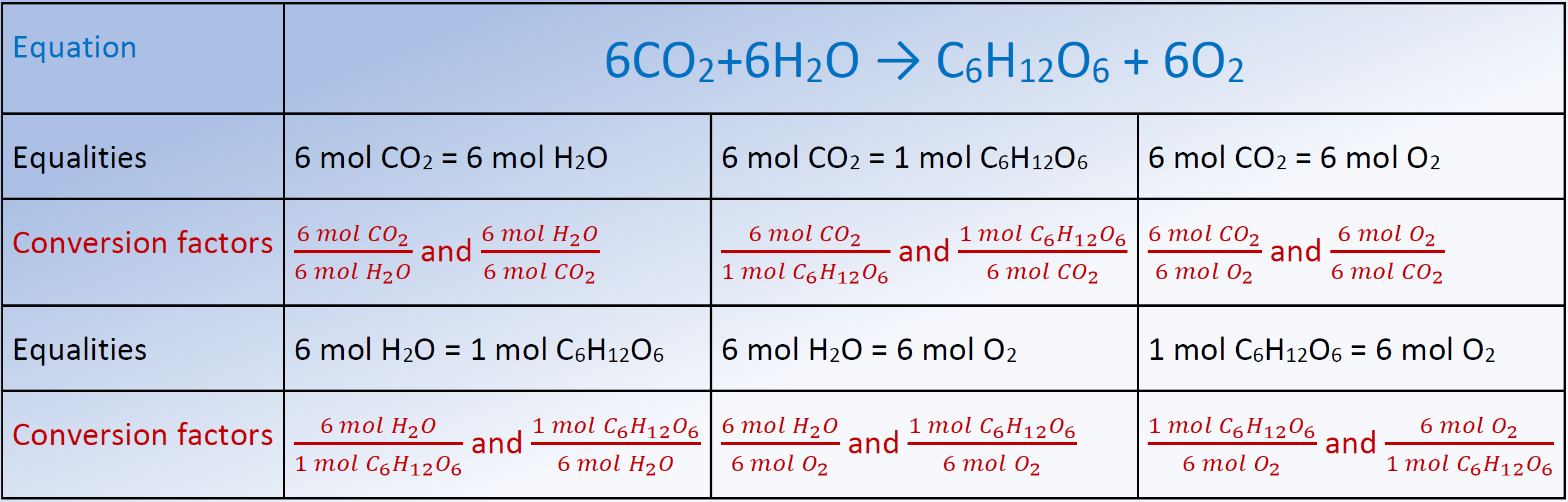
žalobca ventilácia chemical reaction calculator
Web Apply A Stoichiometric Conversion Factor To Convert Between The Molar Quantities Of Two Substances That Participate In A Chemical Reaction.
This Tutorial Provides A Brief Overview Of Dimensional Analysis, Including Conversion.
Web This Stoichiometry Calculator Helps To Calculate The Stoichiometric Coefficients & Relative Amounts Of Reactants And Products In Moles And Grams.
1 Gal = 3.7854 L.
Related Post: