F Test Chart
F Test Chart - Web f distribution table 1 d.f.n. A statistical f test uses an f statistic to compare two variances, s 1 and s 2, by dividing them. F test in regression analysis to test for the overall significance of a regression model. Web f test to compare two variances. When referencing the f distribution, the numerator degrees of freedom are always given first , as switching the order of degrees of freedom changes the distribution (e.g., f (10,12) does not equal f (12,10) ). = degrees of freedom in denominator α = 0.005 d.f.n. For example, if you have an alpha level of.05, then your right tail area is.05 (5 percent), and you’ll look up the f. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 15 20 24. F = s 2 1 / s 2 2. Web the f statistic table is actually a collection of tables. Web f distribution table 1 d.f.n. A statistical f test uses an f statistic to compare two variances, s 1 and s 2, by dividing them. For example, if you have an alpha level of.05, then your right tail area is.05 (5 percent), and you’ll look up the f. Start by finding the table that corresponds to your significance level.. = degrees of freedom in denominator α = 0.005 d.f.n. It is designed to help determine the threshold beyond which the f statistic is expected to exceed a controlled percentage of the time (e.g., 5%) when the null hypothesis is accurate. This table contains the upper critical values of the f distribution. A statistical f test uses an f statistic. F = s 2 1 / s 2 2. The result is always a positive number (because variances are always positive). Web the f statistic table is actually a collection of tables. This table contains the upper critical values of the f distribution. Web f test to compare two variances. F test in regression analysis to test for the overall significance of a regression model. The result is always a positive number (because variances are always positive). = degrees of freedom in denominator α = 0.005 d.f.n. This table contains the upper critical values of the f distribution. When referencing the f distribution, the numerator degrees of freedom are always. Start by finding the table that corresponds to your significance level. When referencing the f distribution, the numerator degrees of freedom are always given first , as switching the order of degrees of freedom changes the distribution (e.g., f (10,12) does not equal f (12,10) ). Web f distribution table 1 d.f.n. It is designed to help determine the threshold. Web this table shows the f critical value based on the degrees of freedom in the numerator and denominator in the f ratio and the level of alpha you choose. Which specific table you use will depend on which alpha level you use. F test in regression analysis to test for the overall significance of a regression model. The result. If the variances are equal, the ratio of the variances. Start by finding the table that corresponds to your significance level. For example, if you have an alpha level of.05, then your right tail area is.05 (5 percent), and you’ll look up the f. Web f test to compare two variances. Which specific table you use will depend on which. Then, find the intersection of the column and rows that corresponds to your numerator and denominator df. If the variances are equal, the ratio of the variances. Web the f statistic table is actually a collection of tables. The three most common scenarios in which you’ll conduct an f test are as follows: = degrees of freedom in numerator d.f.d. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 15 20 24. Which specific table you use will depend on which alpha level you use. The result is always a positive number (because variances are always positive). If the variances are equal, the ratio of the variances. F = s 2 1 / s 2 2. It is designed to help determine the threshold beyond which the f statistic is expected to exceed a controlled percentage of the time (e.g., 5%) when the null hypothesis is accurate. Which specific table you use will depend on which alpha level you use. When referencing the f distribution, the numerator degrees of freedom are always given first , as. If the variances are equal, the ratio of the variances. = degrees of freedom in denominator α = 0.005 d.f.n. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 15 20 24. F = s 2 1 / s 2 2. When referencing the f distribution, the numerator degrees of freedom are always given first , as switching the order of degrees of freedom changes the distribution (e.g., f (10,12) does not equal f (12,10) ). Web this table shows the f critical value based on the degrees of freedom in the numerator and denominator in the f ratio and the level of alpha you choose. Then, find the intersection of the column and rows that corresponds to your numerator and denominator df. The result is always a positive number (because variances are always positive). Start by finding the table that corresponds to your significance level. Web f distribution table 1 d.f.n. F test in regression analysis to test for the overall significance of a regression model. The three most common scenarios in which you’ll conduct an f test are as follows: It is designed to help determine the threshold beyond which the f statistic is expected to exceed a controlled percentage of the time (e.g., 5%) when the null hypothesis is accurate. A statistical f test uses an f statistic to compare two variances, s 1 and s 2, by dividing them. For example, if you have an alpha level of.05, then your right tail area is.05 (5 percent), and you’ll look up the f. This table contains the upper critical values of the f distribution.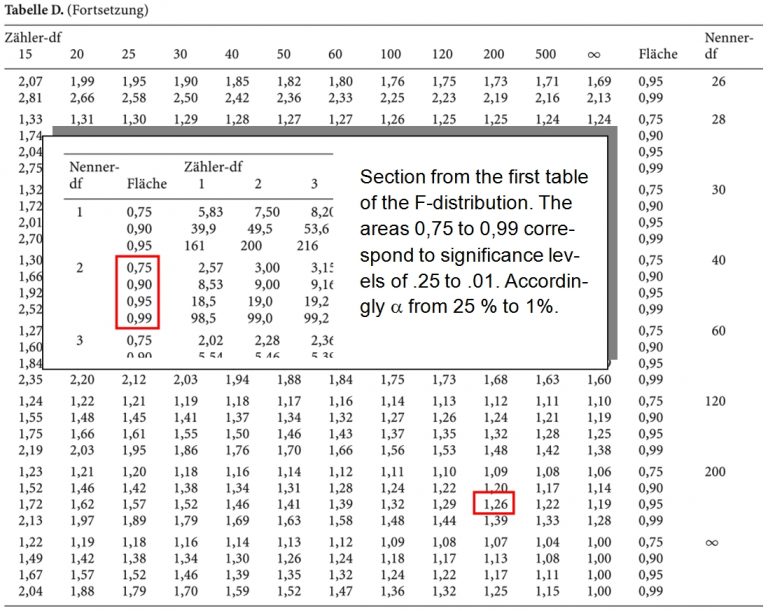
FTest
FTest Definition, Statistics, Calculation, Interpretation, Example
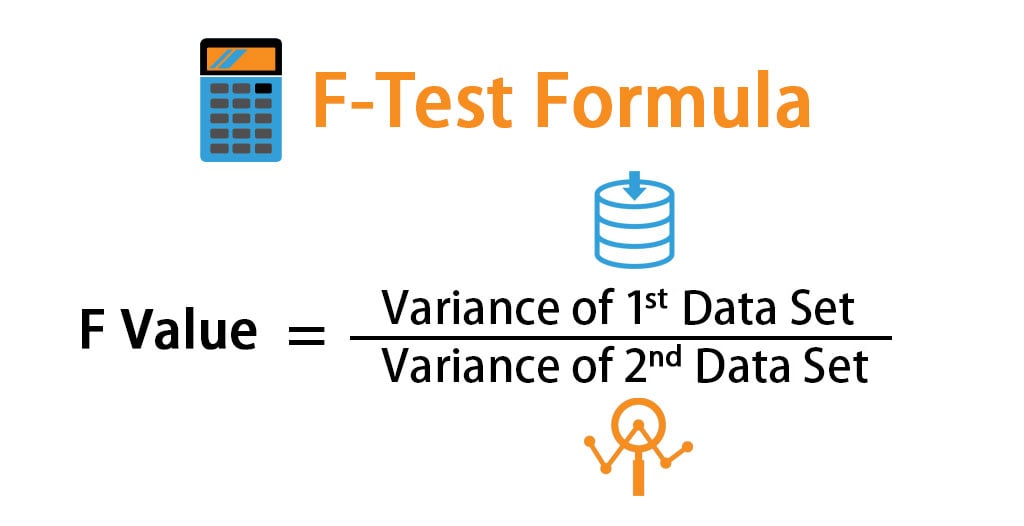
FTest Formula How To Calculate FTest (Examples With Excel Template)
Ftest

How to Perform Fisher's Test (FTest) Example Question 12 The

How to Read the FDistribution Table Statology
[Solved] I have a question about F critical How to find using 5 level
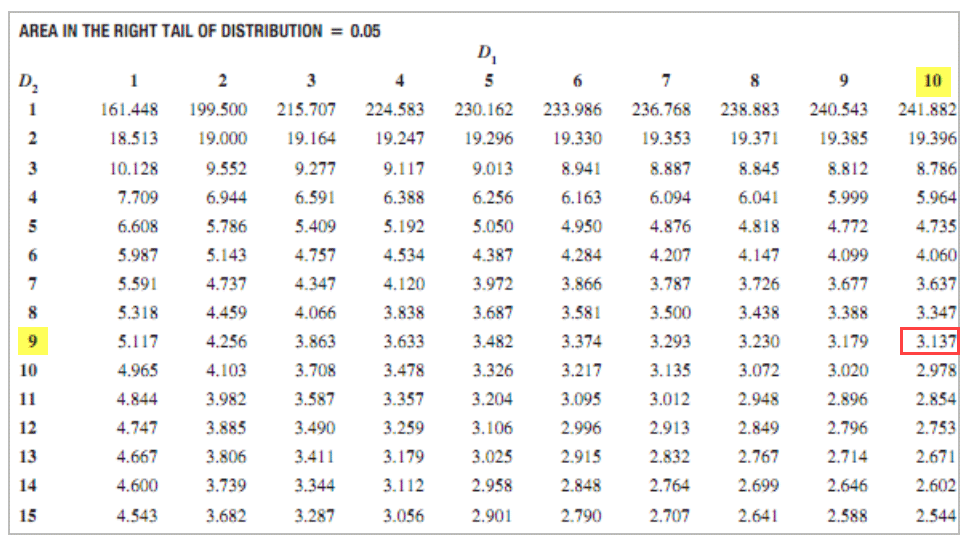
F Test Table

F test YouTube
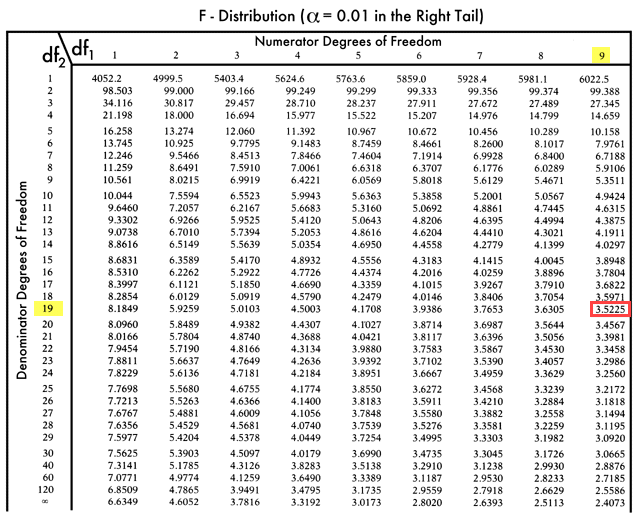
Anova F Table Calculator Matttroy
Web The F Statistic Table Is Actually A Collection Of Tables.
= Degrees Of Freedom In Numerator D.f.d.
Web F Test To Compare Two Variances.
For The Four F Tables Below, The.
Related Post: