Sacral Diagnosis Chart
Sacral Diagnosis Chart - Web pie chart showing the relative incidence of various types of sacral masses. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that section of the spinal cord. When the sacroiliac joints become inflamed or irritated, it can cause lower back pain and. Web sacroiliitis can be hard to diagnose. S1 nerves affect the hips and groin. S4 and s5 nerves affect the perineal area. The sacrum is a single bone comprised of five separate vertebrae. Web begin with a standing flexion test (figure 1) to determine laterality of the dysfunction.the side of the dysfunction is determined by the superior psis. S2 nerves affect the back of the thighs. Web what is it? S2 nerves affect the back of the thighs. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that part of the spinal cord. It is also the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress. Types of sacral spine injury. Sacral torsion may cause some low back pain or limit lower back movement. It is also the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress. Injuries to the sacral spine are less common than injuries to other areas of the spine. Web what is it? S1 nerves affect the hips and groin. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that section of the spinal cord. Web what are the symptoms of a blocked sacral chakra? Radiographic alternations caused by sacral tumours are notoriously subtle. Web be able to diagnose sacral dysfunction based on landmarks and motion testing. Learn to easily treat sacral diagnoses using ligamentous articular strain (las) in the other 40 seconds. Web begin with a standing flexion test (figure 1) to determine laterality. This robust bone can endure a lot of pressure and motion. It's been linked to a group of diseases that cause inflammatory arthritis of the spine. It is also the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress. Sacral tumours account for up to 7% of spinal tumour and encompass a wide range of primary and secondary neoplasms. Web sacral. Learn to easily treat sacral diagnoses using ligamentous articular strain (las) in the other 40 seconds. Alternatively, perform the asis compression test, with the patient supine, by compressing bilaterally anterior to posterior at. Treatment might involve physical therapy and medicines. Web what is it? Web sacroiliitis can be hard to diagnose. Web be able to diagnose sacral dysfunction based on landmarks and motion testing. Web the rotation of the upper part of the sacrum may occur towards the front side of the body (i.e., anterior), while the bottom part of the sacrum will rotate towards the back side of the body (i.e., posterior). Web what is it? Web begin with a. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that part of the spinal cord. Primary malignant sacral tumors present significant diagnostic challenges, especially for early diagnosis. Consensus for management of sacral fractures: The sacrum is a bone at the back of the pelvis between the hip bones. Root cause of sacral torsion, sacral shear, and anterior sacral tilt. Web with the patient prone, apply posterior to anterior pressure (“spring”) onto the sacral base. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that section of the spinal cord. Treatment might involve physical therapy and medicines. Symptoms of a blocked sacral chakra can include: It's been linked to a group of diseases that cause inflammatory arthritis of the spine. Web when is sa/crs diagnosed? Symptoms of a tarlov cyst vary based on the size and location of the cyst. It is also the least likely area for spinal nerves to compress. Web the rotation of the upper part of the sacrum may occur towards the front side of the body (i.e., anterior), while the bottom part of the sacrum. Web when is sa/crs diagnosed? The sacral plexus is a network of nerves emerging from. Web what is it? S2 nerves affect the back of the thighs. Web the sacral spine (sacrum) is located below the lumbar spine and above the tailbone, which is known as the coccyx. The sacrum has a critical role. Injuries to the sacral spine are less common than injuries to other areas of the spine. Web be able to diagnose sacral dysfunction based on landmarks and motion testing. Types of sacral spine injury. Sacral torsion may cause some low back pain or limit lower back movement. Learn to easily treat sacral diagnoses using ligamentous articular strain (las) in the other 40 seconds. Radiographic alternations caused by sacral tumours are notoriously subtle. Normal spring indicates a bilateral or unilateral sacral flexion, or anterior sacral torsion. Web what are the symptoms of a blocked sacral chakra? In 20 seconds or less. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. The sacrum is a single bone comprised of five separate vertebrae. Because there is such a wide range of characteristics with sa/crs (from missing only a small part of the sacrum to missing all of the sacrum, lumbar and part of the thoracic spine) diagnosis does not always happen prior to birth. Ligament will be found between the ila and the ischial tuberosity on each side. Medically reviewed by jordana haber hazan, md. Studies show that only 5% to 8% of people diagnosed with a tarlov cyst experience symptoms.
Sacral fractures An updated and comprehensive review Injury

OMT OCMM Diagnosis Part 2 Sacral Hold, Normal Motions YouTube

Sacral Torsion Diagnosis YouTube
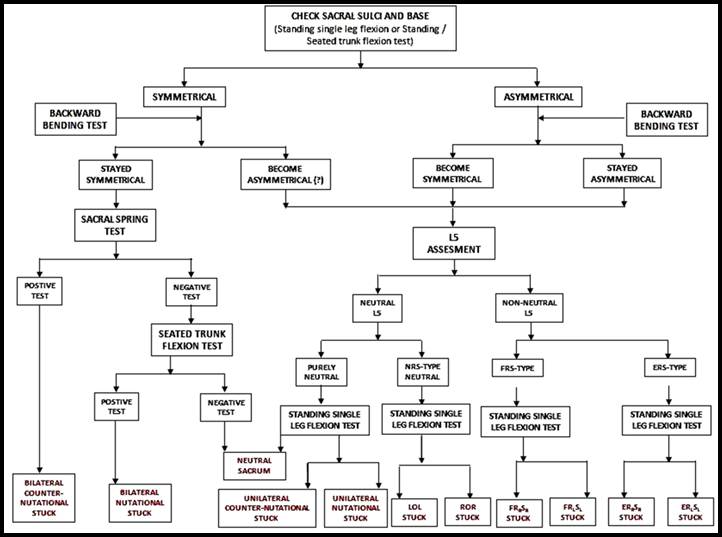
Soccer Syndrome 3 Common Sacral Malalignments and Its Manual

Sacrum Hesch_edited2 Physical therapy student, Physical therapy

Osteopathic diagnosis of the sacrum. Positivity, Diagnosis, Negativity

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Pin on Medicine AKA love

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis

Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction Osmosis
Symptoms Of A Blocked Sacral Chakra Can Include:
What Are The Symptoms Of A Tarlov Cyst?
S4 And S5 Nerves Affect The Perineal Area.
The Sacrum Is A Bone At The Back Of The Pelvis Between The Hip Bones.
Related Post: